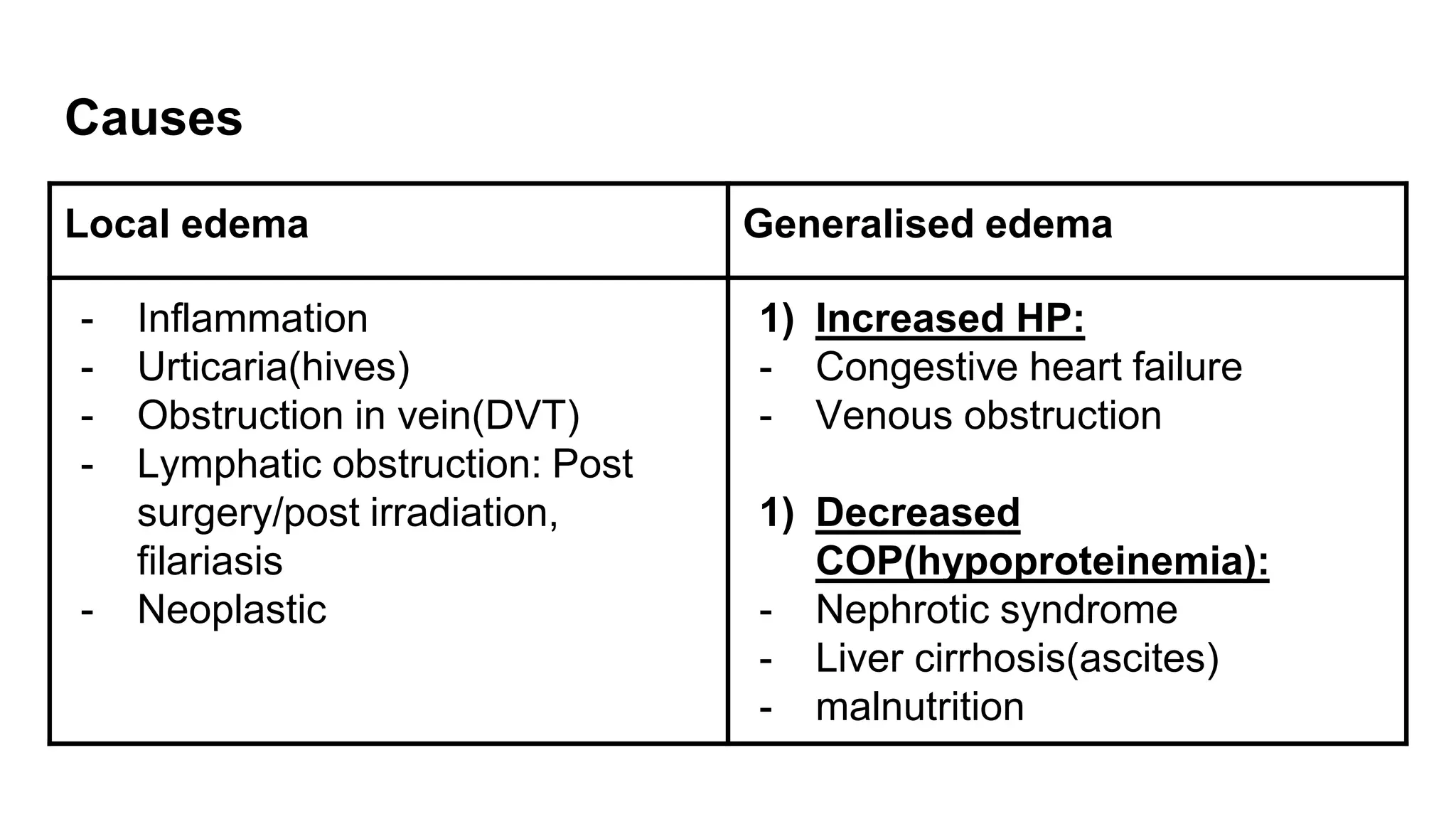
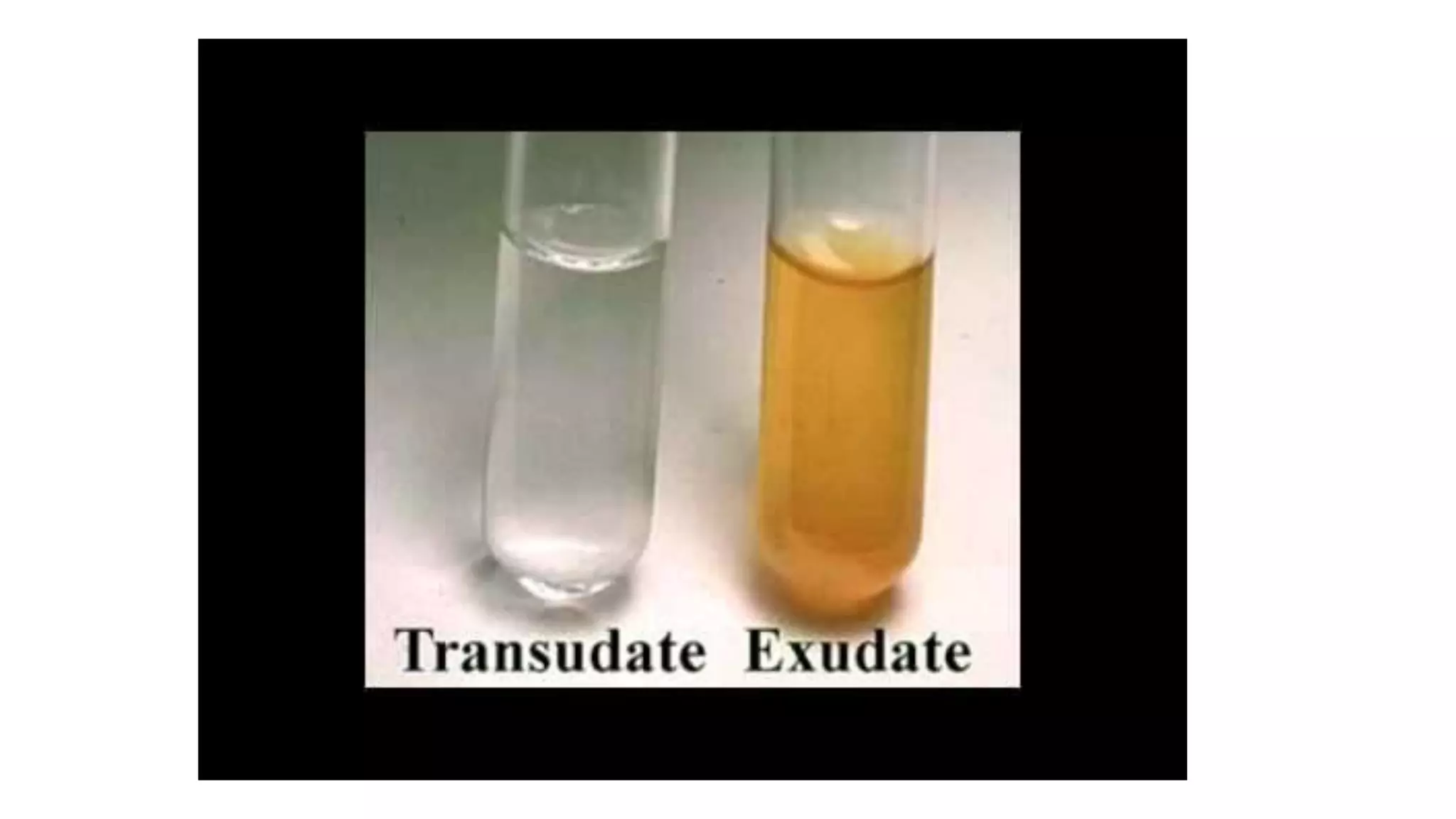
This document discusses transudate and exudate, types of edema fluid. Transudate results from increased hydrostatic pressure or decreased plasma proteins, causing protein-poor fluid to accumulate. Exudate occurs due to increased vascular permeability in inflammatory conditions, producing protein-rich fluid. The main differences between transudate and exudate are that transudate is clear and serous with low protein, cells and LDH, while exudate is cloudy/purulent with high protein, cells including neutrophils, and LDH. Transudate results from non-inflammatory causes while exudate occurs due to inflammation.