Embed presentation
Downloaded 543 times


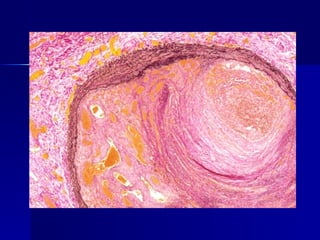











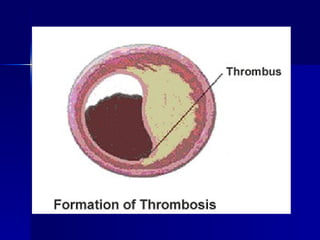





Thrombosis is the formation of a solid blood clot or thrombus within a blood vessel. Virchow's triad describes the three main factors that predispose to thrombosis: endothelial injury, alterations in blood flow, and hypercoagulability. Thrombi can form in arteries or veins and may cause ischemia or embolism, respectively. The predisposing factors for thrombosis include both genetic deficiencies that increase coagulation as well as acquired conditions like prolonged immobilization, oral contraceptive use, and cancer.


















