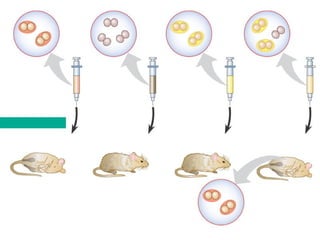
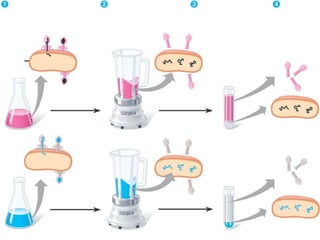
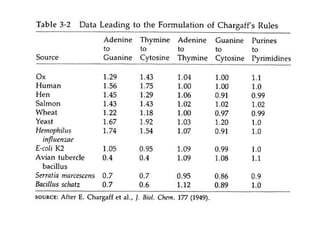
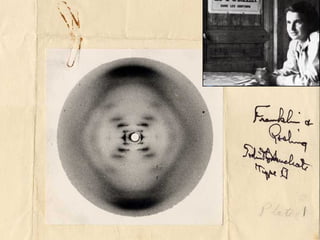
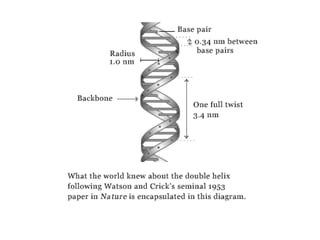
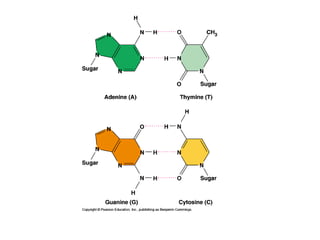
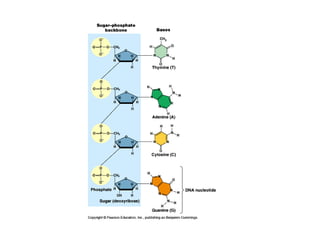
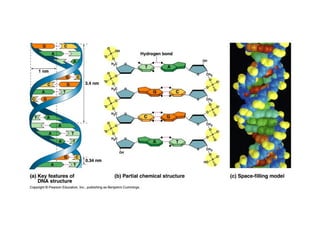
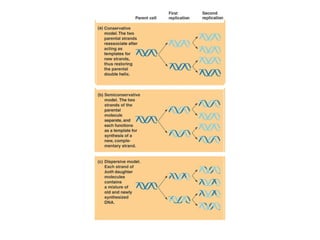
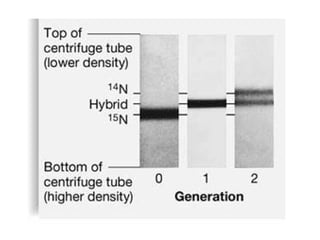
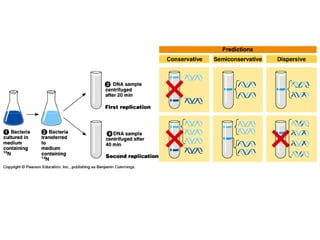
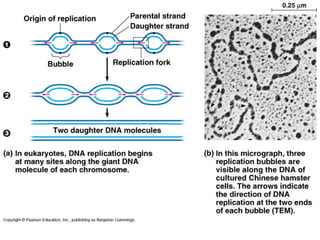
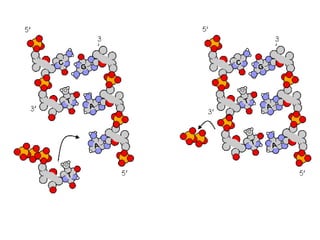
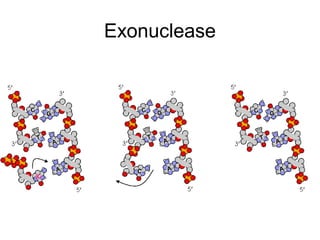
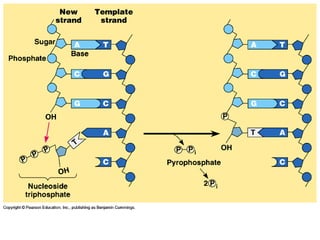
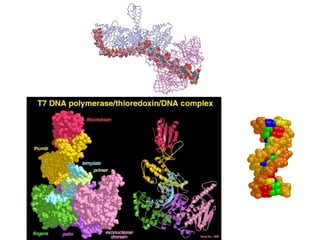
