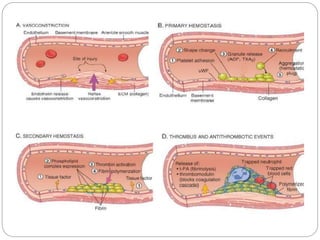
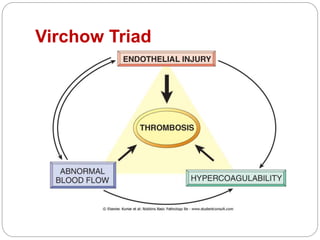
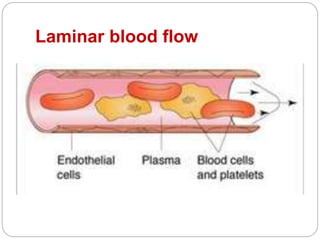
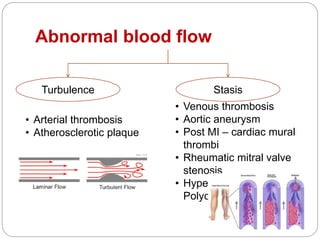
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel or cavity of the heart. Virchow identified three main factors that contribute to thrombosis: endothelial injury, changes in blood flow, and hypercoagulability. Thrombi can propagate or embolize, becoming lodged in another vessel and resulting in infarction of downstream tissue. Infarctions appear pale/white in solid organs and red/hemorrhagic in lungs/other tissues. Over time, infarcted tissue progresses from coagulative necrosis to phagocytosis and scar formation.