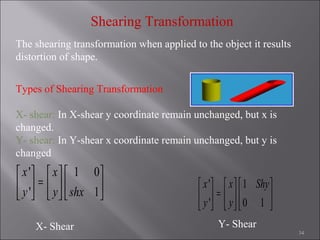
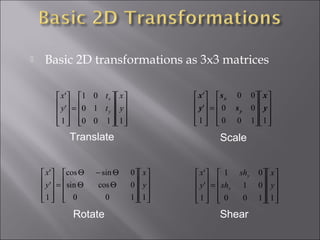
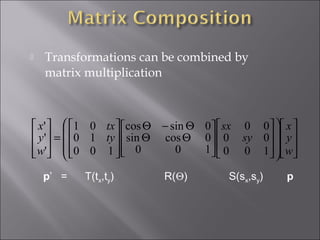
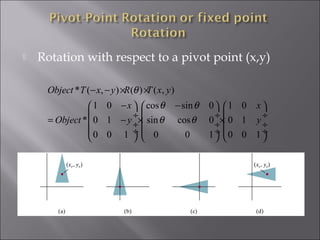
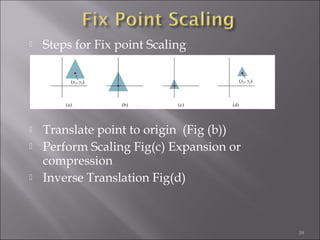
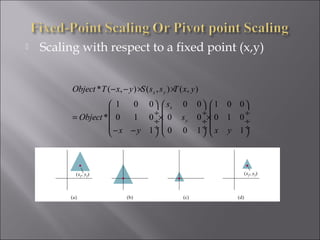
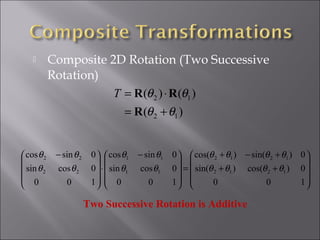
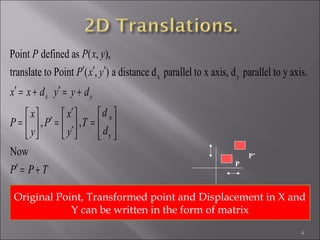
1) 2D geometric transformations include translations, scaling, and rotations. They can be represented by transformation matrices.
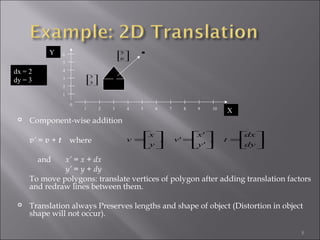
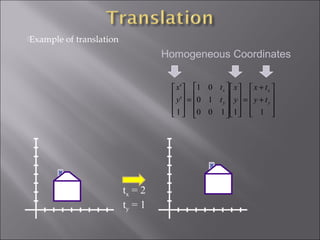
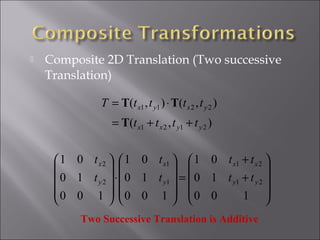
2) Translation moves an object by adding offsets to x and y coordinates. It can be represented by a 3x3 matrix with 1s on the diagonal and offsets as the last column.
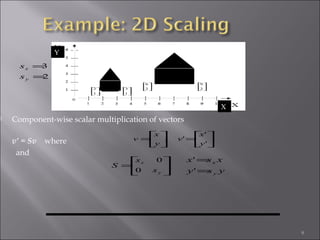
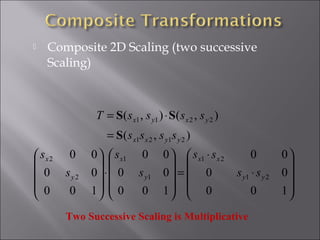
3) Scaling enlarges or shrinks an object by multiplying x and y coordinates by scaling factors. It can be represented by a 2x2 diagonal matrix with scaling factors.
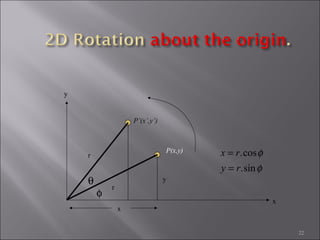
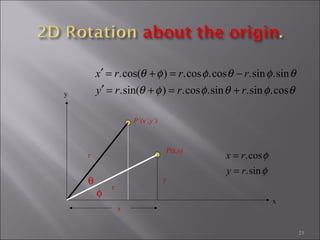
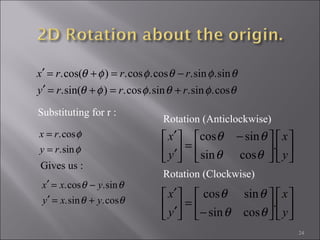
4) Rotation rotates an object by applying a trigonometric transformation to x and y coordinates. It can be represented by a 2x2 rotation matrix containing cosine and sine of the rotation angle.

















![ In matrix form, it can be shown as
Here
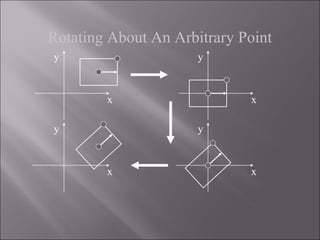
TR is Translation Matrix (Translation towards Origin)
RƟ is Rotation Matrix (Rotation Matrix can be clockwise and
anticlockwise Rotation)
TR
-1
is Translation matrix (Away from origin)
29
[ ] [ ][ ][ ]
1
R RT T R Tθ
−
=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2dtransformation-170418110541/85/2-d-transformation-29-320.jpg)


![33
Translate [1,3] by [7,9]
Scale [2,3] by 5 in the X direction and 10 in the Y direction
Rotate [2,2] by 90°
(π/2)
=
⋅
1
12
8
1
3
1
100
910
701
=
⋅
1
30
10
1
3
2
100
0100
005
−
=
⋅
−
=
⋅
−
1
2
2
1
2
2
100
001
010
1
2
2
100
0)2/cos()2/sin(
0)2/sin()2/cos(
ππ
ππ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2dtransformation-170418110541/85/2-d-transformation-33-320.jpg)