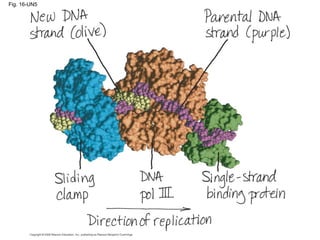
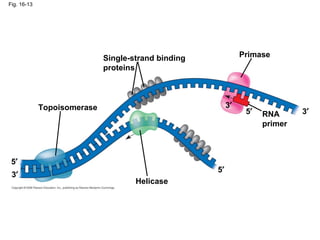
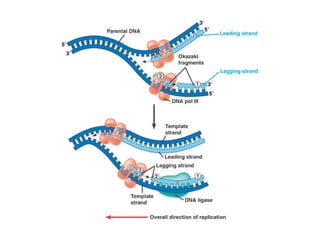
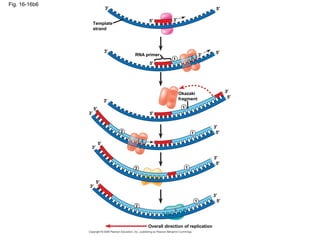
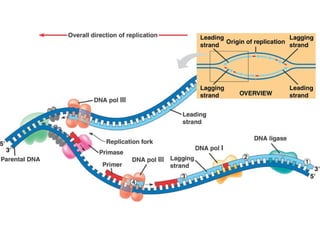
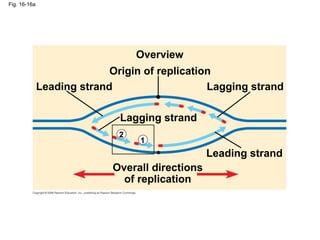
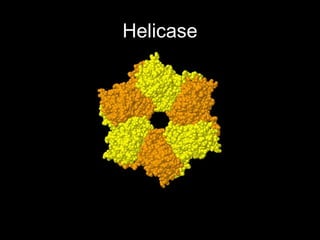
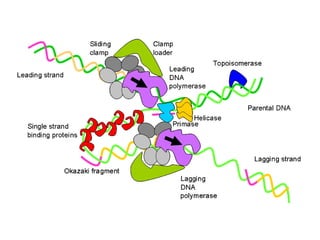
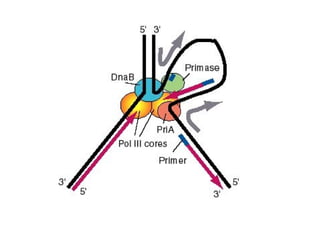
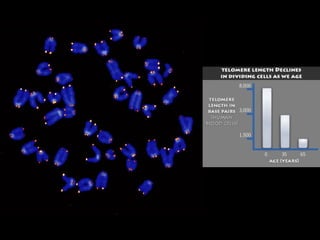
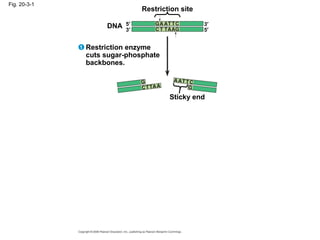
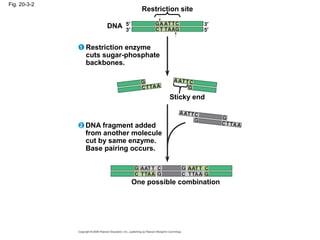
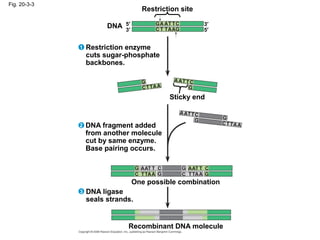
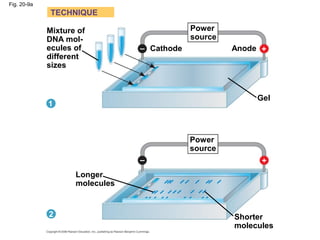
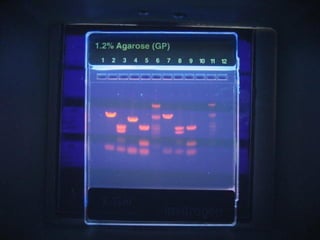
