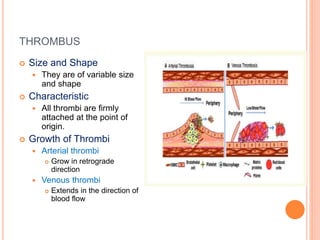
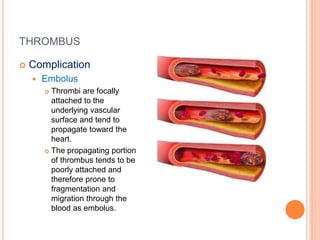
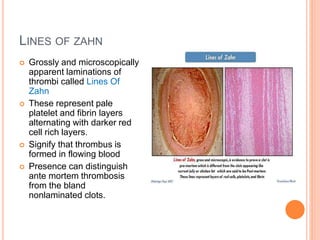
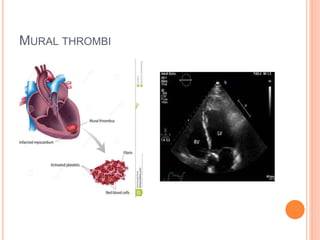
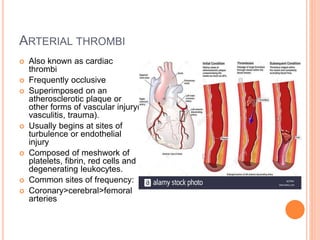
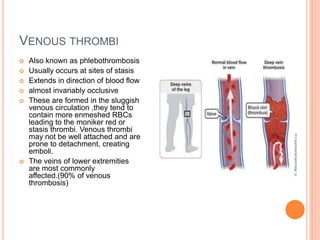
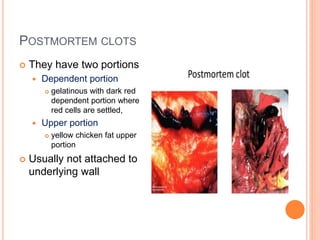
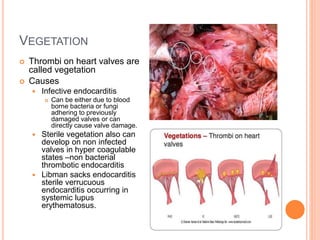
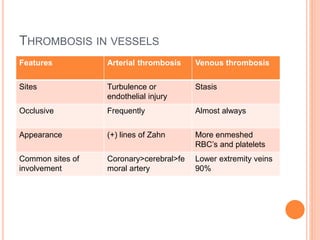
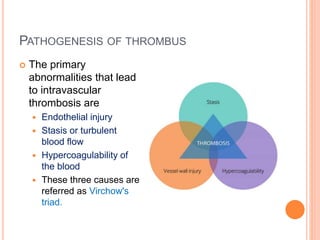
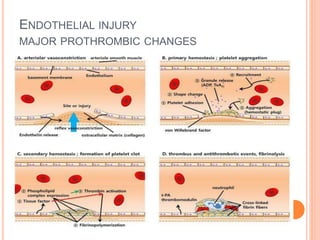
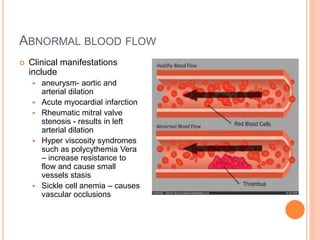
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel. A thrombus is a blood clot that forms in a vessel and remains attached. Thrombi develop at sites of endothelial injury, abnormal blood flow, or hypercoagulability. Arterial thrombi typically arise at sites of atherosclerosis or turbulence, while venous thrombi occur where blood flow is slow. Treatment involves anticoagulants to prevent thrombi from growing or new clots forming.