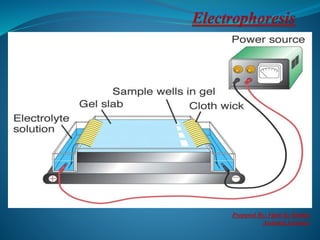
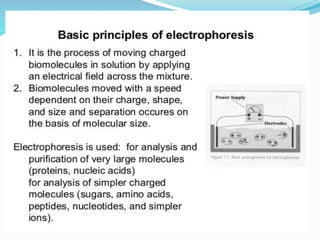
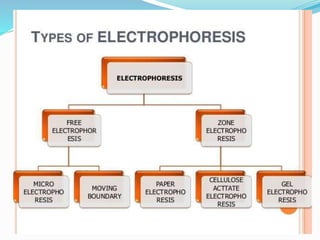
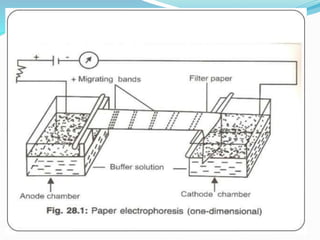
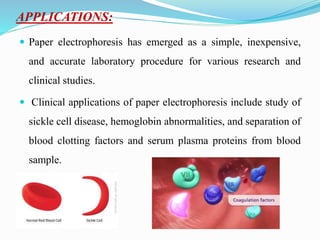
Electrophoresis is a method for separating charged particles in a solution under an electric field, with applications in protein analysis and various clinical studies. It can be performed using different techniques, such as zone electrophoresis and paper electrophoresis, each having its own advantages and disadvantages. Factors affecting migration include charge, size, shape, electric field strength, and buffer composition, making it a versatile tool in biochemistry, genetics, and forensics.