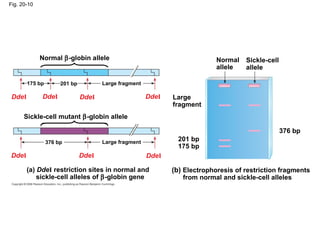
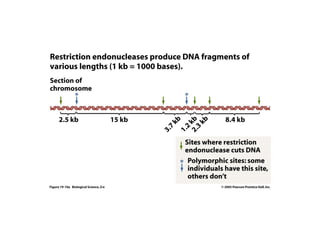
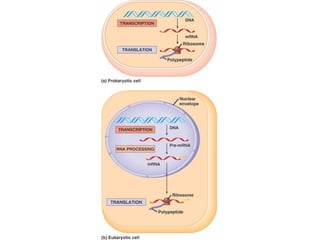
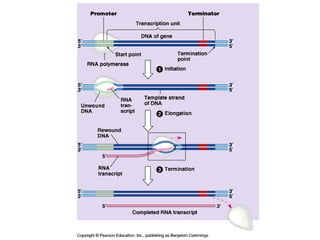
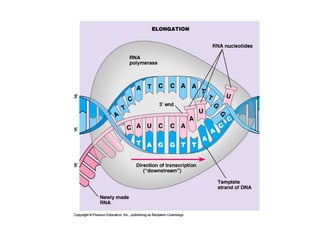
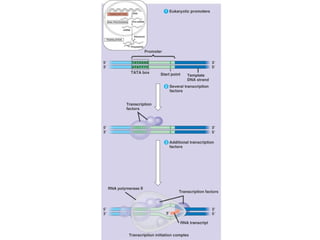
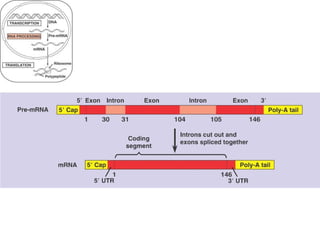
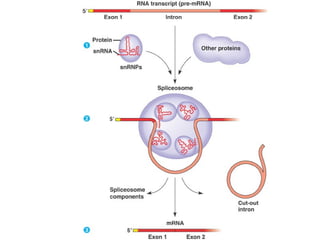
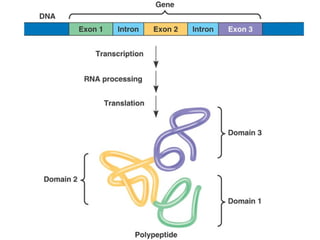
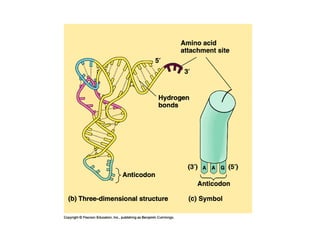
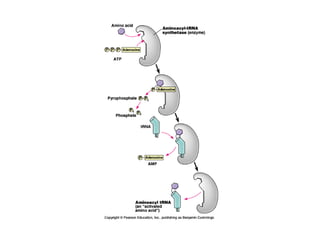
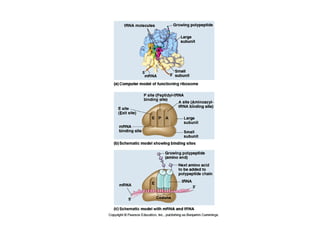
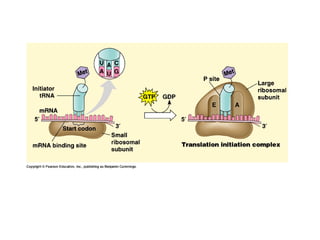
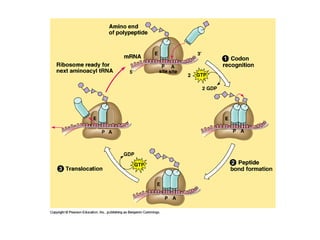
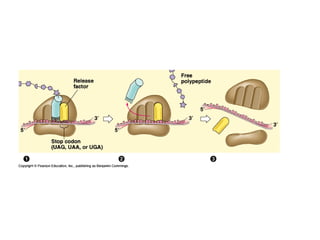
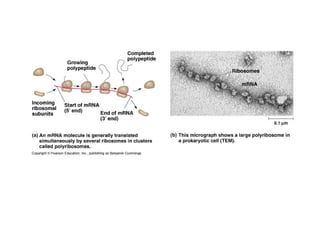
