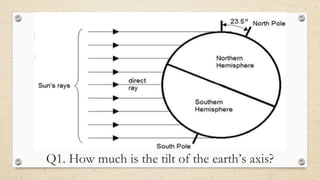
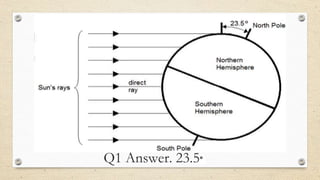
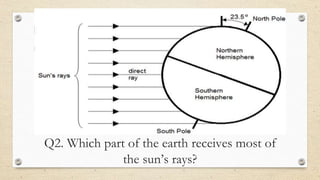
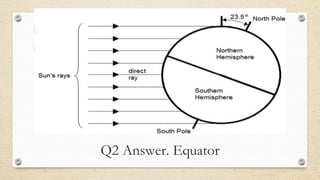
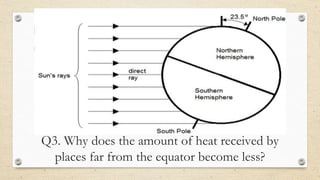
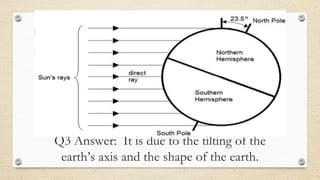
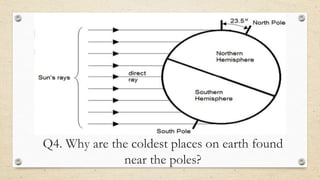
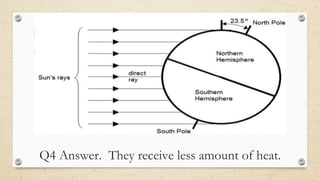
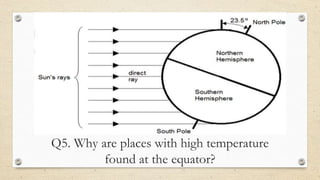
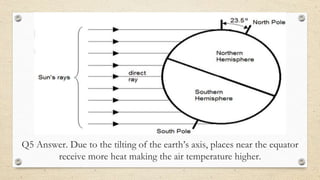
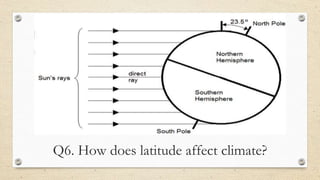
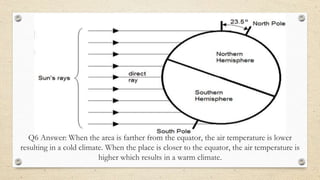
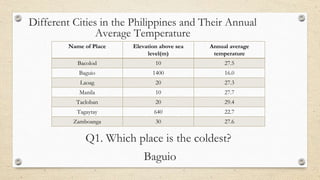
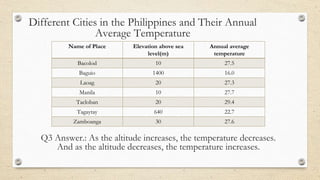
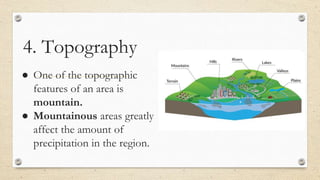
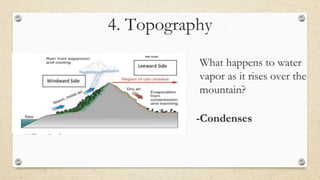
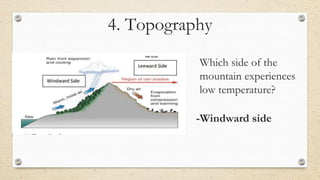
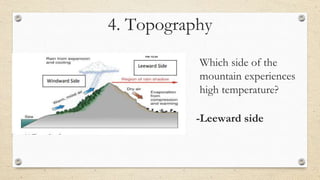
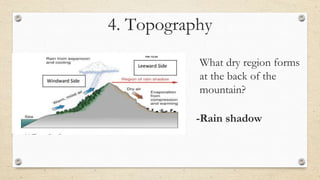
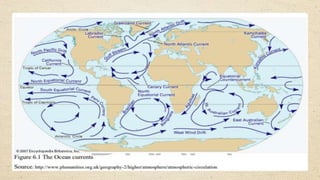
This document discusses the differences between weather and climate and various factors that affect climate, including latitude, altitude, distance from the ocean, topography, and ocean currents. It provides examples of each factor and how they influence temperature. Questions are also included to check understanding of these concepts. The key points are that climate refers to long-term patterns while weather is short-term conditions, and factors like latitude, altitude, and distance from water bodies determine how much heat and precipitation an area receives.