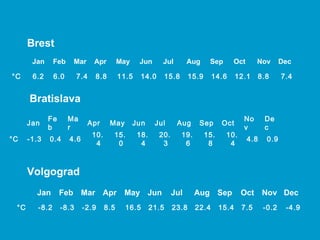
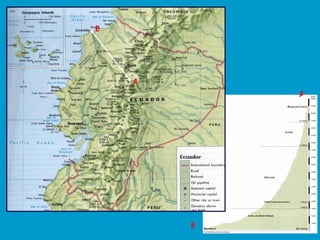
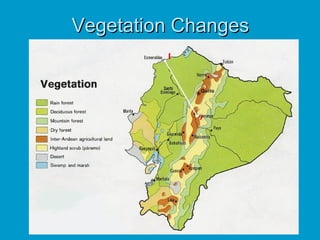
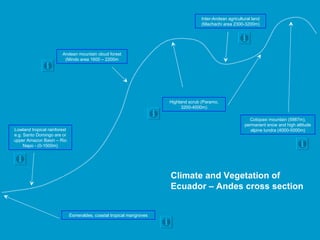
The document discusses several key factors that influence climate:
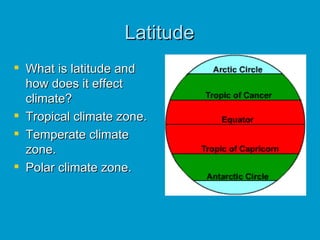
1) Latitude determines tropical, temperate, and polar climate zones.
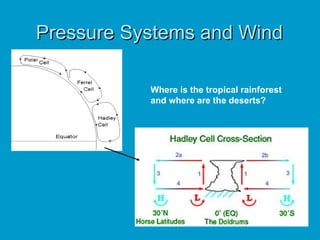
2) Pressure systems and winds influence where tropical rainforests and deserts are located.
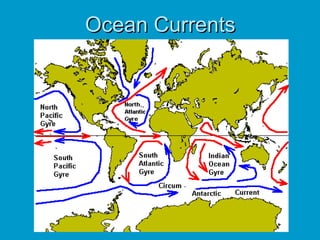
3) Ocean currents impact regional climates.
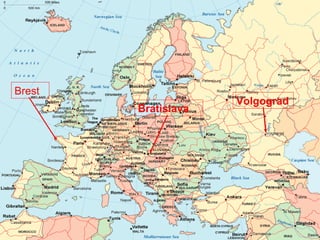
4) Distance from the coast (continentality) affects temperature, as land warms and cools faster than oceans.