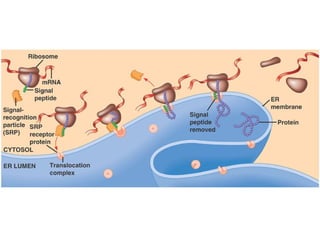
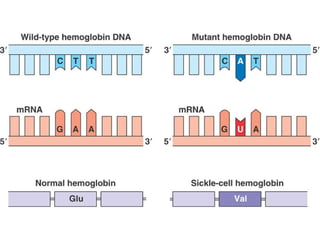
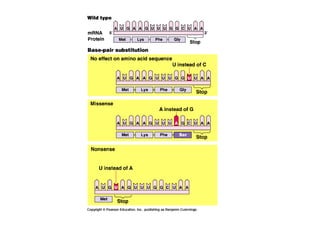
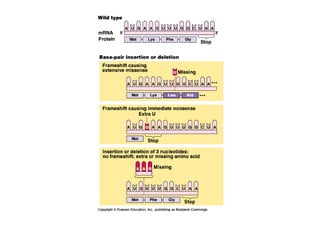
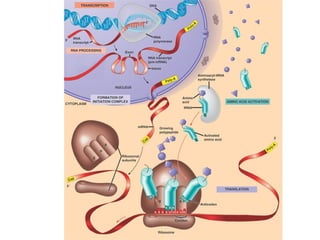
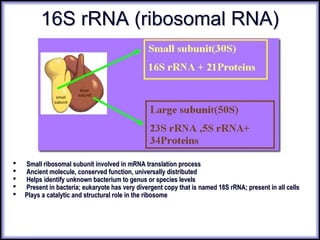
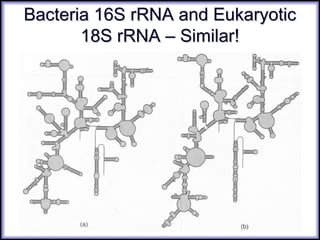
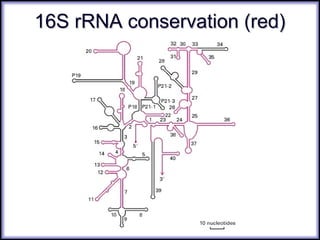
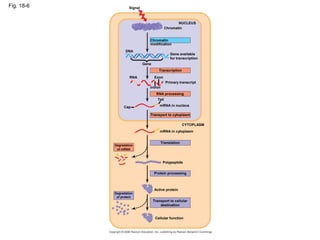
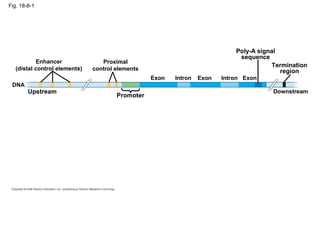
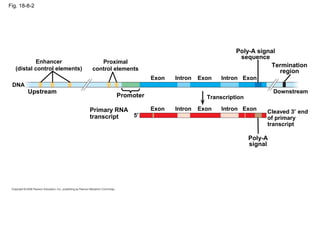
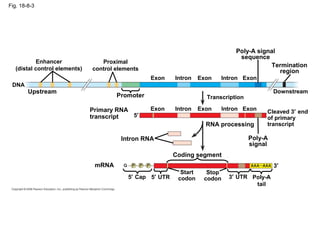
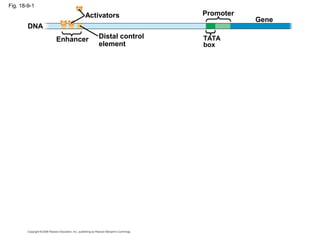
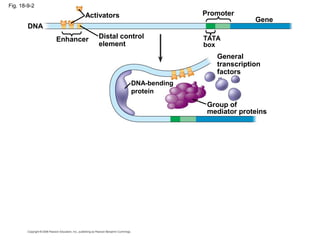
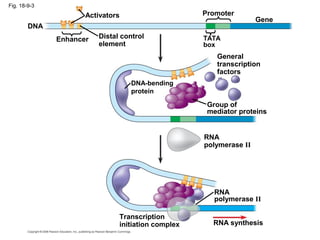
