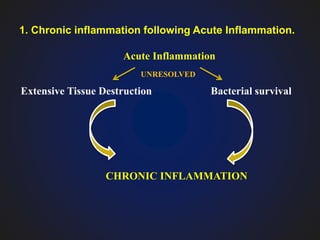
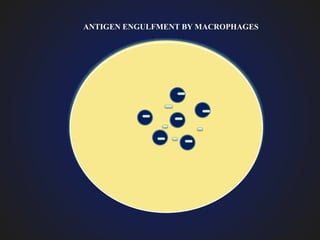
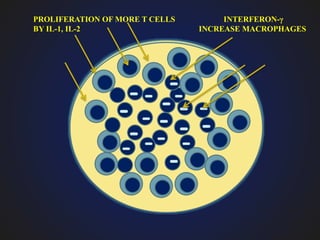
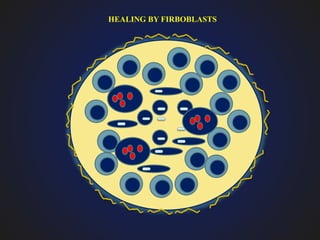
1. Chronic inflammation is defined as prolonged inflammation where tissue destruction and inflammation occur simultaneously over a long period.
2. It can occur through three pathways: following acute inflammation, recurrent acute attacks, or starting gradually without an initial acute phase.
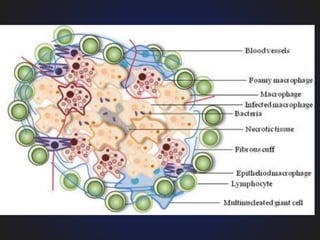
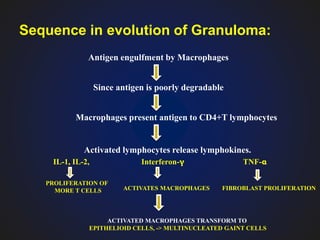
3. Chronic inflammation is characterized by mononuclear infiltration, ongoing tissue damage or necrosis, and proliferative changes in tissues.