Embed presentation



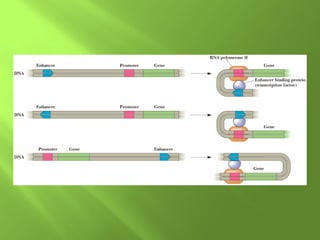
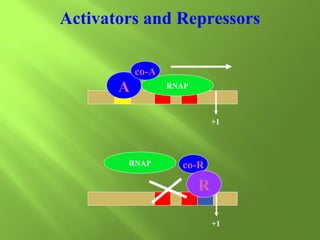


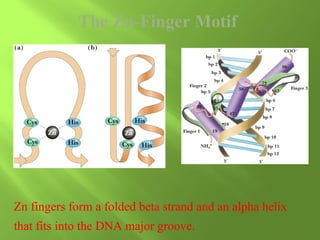

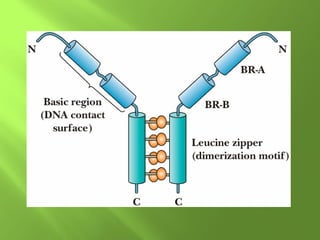
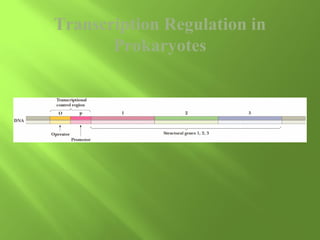
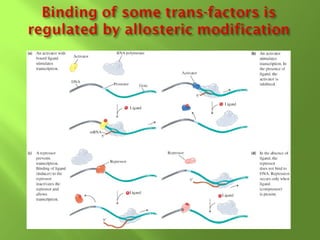
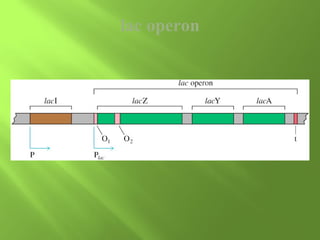
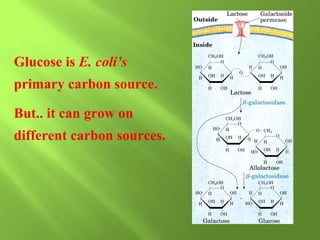
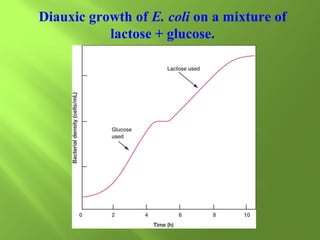
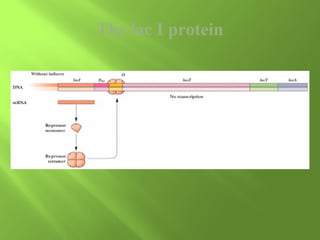
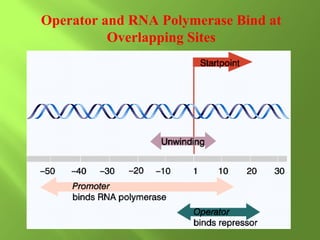
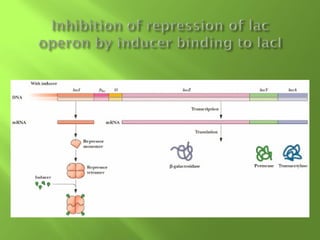
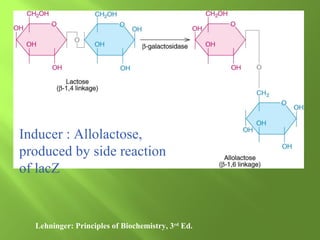
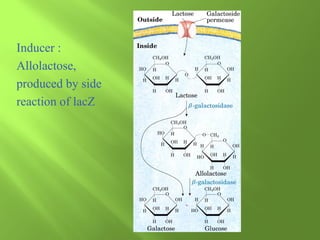
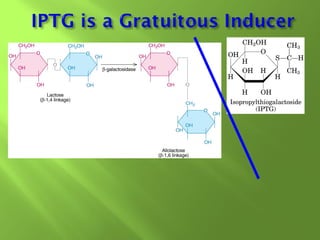
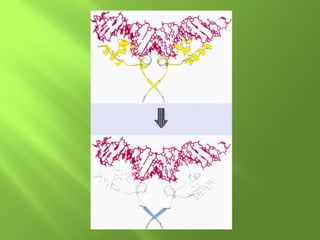
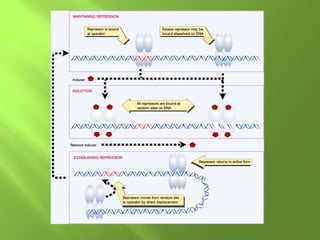
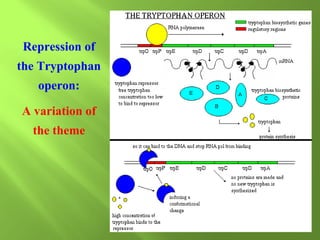
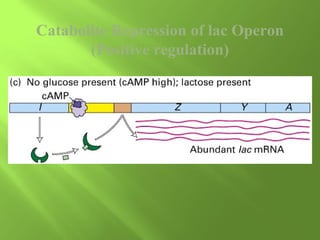
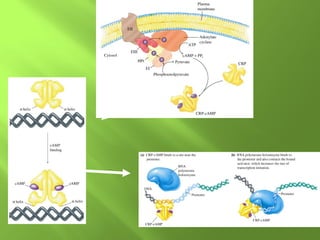
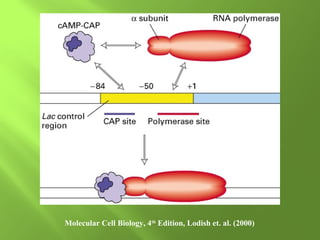
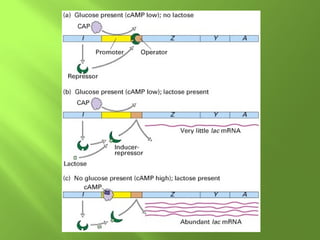