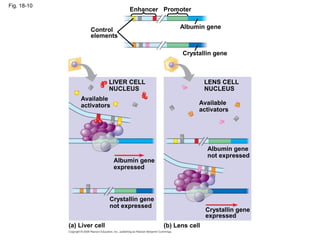
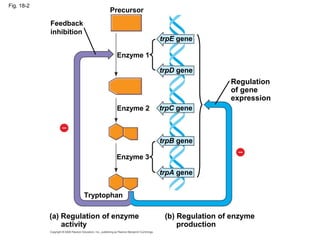
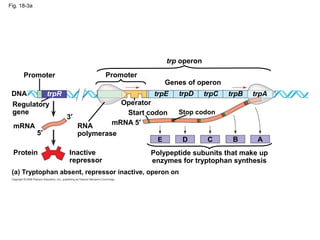
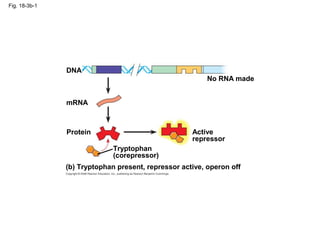
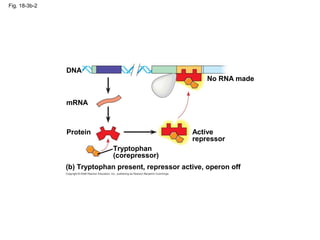
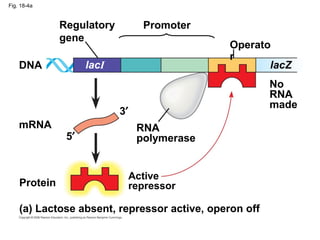
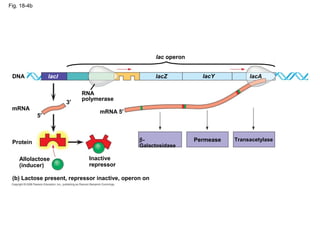
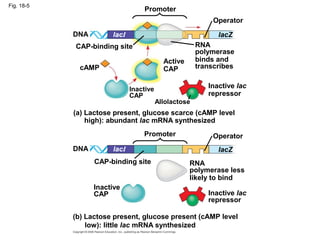
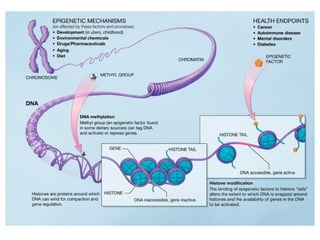
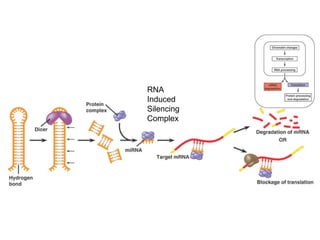
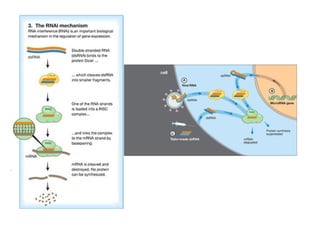
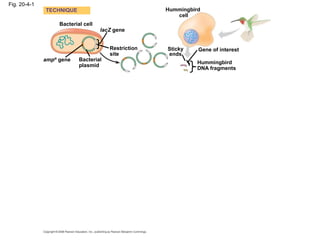
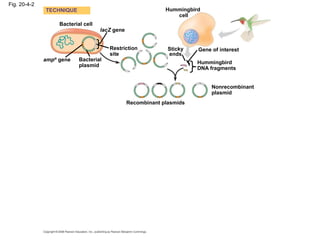
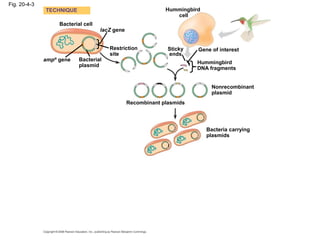
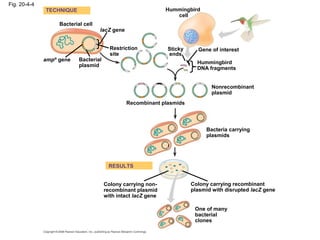
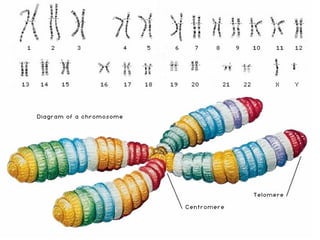
