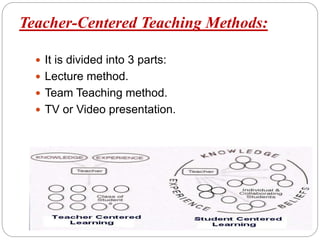
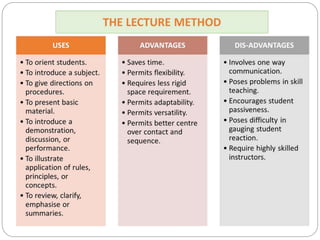
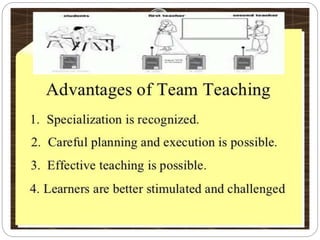
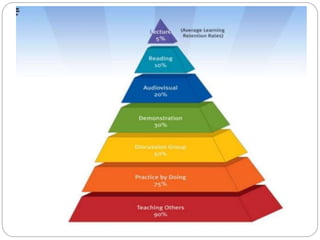
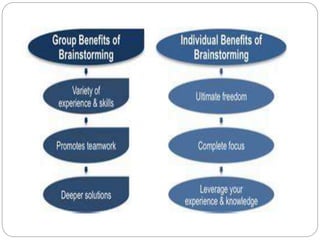
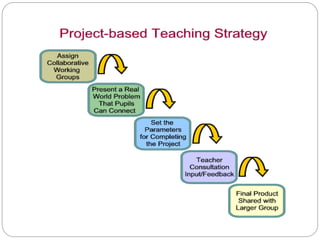
The document discusses various teaching methodologies, emphasizing that the choice of approach often reflects a teacher's educational philosophy. It highlights teacher-centered methods, including the lecture method and TV/video presentations, and presents a mixed approach, such as brainstorming, which fosters collaborative idea generation. The focus is on adapting teaching strategies to enhance student engagement and learning, prioritizing experiential over rote learning.