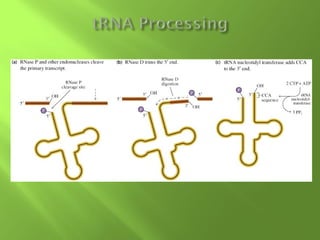
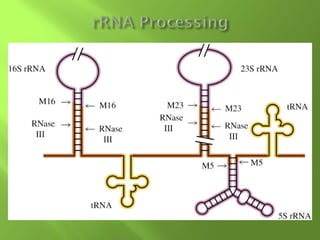
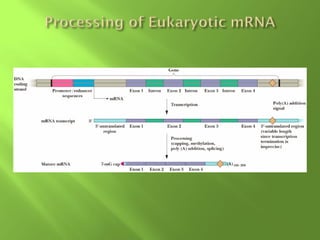

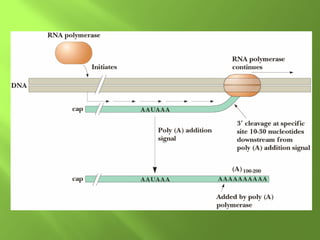
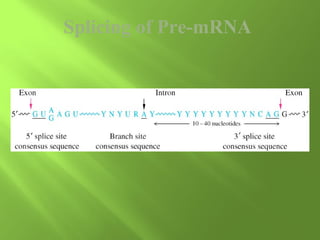
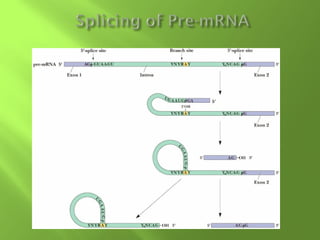

The document discusses various mechanisms of transcriptional regulation and RNA processing in cells. It describes motifs like helix-turn-helix, zinc finger, and leucine zipper that allow proteins to bind to DNA and regulate transcription. It also discusses examples of transcriptional regulation in prokaryotes like the lac operon in E. coli and mechanisms of RNA processing like 5' capping, splicing, and degradation.




































