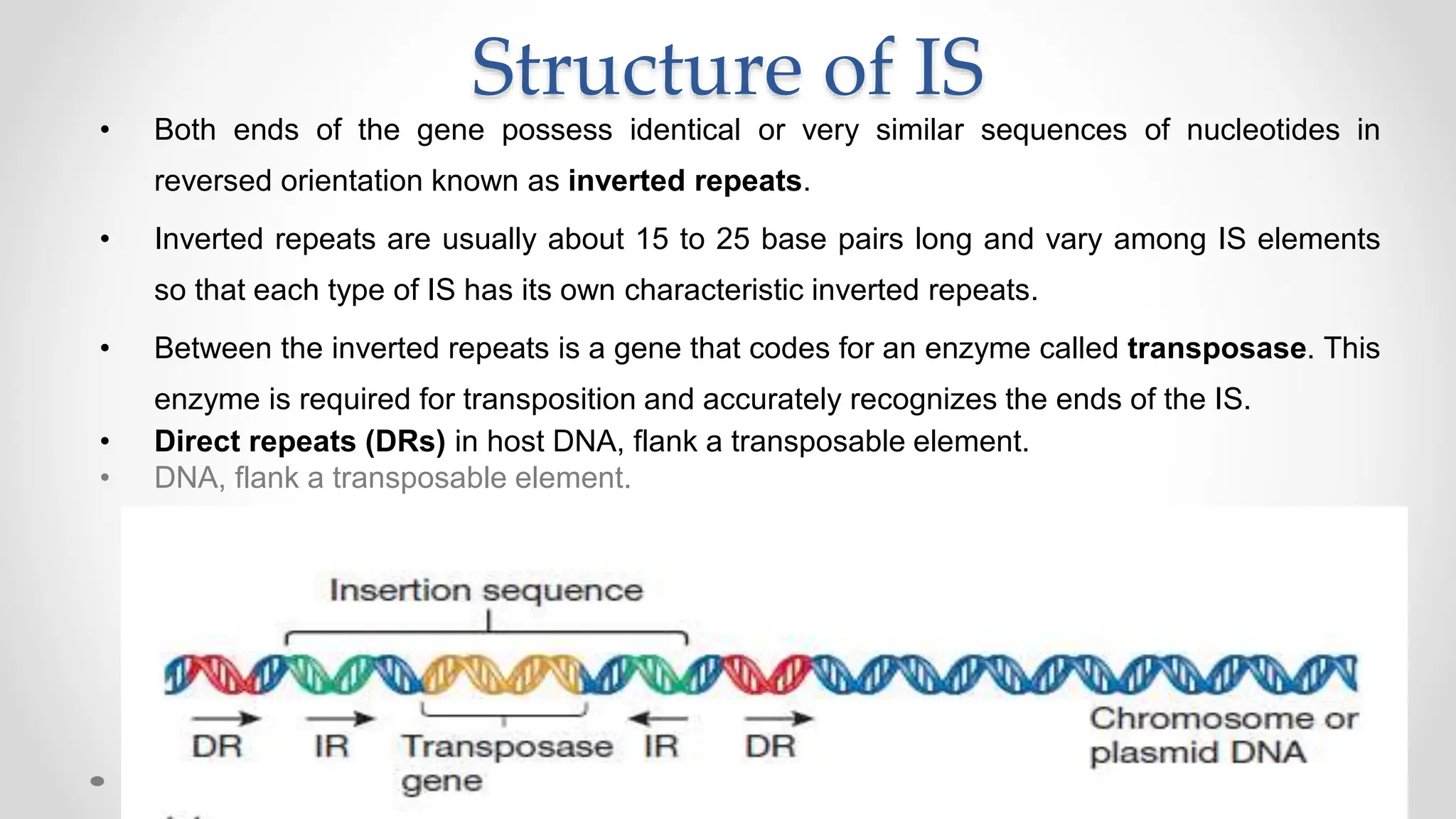
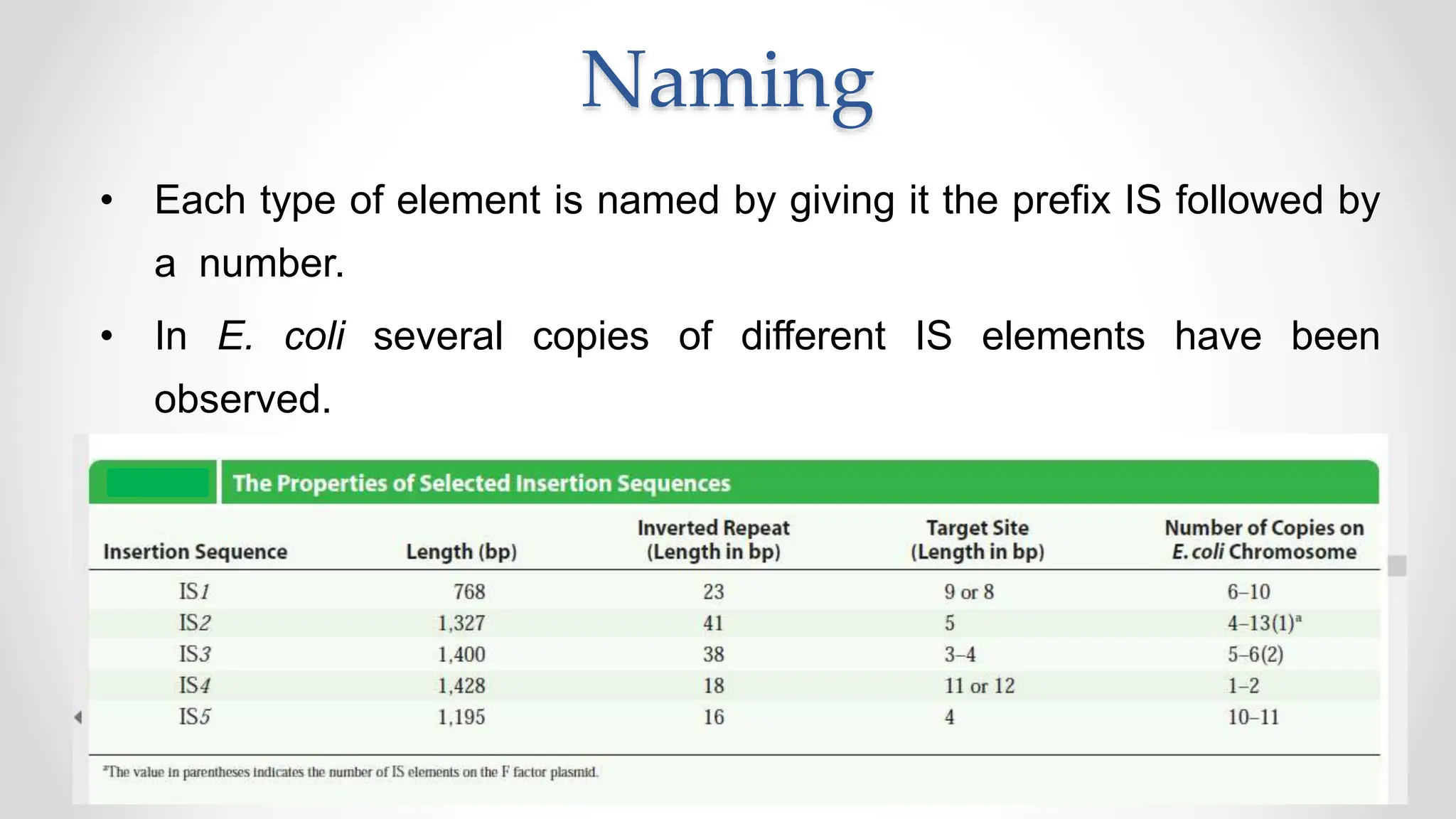
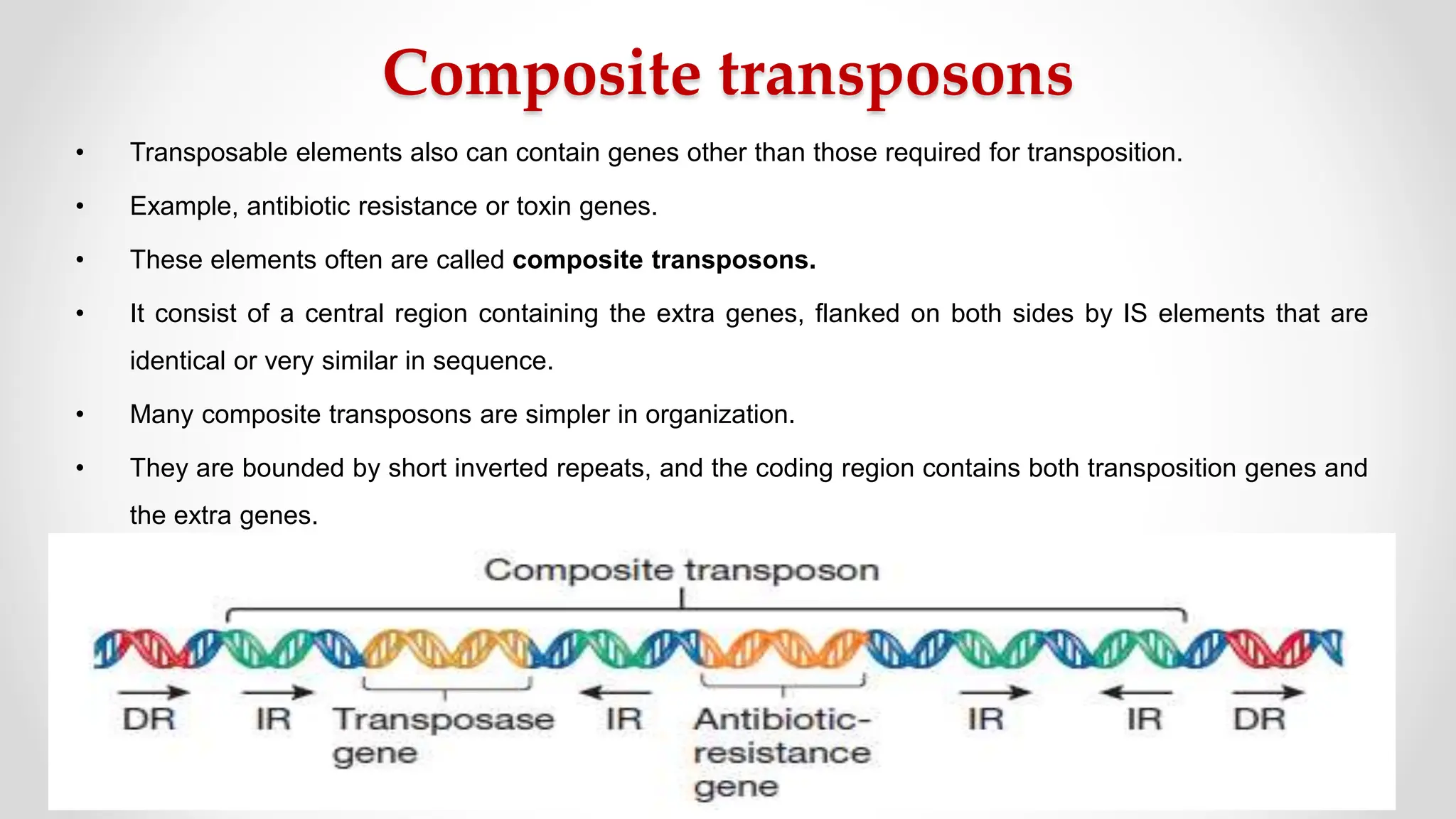
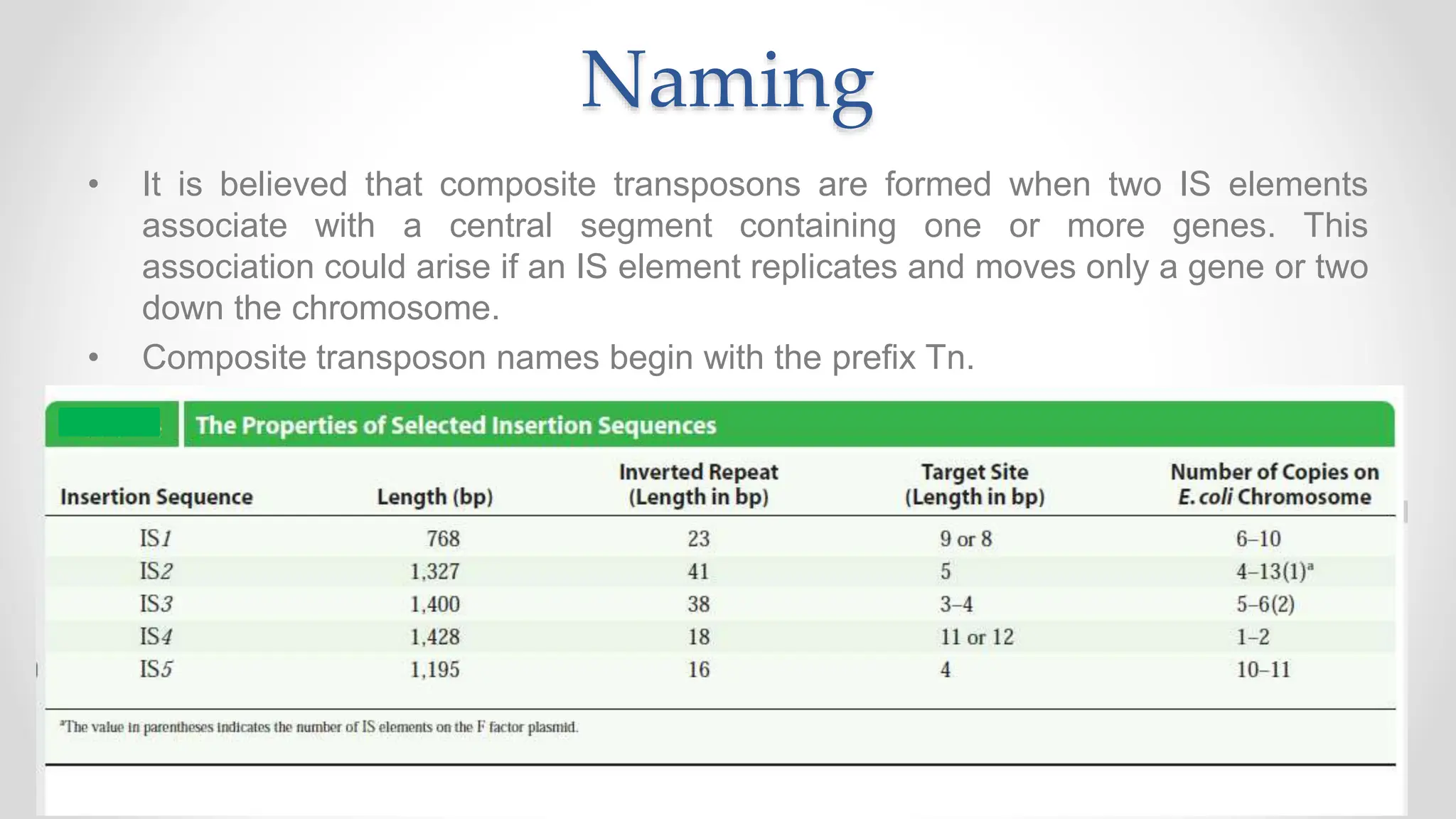
