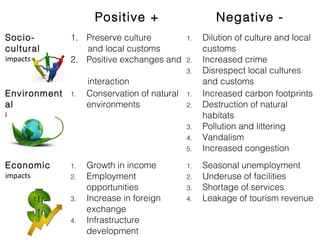
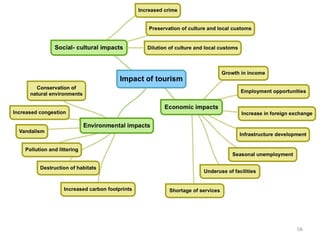
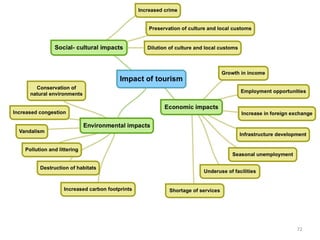
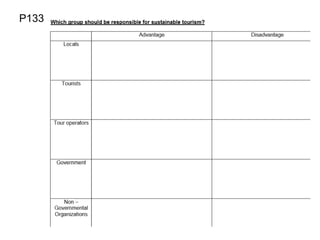
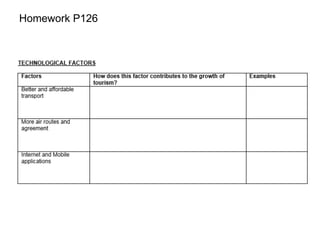
The document discusses different types of tourism:
1) Honeypot tourism refers to popular attractions that attract large numbers of tourists, such as the Taj Mahal and Colosseum.
2) MICE tourism focuses on destinations that provide amenities for meetings, incentives, conferences, and exhibitions, like convention centers in Singapore.
3) Medical tourism has risen with destinations offering good medical facilities and procedures, like cosmetic surgery in South Korea.

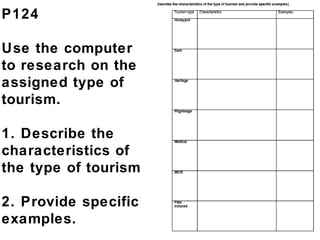














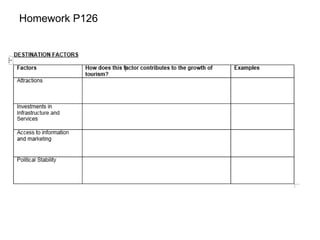
![Homework P125 – Describe the domestic and
international travel patterns shown in Fig. 4. [3]
ONLY PART (AI)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tourism-181119042421/85/Tourism-17-320.jpg)





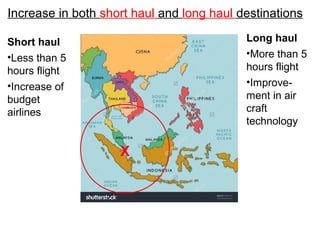







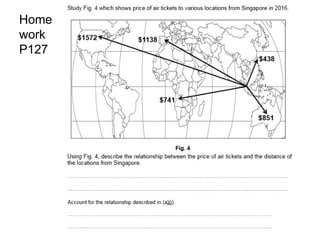
![Using Fig. 4, describe the relationship between the price
of air tickets and the distance of the locations from
Singapore. [3]
- Most Expensive : Locations that are further away from
Singapore such as North America are the most
expensive at $1572.
- Cheapest : Locations that are nearest to Singapore
such as Hong Kong is the cheapest at $438
- ANOMALIE : However prices of air tickets to Australia
is more expensive at $851 compared to Africa at $741
although Australia is nearer to Singapore than Africa.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tourism-181119042421/85/Tourism-38-320.jpg)
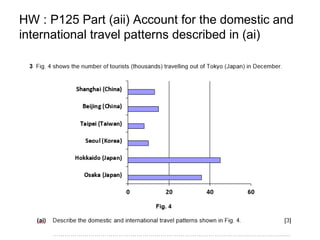
![Account for the domestic and international travel patterns
described in (ai) [3]
Domestic tourism are higher than International tourism out of
Tokyo due to the following reasons:
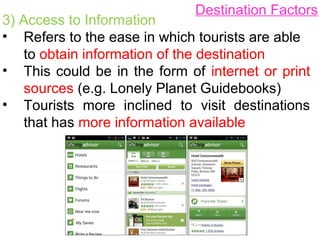
1)There could be greater access of information about Tokyo in
the Internet or print sources in Japan. Therefore it encourages
Hokkaido and Osaka tourists to visit Tokyo.
2) There could be prevalent marketing of Tokyo throughout
Japan to allow Japanese to get access to information more
readily. / As compared with the International mass media
platforms, there could be lesser advertisements which
resulted in lesser International tourists to Tokyo.
3) Due to better and more affordable transport systems within
Japan, the shorter and cheaper travel modes encouraged
more domestic than international tourism.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tourism-181119042421/85/Tourism-40-320.jpg)



![Account for the relationship between the price of air
tickets and the distance of the locations from Singapore
in Fig. 4. [3]
- Locations that are further away requires more
travelling time, this will result in more expensive air
tickets due to fuel and manpower costs.
- Locations that are nearer are cheaper due to the rise
of budget aircraft which has a cheaper cost due to the
shorter distance.
- Air tickets to certain countries may be more expensive
due to its popularity which increases the demand to
such places.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tourism-181119042421/85/Tourism-45-320.jpg)