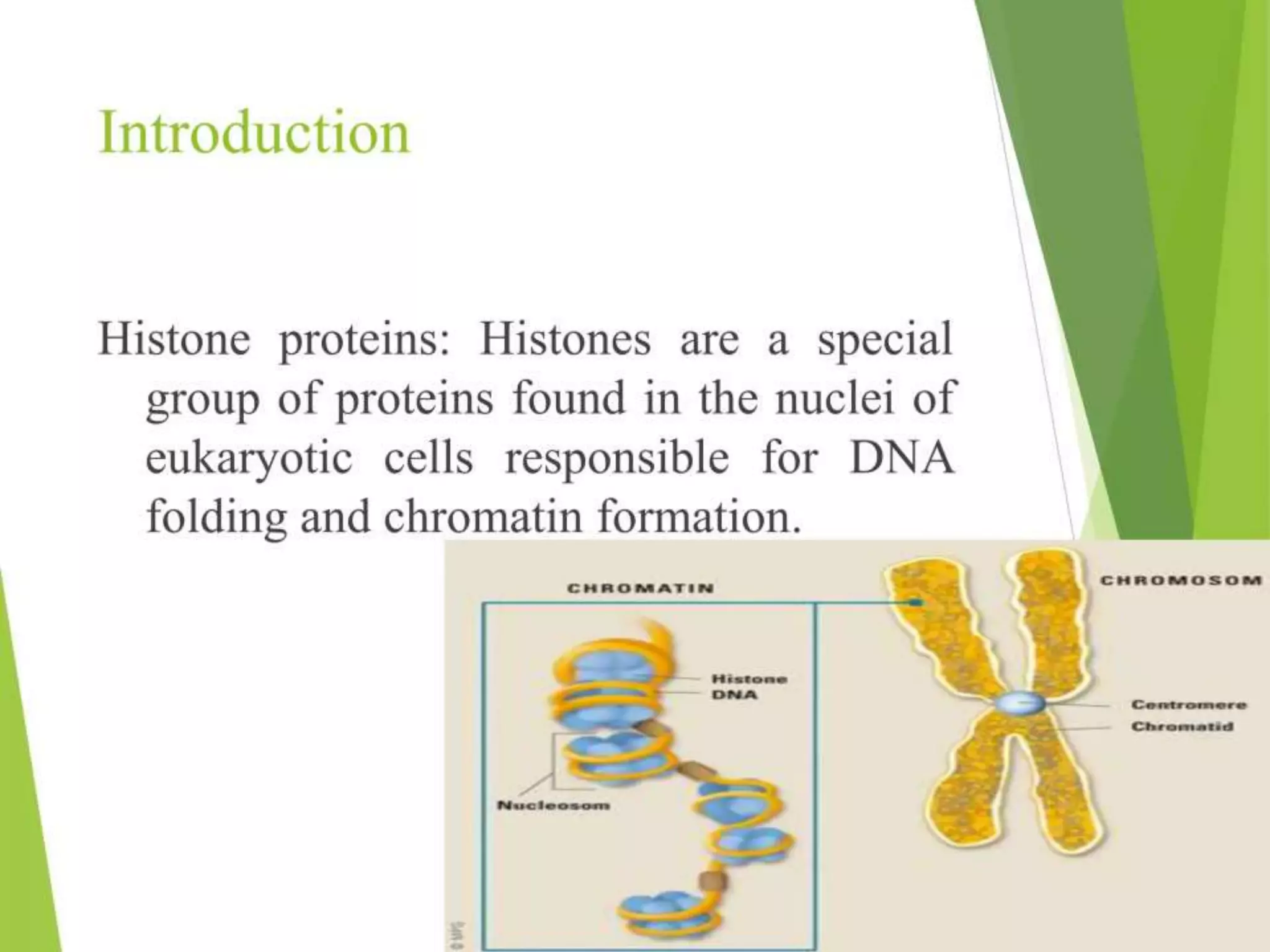
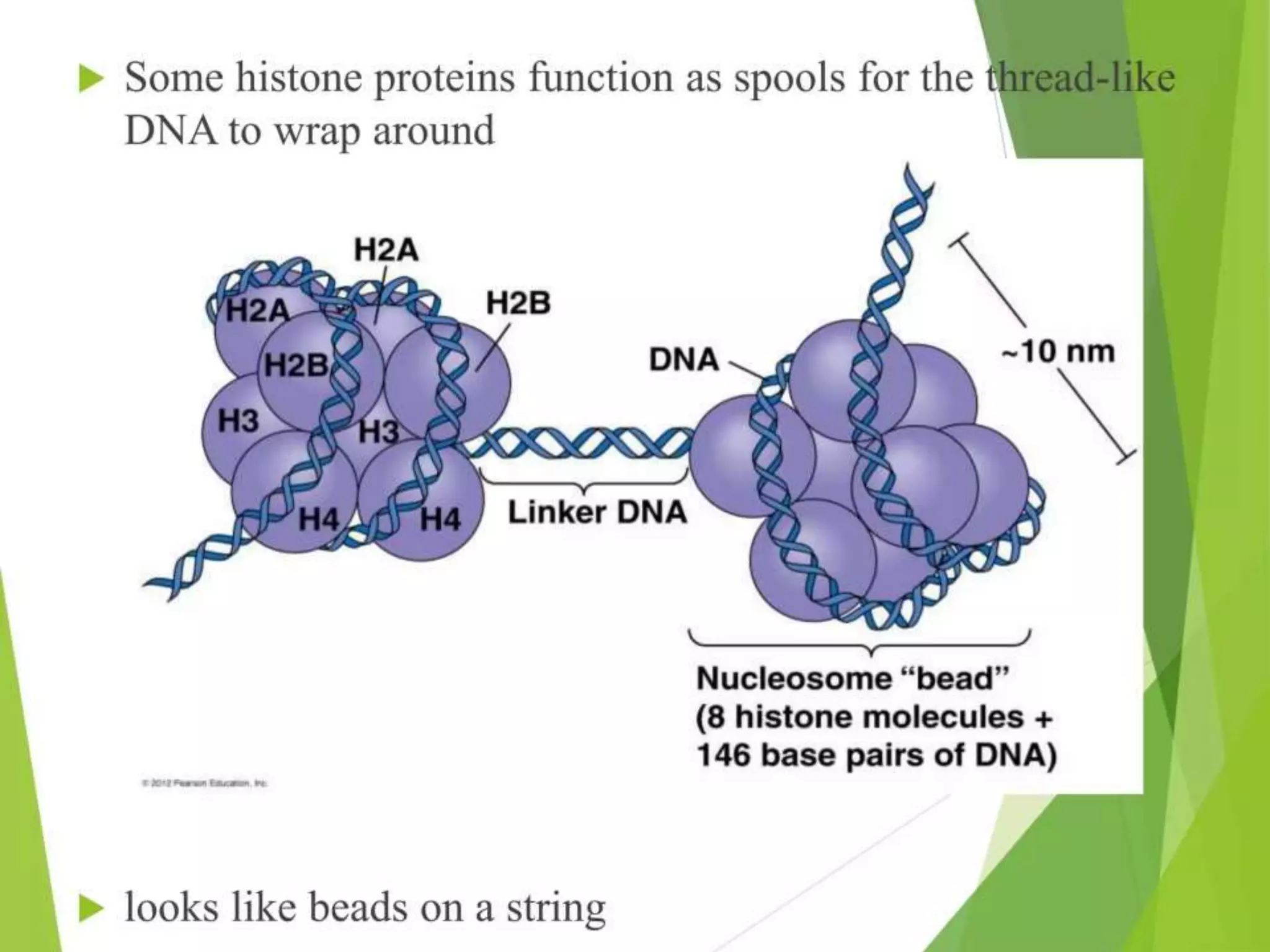
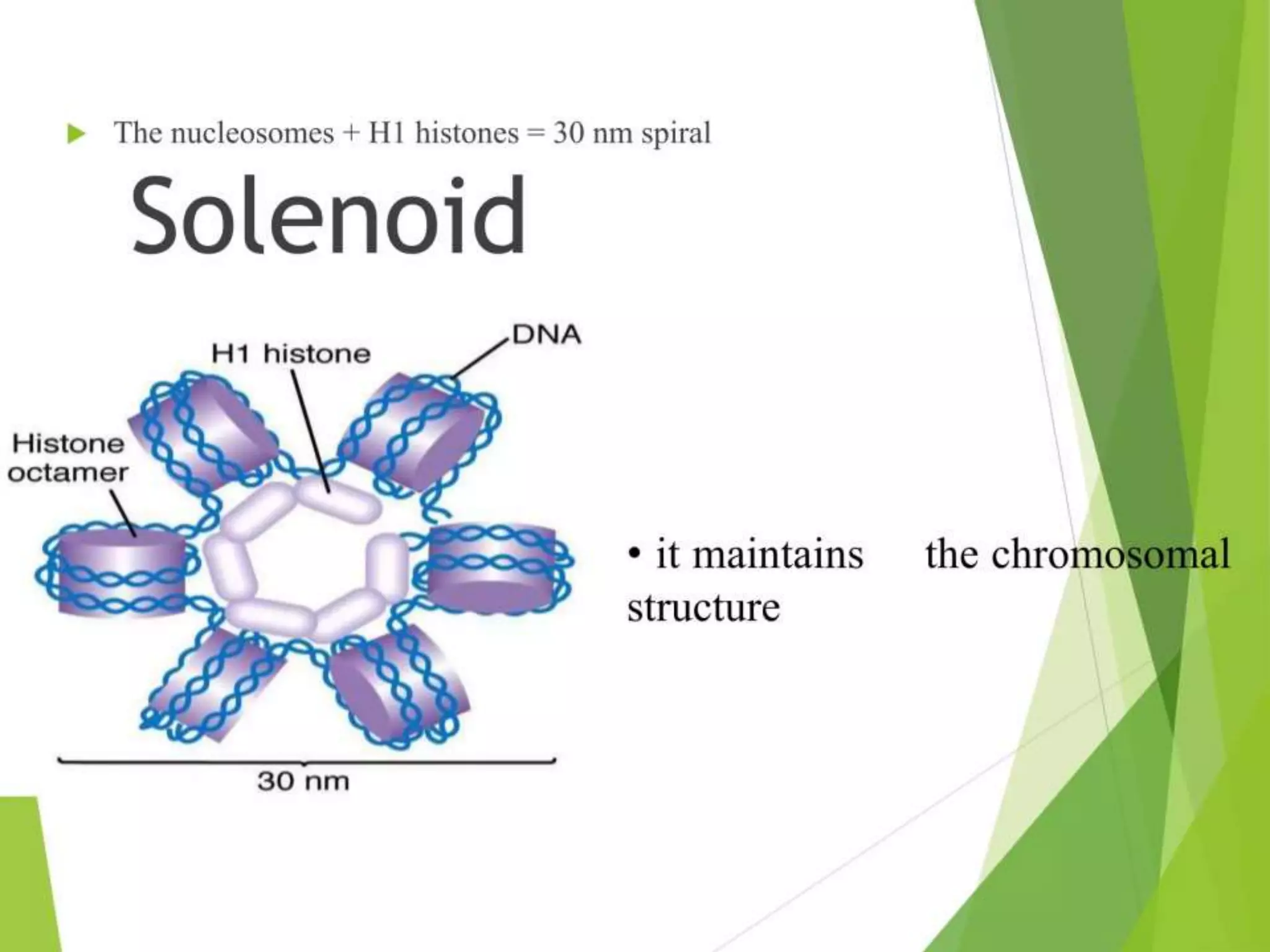