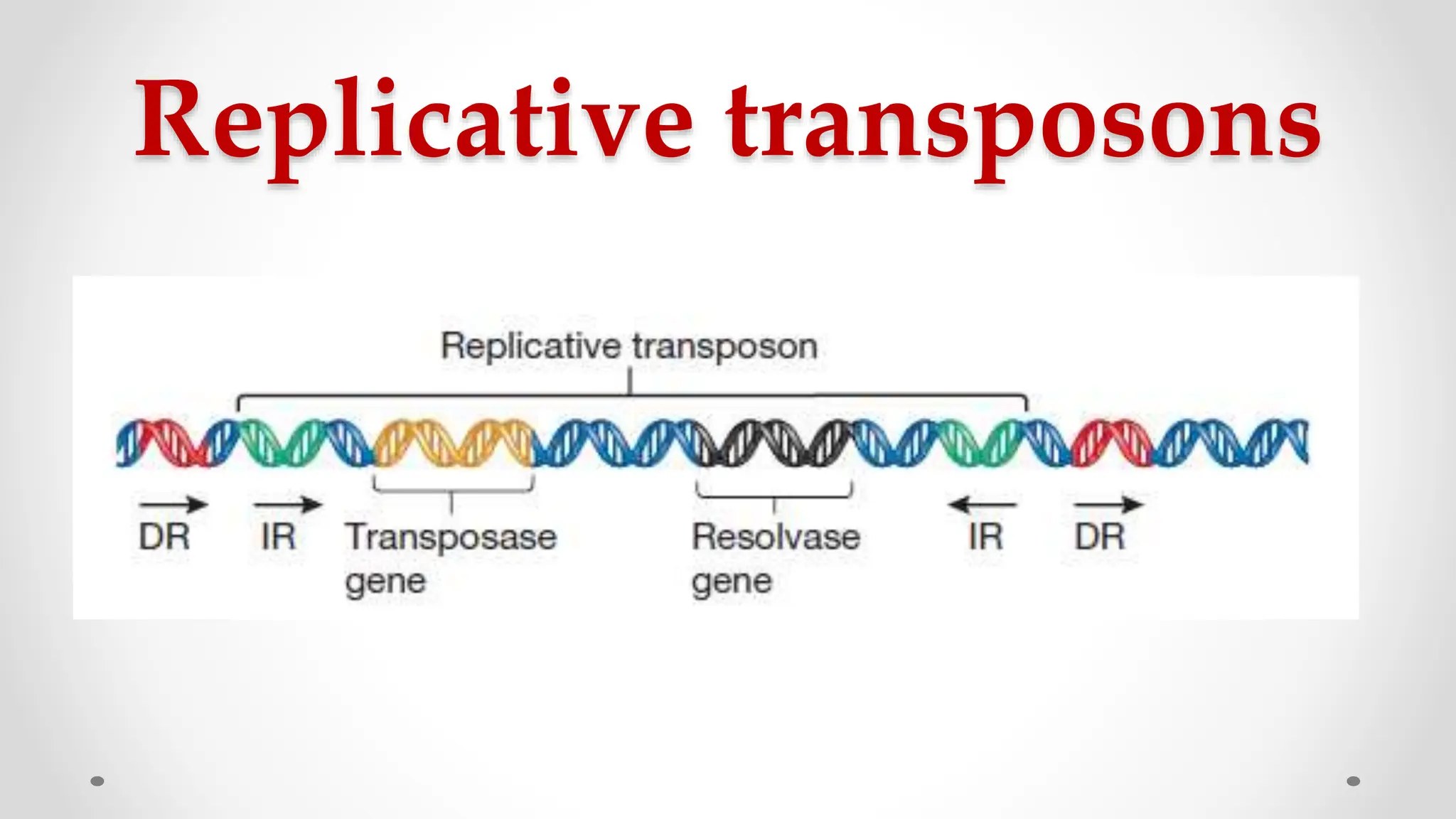
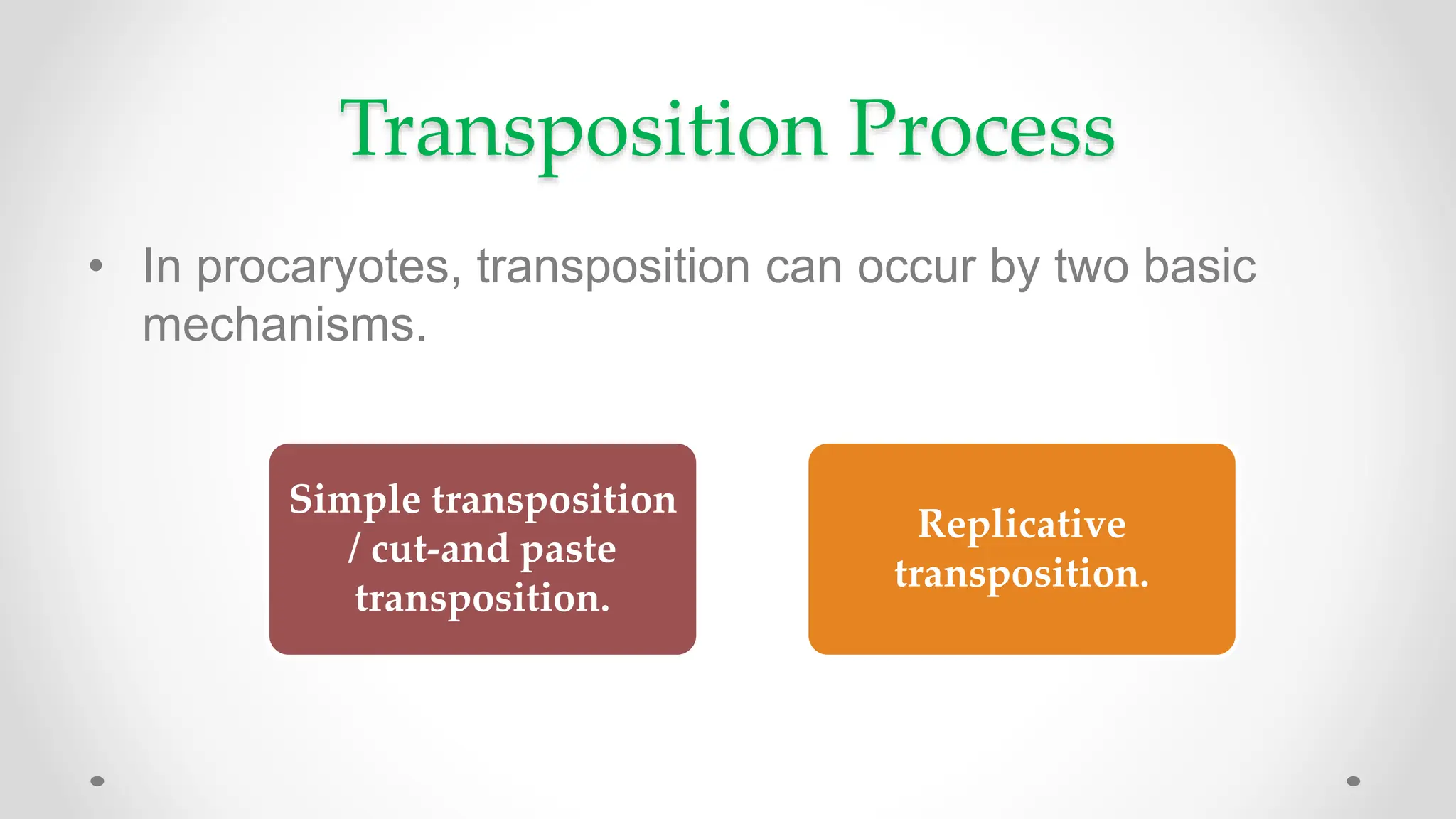
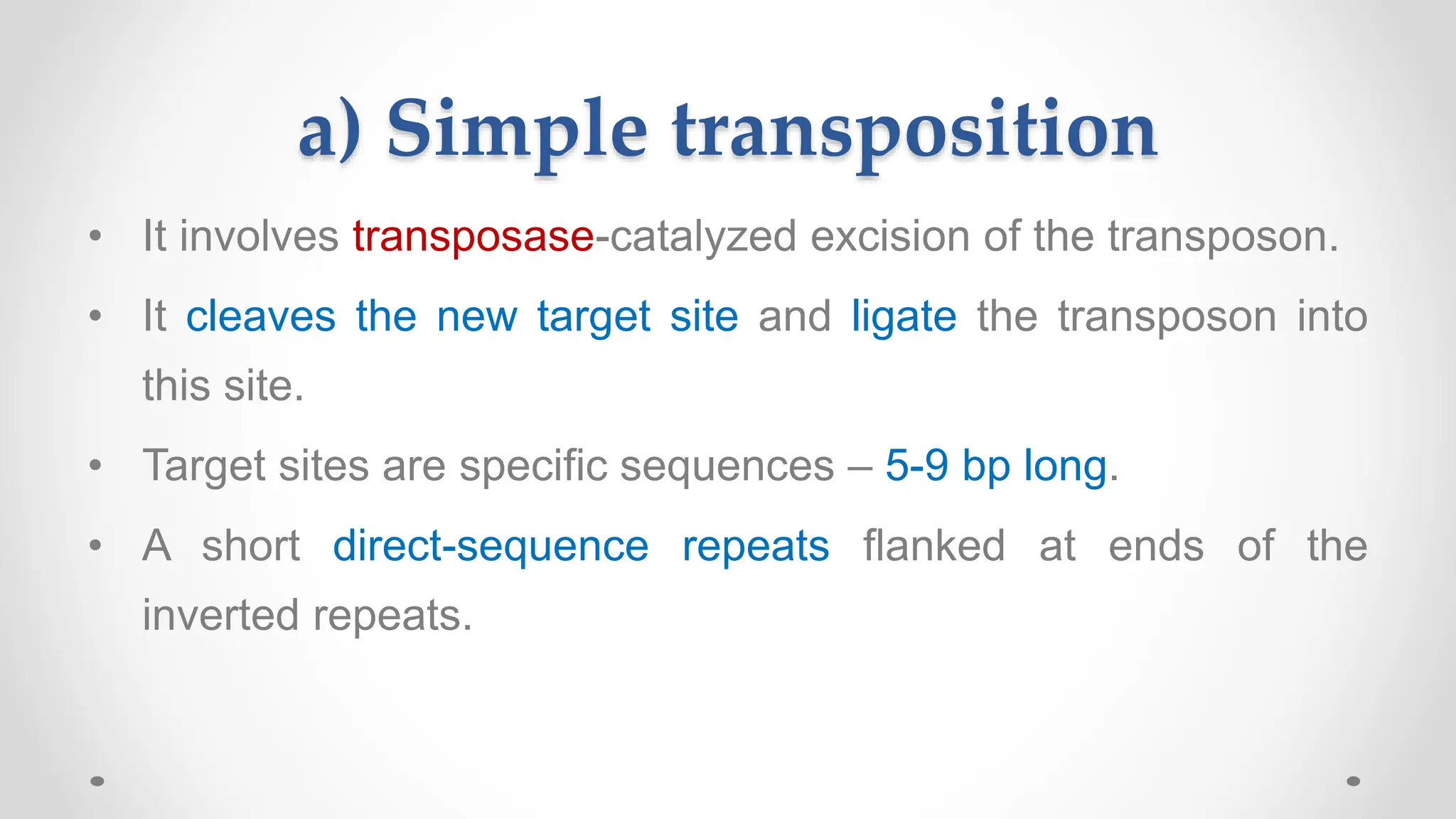
