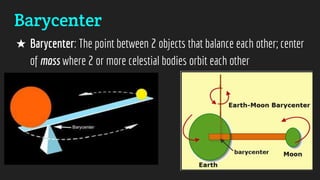
The document discusses the various motions of the Earth including its rotation, revolution around the sun, precession, and nutation. It explains how these motions affect seasons and tides on Earth. Additionally, it covers how the sun produces energy through nuclear fusion and transfers it to Earth through radiation, making life possible.