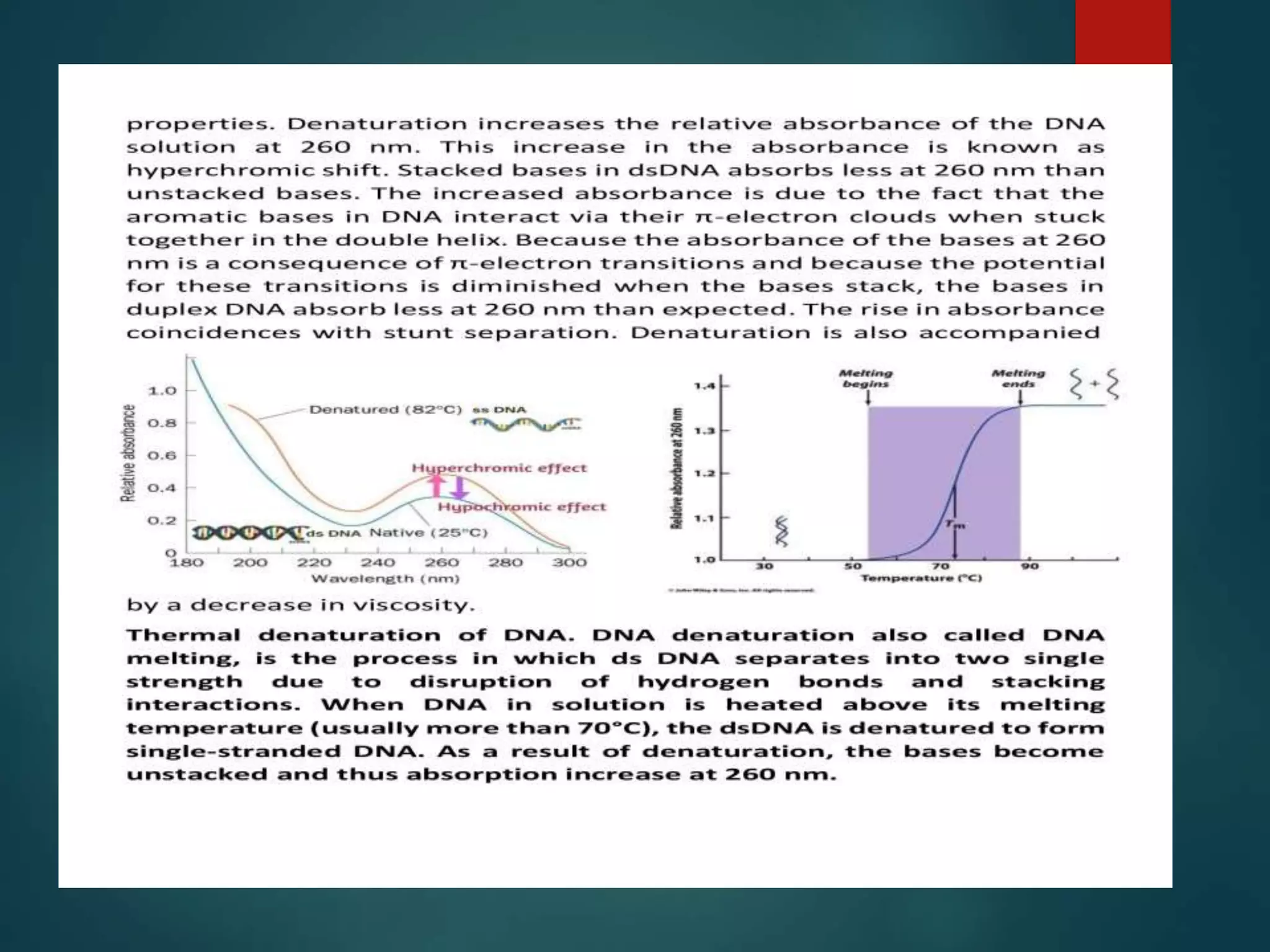
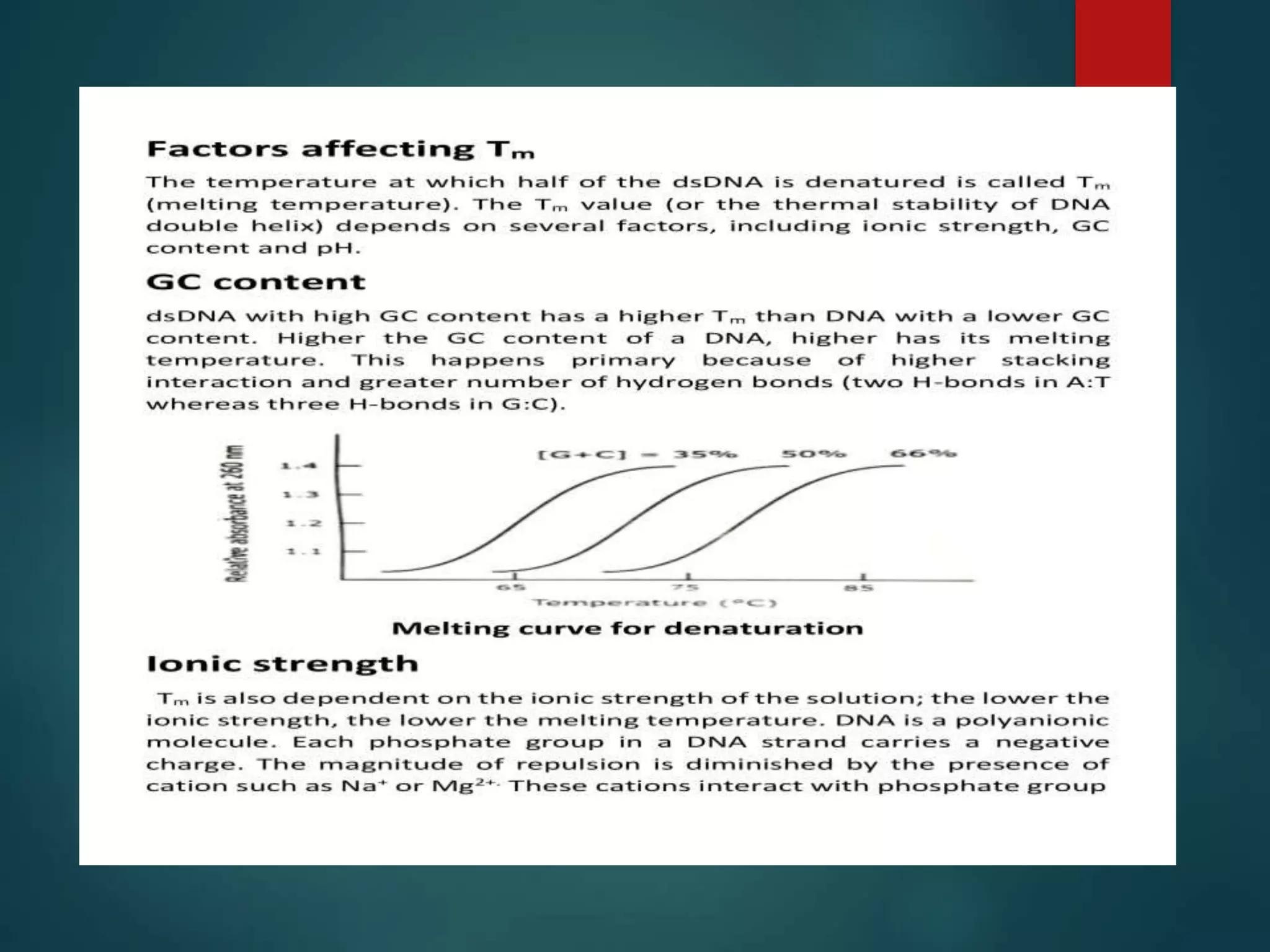
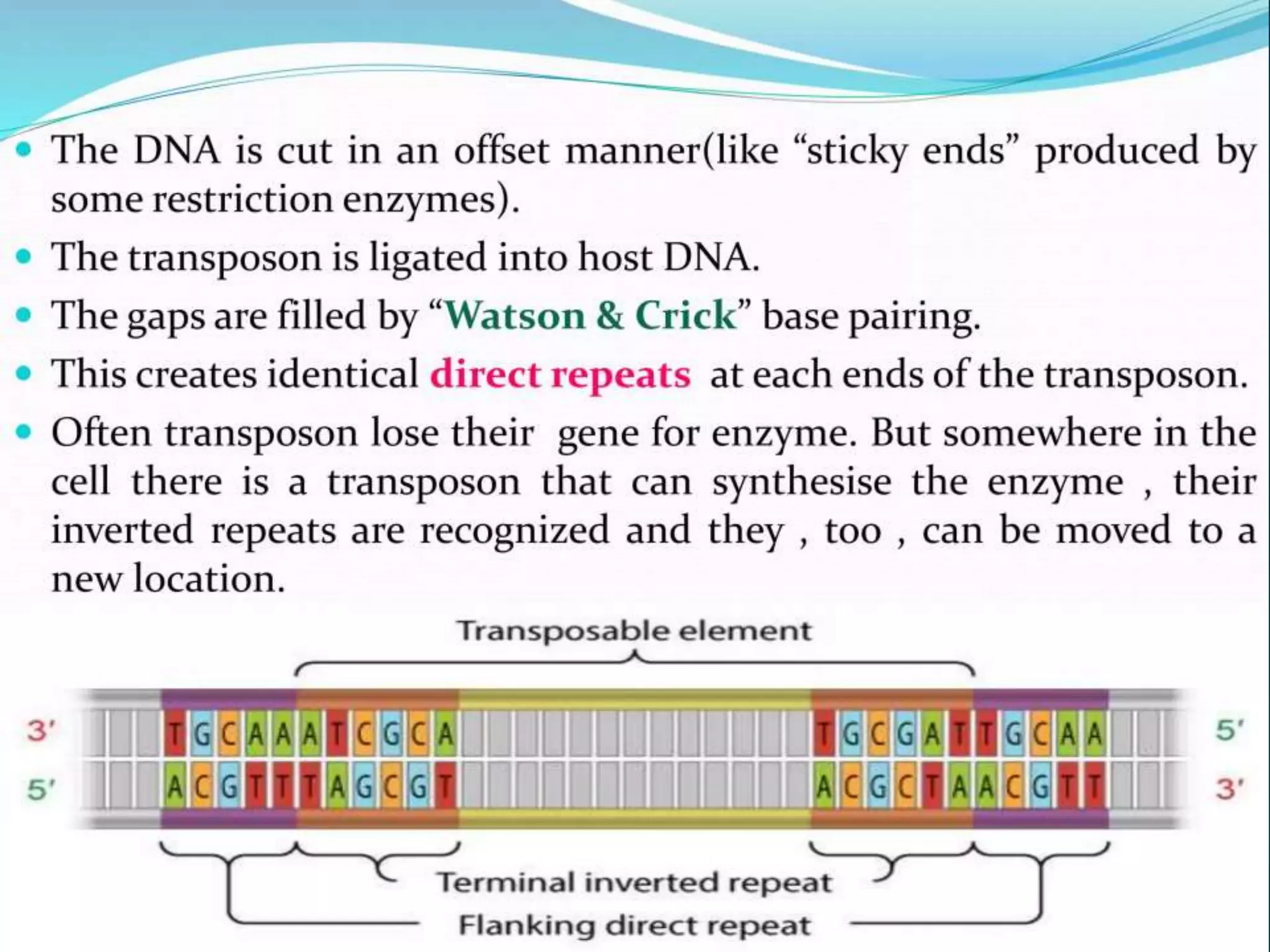