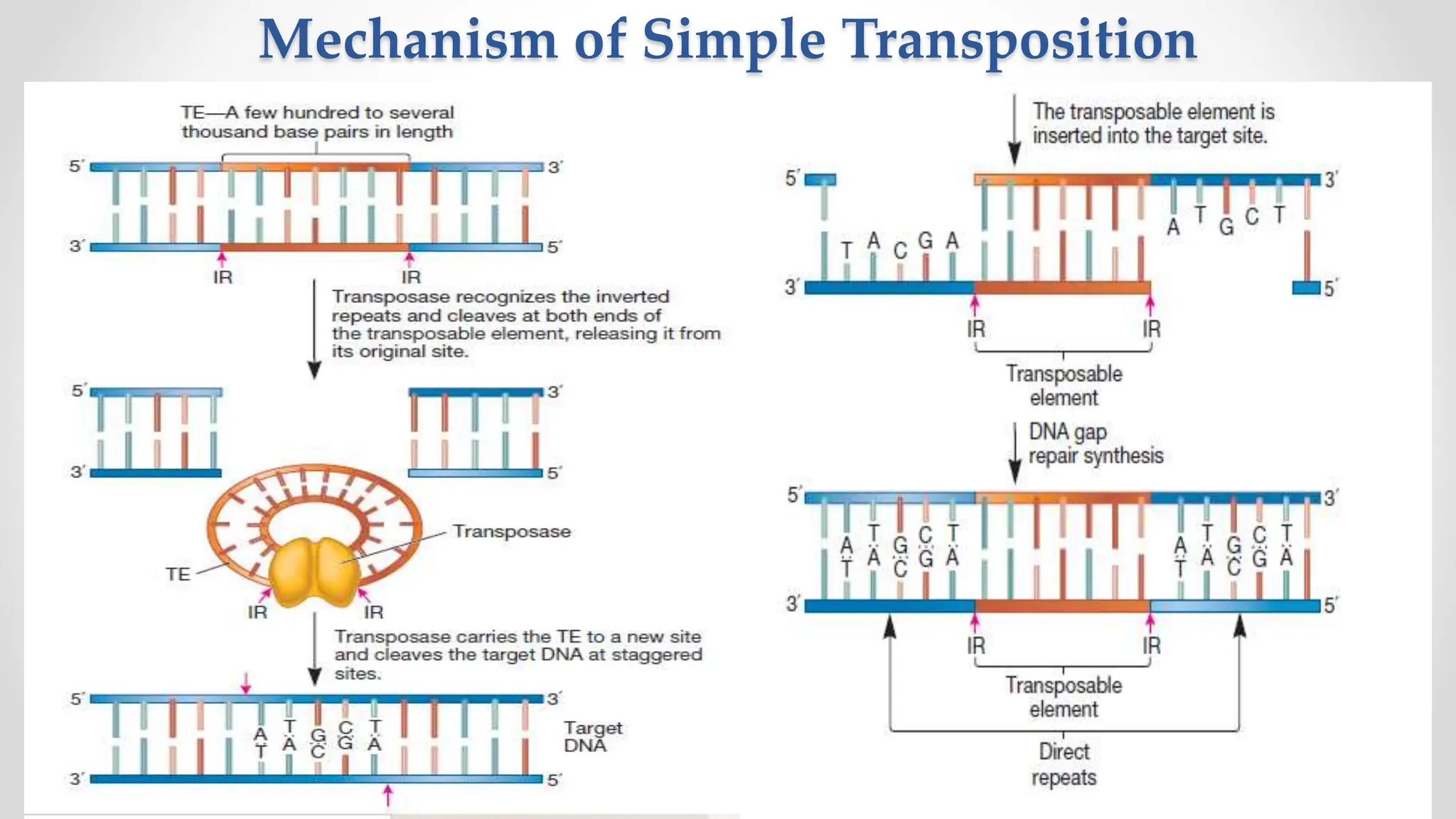
Transposons, or jumping genes, are DNA segments that move and integrate into various chromosomal sites, facilitating the generation of new gene combinations. Discovered by Barbara McClintock in the 1940s, they exist in prokaryotes, viruses, and eukaryotes and can include additional genes, such as those for antibiotic resistance. The transposition process can occur via simple transposition (cut-and-paste) or replicative transposition, impacting genetic material and gene expression.


![Simplest transposable elements - Insertion
sequences (IS)
• An IS element is a short sequence of DNA.
• Around 750 to 1,600 base pairs [bp] in length.
• It contains only the genes that code for an enzyme
required for transposition.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transposons-231230171233-d3aa918f/75/Transposons-types-and-transposition-pptx-4-2048.jpg)