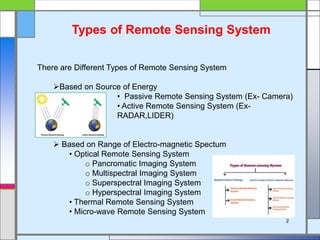
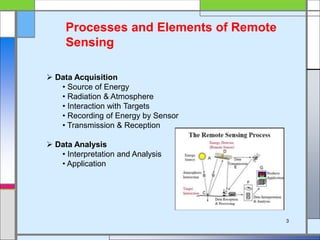
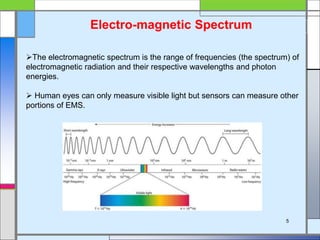
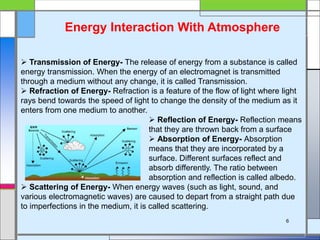
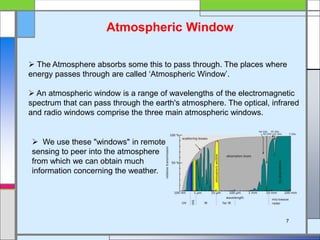
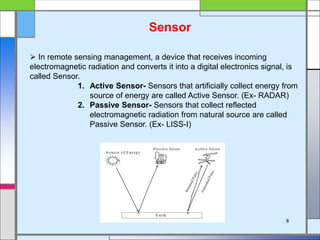
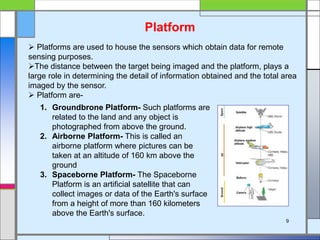
The document provides an overview of remote sensing, defining it as the collection of information about objects without direct contact via sensing and recording energy. It details various types of remote sensing systems, processes involved, and elements such as electromagnetic radiation, energy interaction with the atmosphere, and the importance of sensors and platforms. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of remote sensing, along with its applications in fields like agriculture, hydrology, and disaster management.