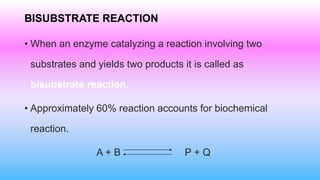
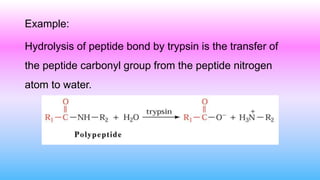
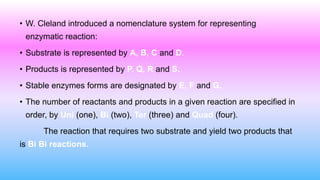
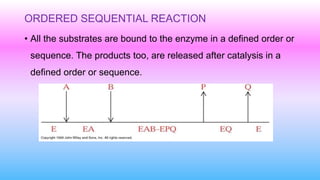
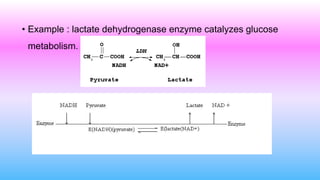
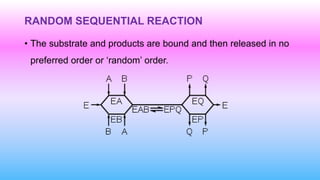
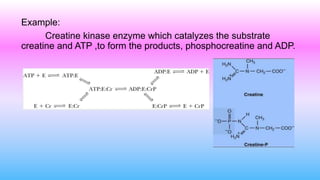
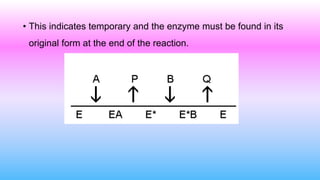
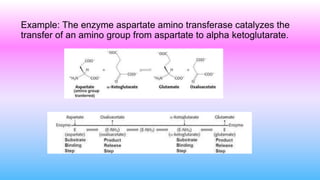
This document discusses bisubstrate reactions, which involve two substrates and produce two products. Approximately 60% of biochemical reactions are bisubstrate reactions. They can be transferase reactions, where a functional group is transferred between substrates, or oxidation-reduction reactions. Bisubstrate reactions fall into two categories: sequential reactions, where substrates bind sequentially before products are released; and ping pong reactions, where an intermediate enzyme form is produced after the first substrate reaction. Common examples of each type of bisubstrate reaction are provided.