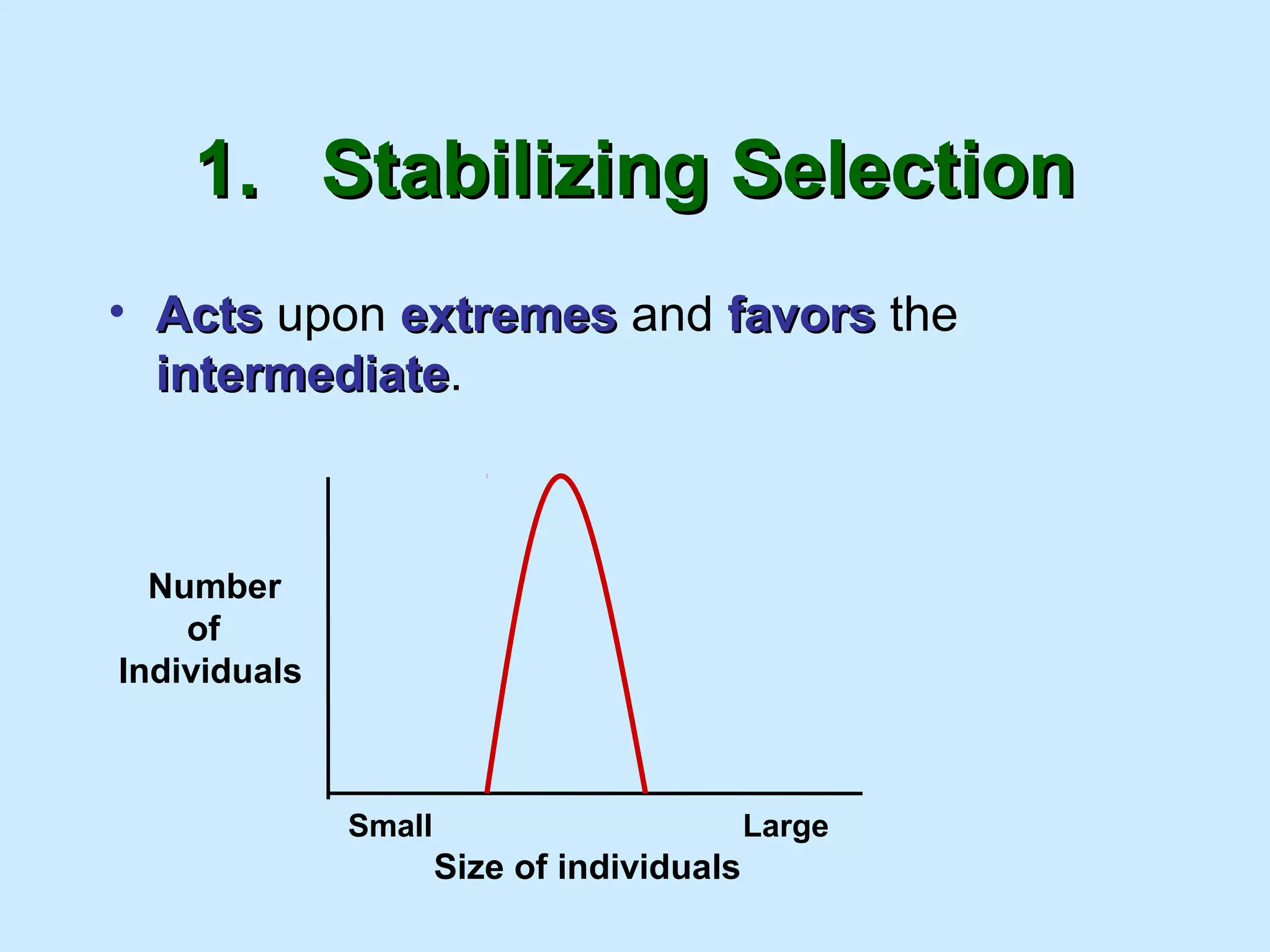
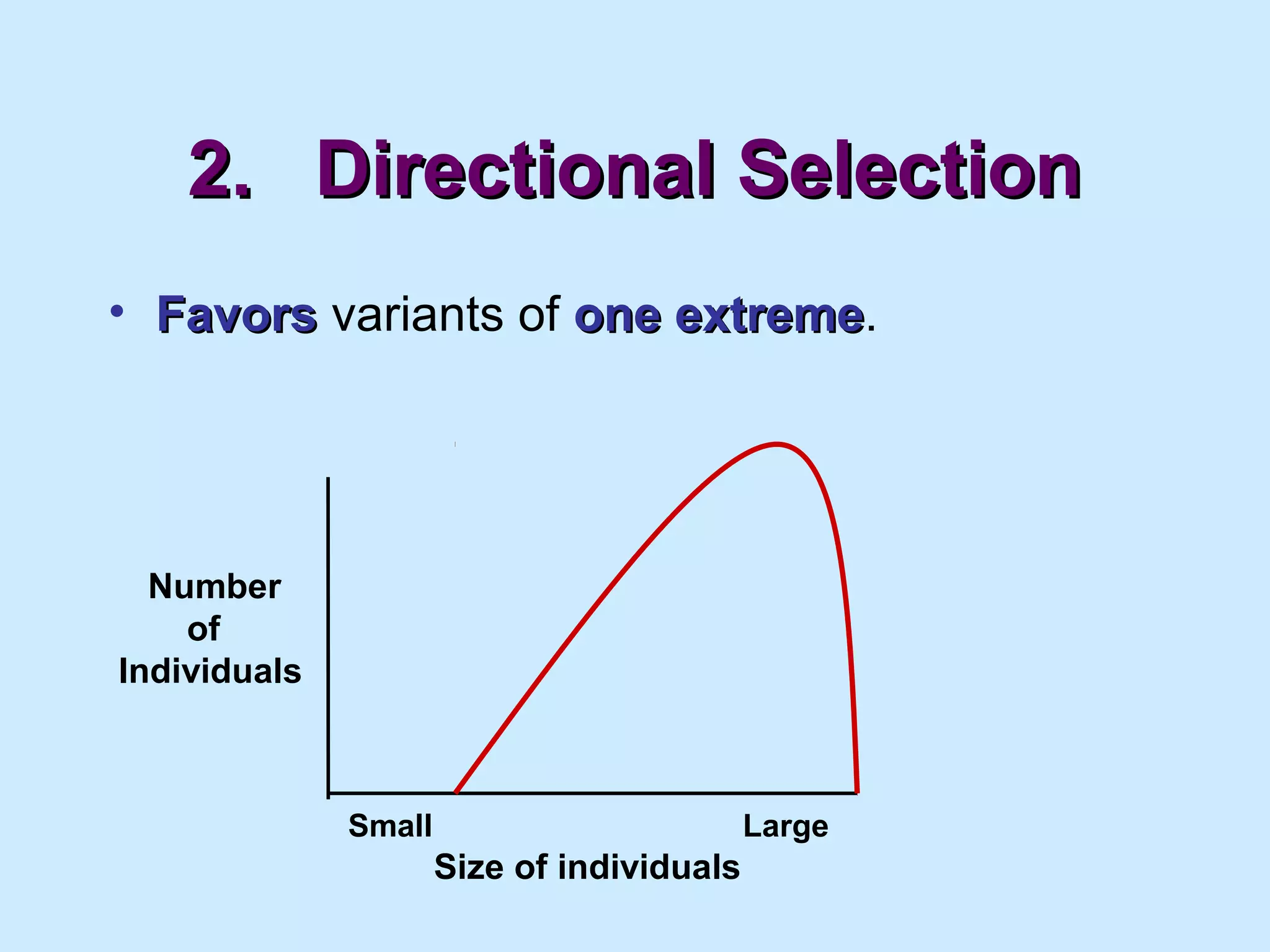
The document summarizes key concepts in evolution including Darwin's theory of natural selection. It discusses early theories of evolution from Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and how Darwin's voyage on the HMS Beagle and observations of species on the Galapagos Islands led him to propose natural selection in his 1859 book On the Origin of Species. Natural selection proposes that individuals with favorable traits are more likely to reproduce and leave more offspring, gradually changing the traits of a population over generations. The document also outlines evidence of evolution such as fossils, taxonomy, and molecular biology as well as mechanisms of microevolution like genetic drift and gene flow that can lead to speciation, the evolution of new species.