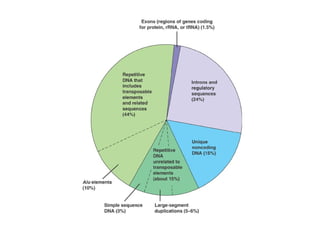
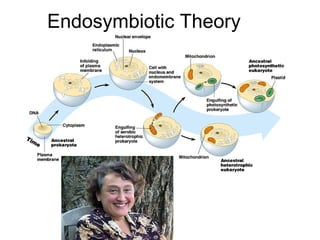
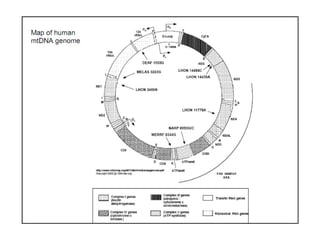
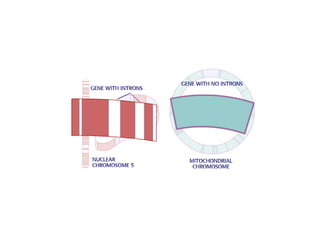
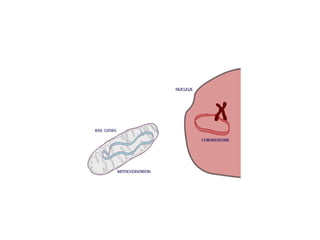
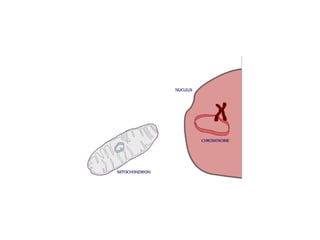
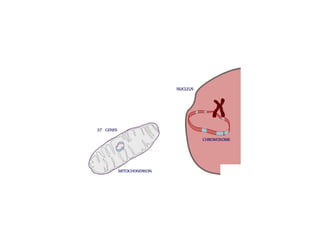
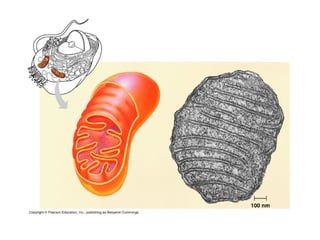
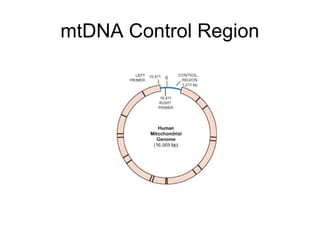
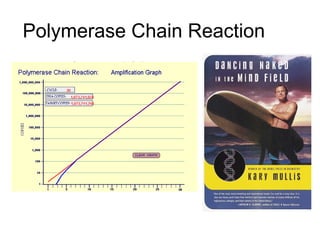
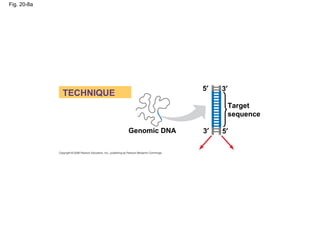
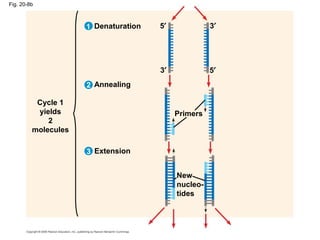
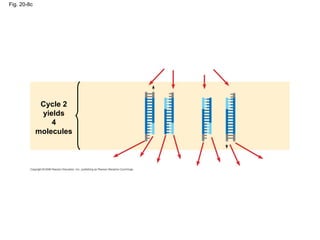
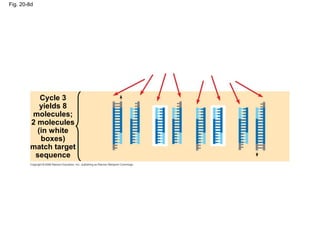
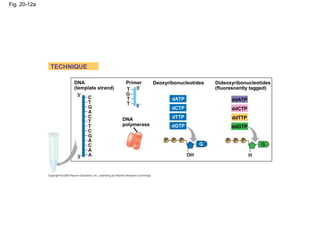
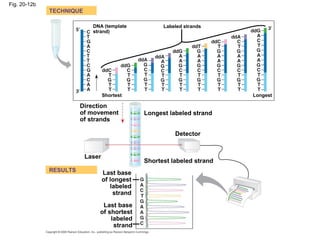
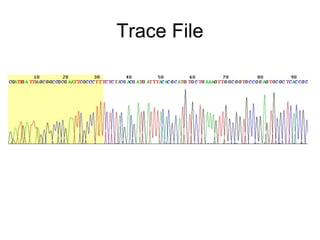
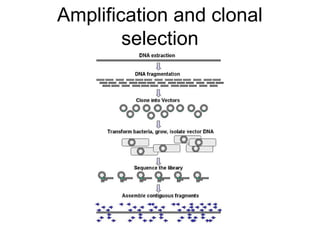
This document discusses DNA replication and gene regulation. It begins with an overview of DNA replication and the enzymes involved, including helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, and ligase. It then discusses gene regulation, showing diagrams of operons like the lac and trp operons. It demonstrates how transcription factors, repressors, inducers, and corepressors control gene expression. Finally, it provides an example of epigenetic gene regulation involving chromatin remodeling and DNA methylation.