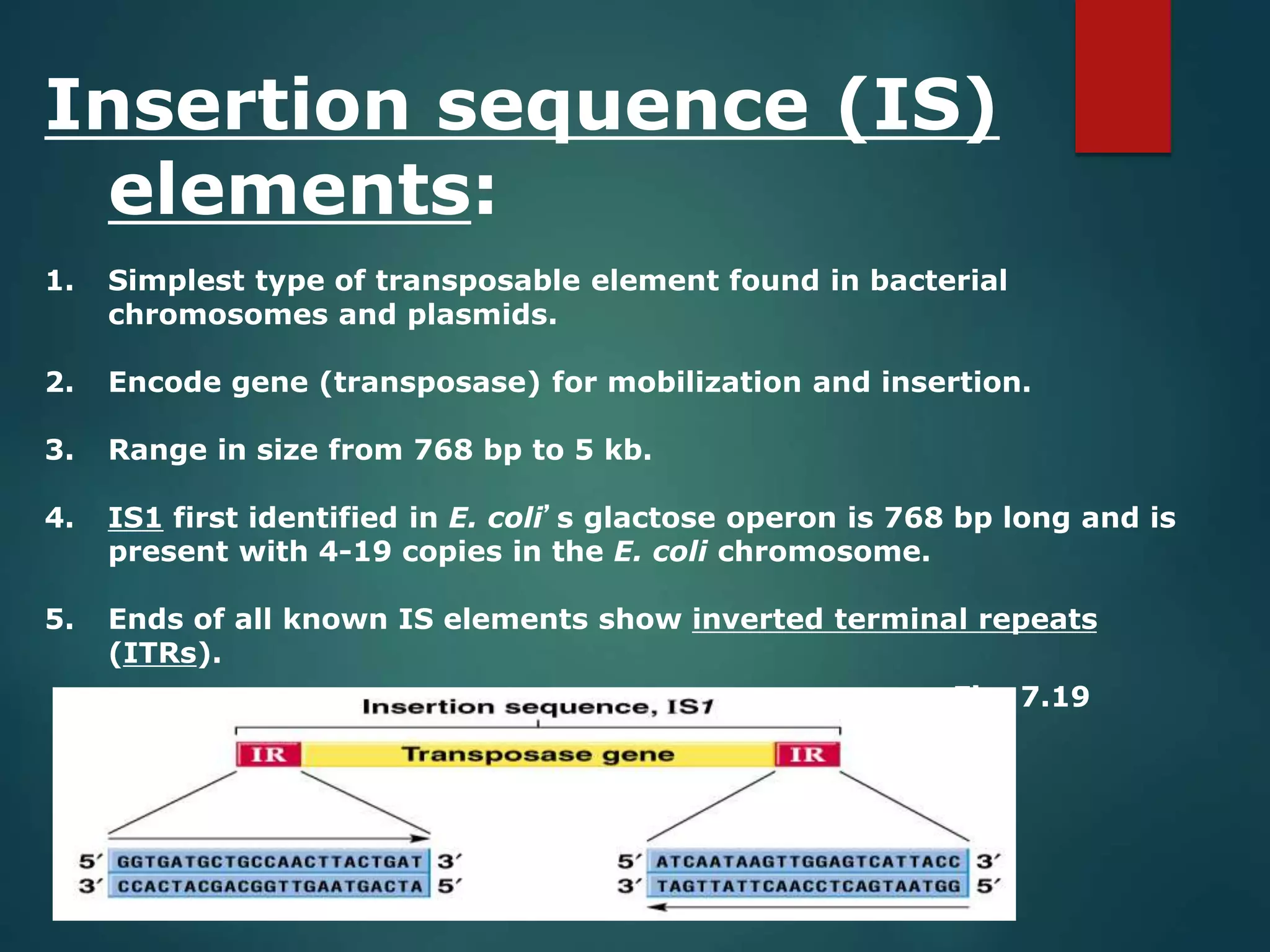
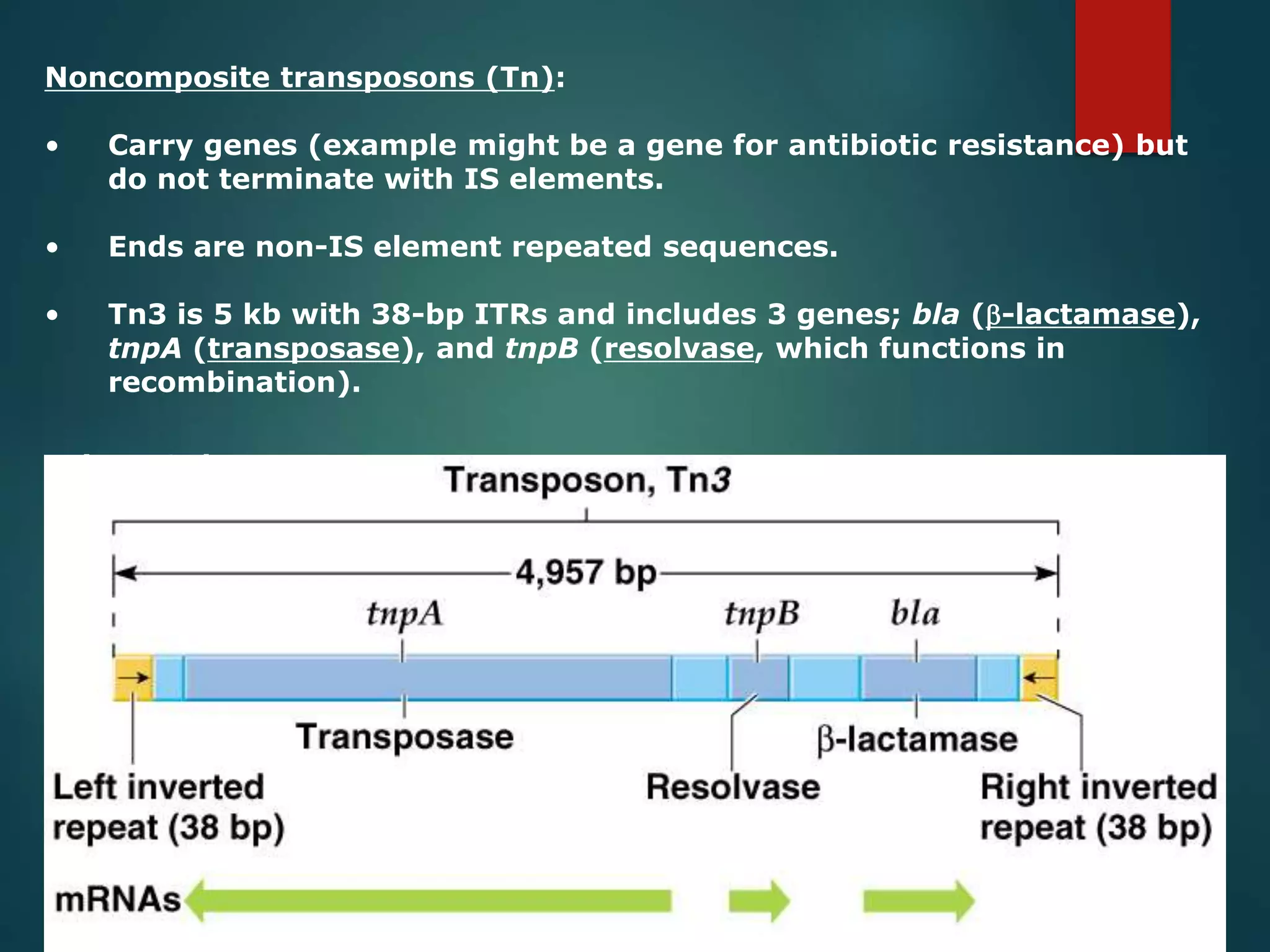
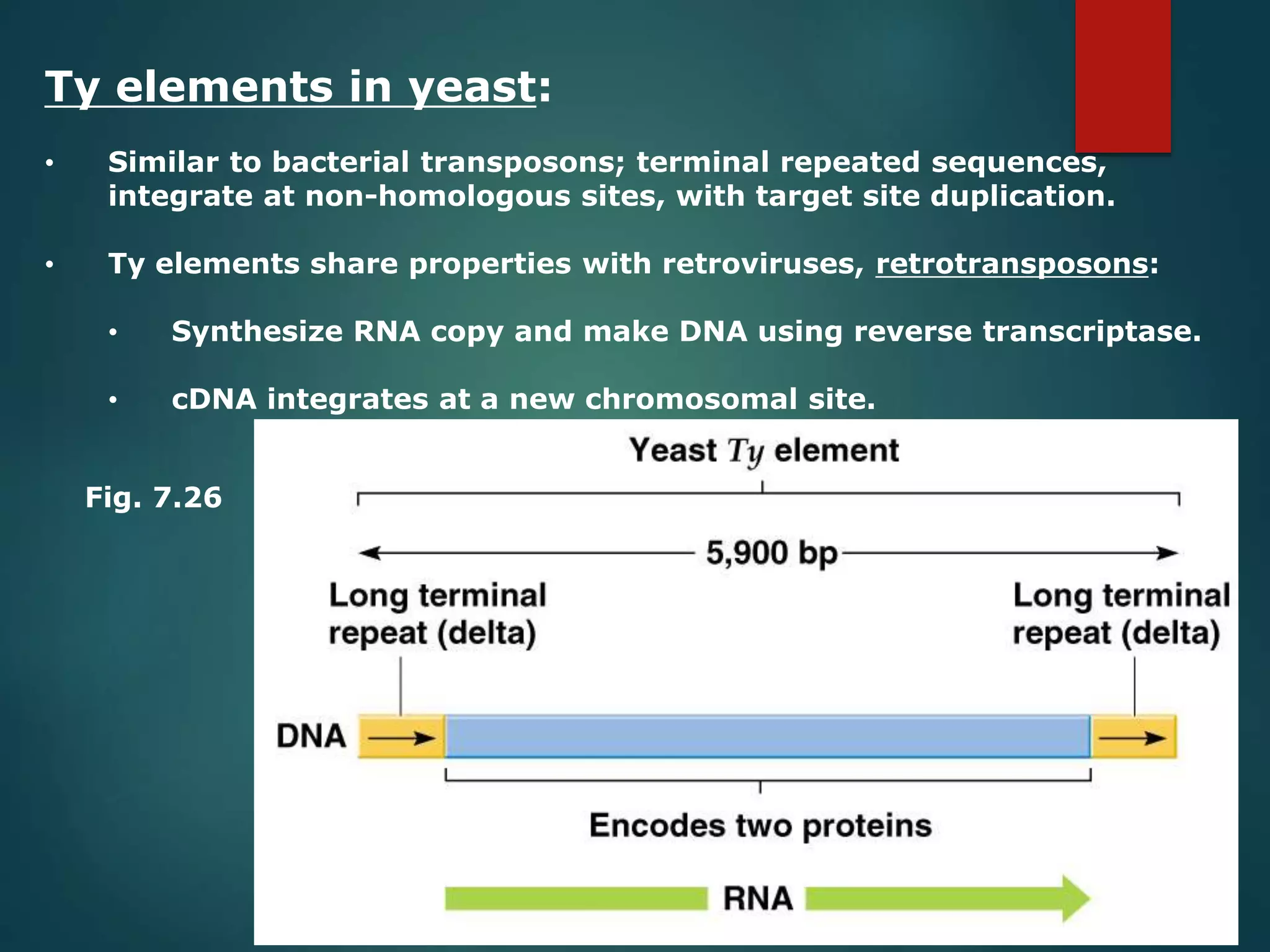
This document discusses chromatin and transposable genetic elements. It defines chromatin as a combination of DNA and proteins that condenses to form chromosomes during cell division in eukaryotes. It is located in the cell nucleus and functions to compact DNA. The document also defines transposable elements as mobile genetic sequences that can move within and between genomes. It describes different types of transposable elements found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, such as insertion sequences, transposons, Ty elements, SINEs, and LINEs. These elements can cause genetic changes by inserting into genes or regulatory sequences.