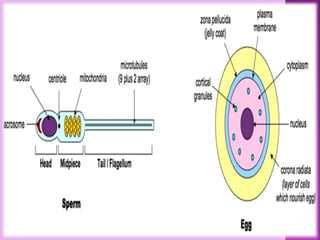
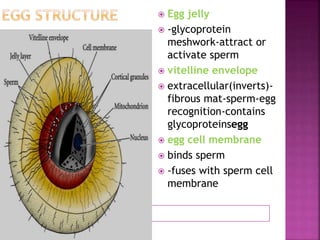
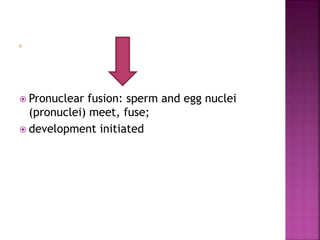
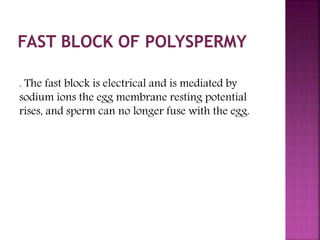
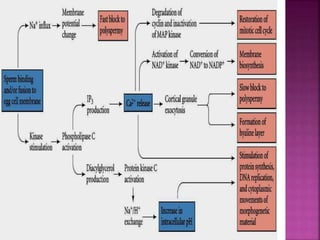
Fertilization involves the fusion of an egg and sperm, combining their genetic material. This process activates the egg and initiates embryonic development. Key events include chemoattraction of sperm to the egg, binding and fusion of gametes, and prevention of polyspermy. Fusion results in the formation of a single cell with a combined genome from both parent cells. This triggers rapid changes in the egg's metabolism and biochemistry that activate it for development. The male and female pronuclei then fuse, forming a single diploid nucleus and initiating the first cell division.