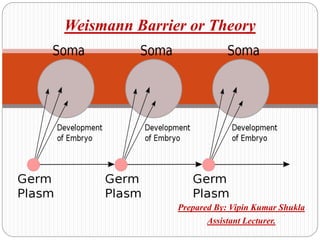
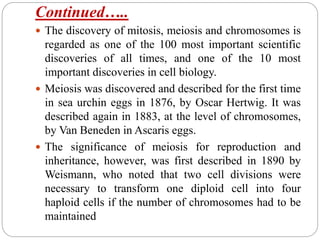
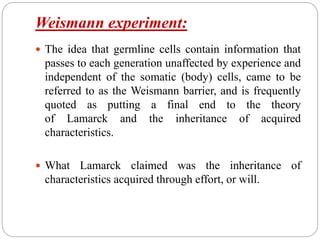
Ernst Weismann was a German biologist who developed the germ plasm theory, also known as the Weismann barrier, which proposed that inheritance only occurs through germ cells like egg and sperm cells, not somatic cells. The genetic information in germ cells is not affected by what happens to somatic cells during an organism's life. Weismann conducted experiments cutting off mice tails over many generations, finding acquired characteristics from environmental effects are not inherited, providing evidence against Lamarckism. The Weismann barrier is central to modern evolutionary theory.