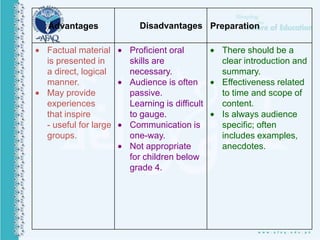
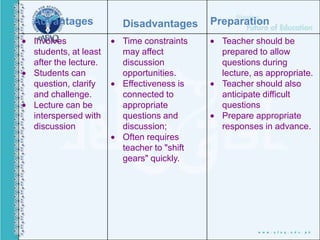
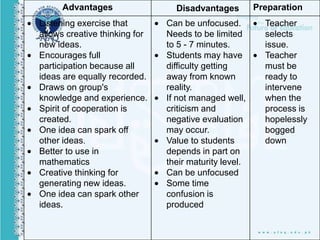
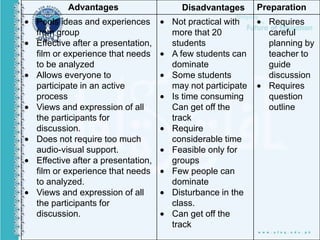
This document discusses various teaching methods and objectives. It begins by defining teaching and methods. It then outlines the objectives of teaching as developing cognition, affective skills, and psychomotor abilities. Several teaching techniques are described in detail like direct instruction, indirect instruction, discussion, cooperative learning and self-directed learning. Specific methods like lecture, demonstration, debate and role playing are also explained. Finally, it lists 30 teaching methods used by the Holy Prophet Muhammad including repetition, memorization, questioning, storytelling, demonstration and practice.










![• "O Mankind! There has come to you
from your Guardian-Lord an exhortation,
a prescription
for the minds, a guidance and
beneficence for those who believe"
[10:57].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/teachingmethodologies-140403110601-phpapp01/85/Teaching-methodologies-11-320.jpg)