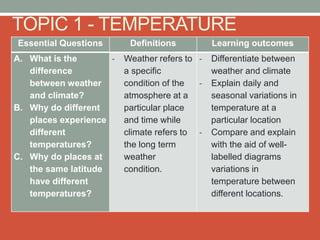
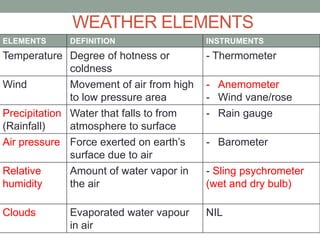
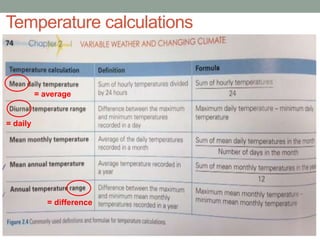
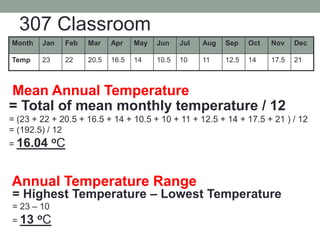
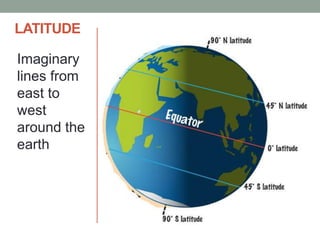
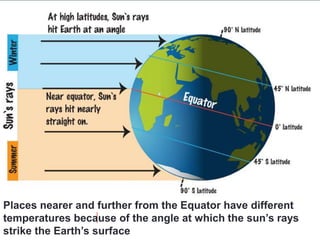
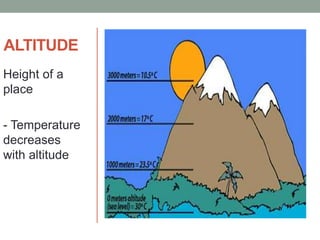
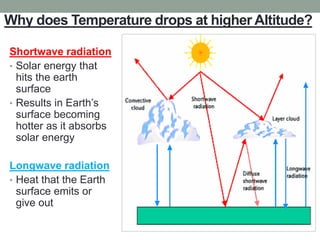
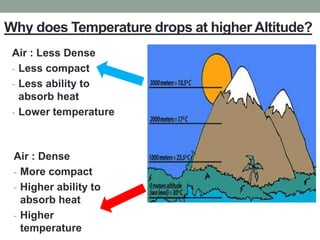
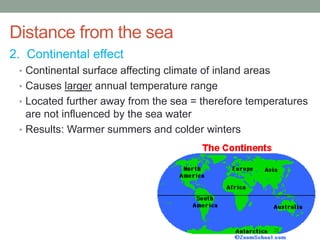
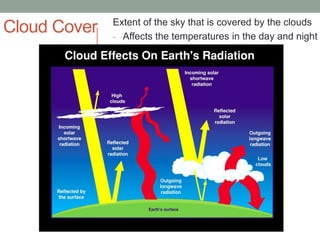
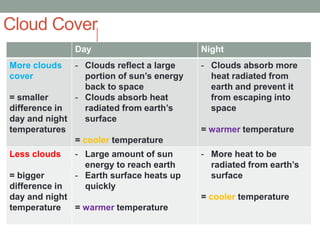
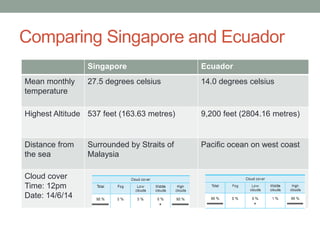
The document discusses temperature, defining weather as short term atmospheric conditions while climate refers to long term patterns, and explores factors that cause variations in temperature between locations including latitude, altitude, distance from bodies of water, and cloud cover. Places at the same latitude can have different temperatures due to other influences on local climate such as elevation, proximity to oceans, and cloud levels that impact how much solar energy reaches and leaves the surface.






![Homework 1
1. What is the difference between
weather and climate? [1]
2. Why do different places experience
different temperatures? [4]
3. With the aid of a well-labelled
diagram, explain why do places at the
same latitude have different
temperatures? [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1-140622023053-phpapp02/85/Topic-1-20-320.jpg)