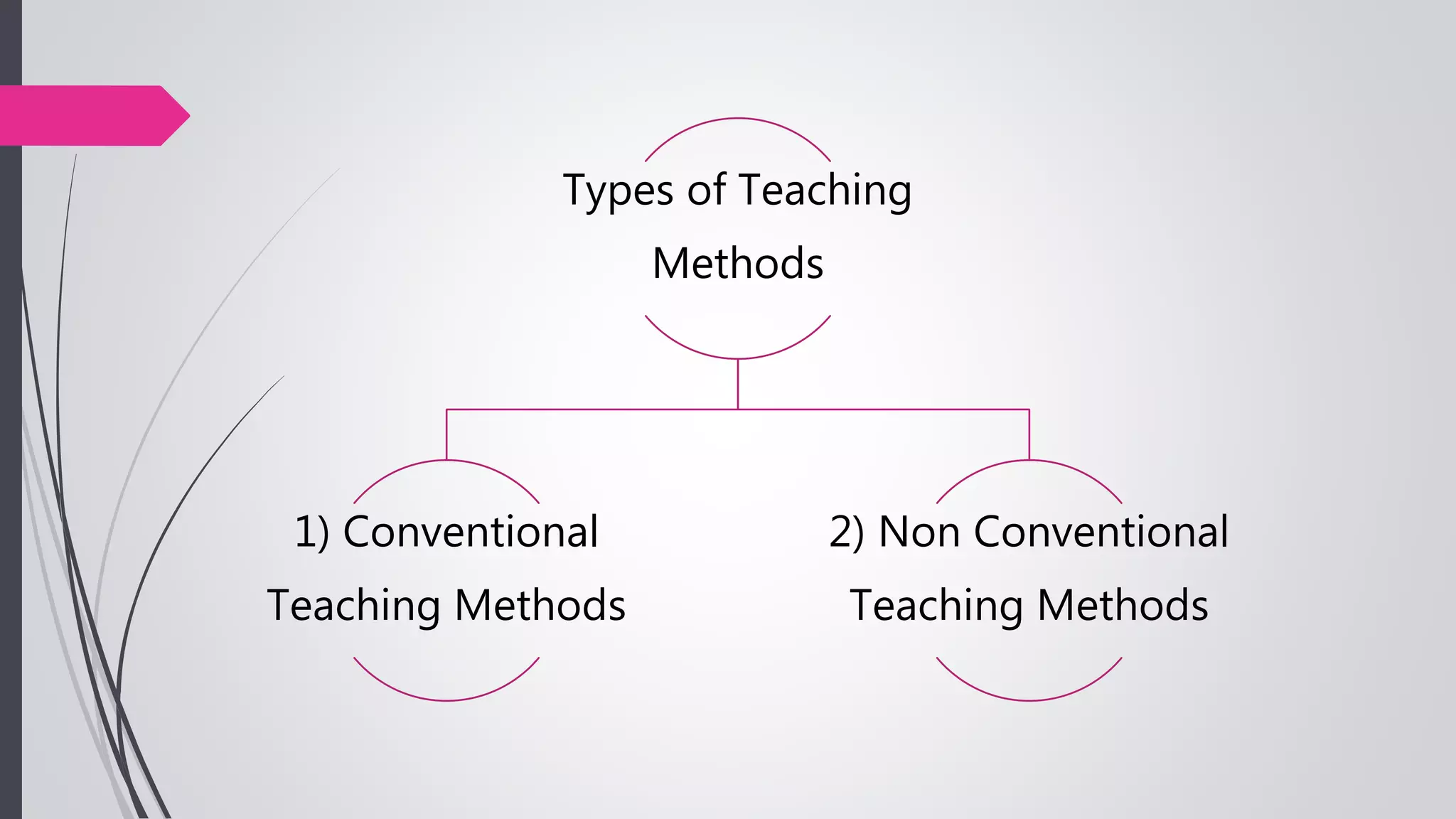
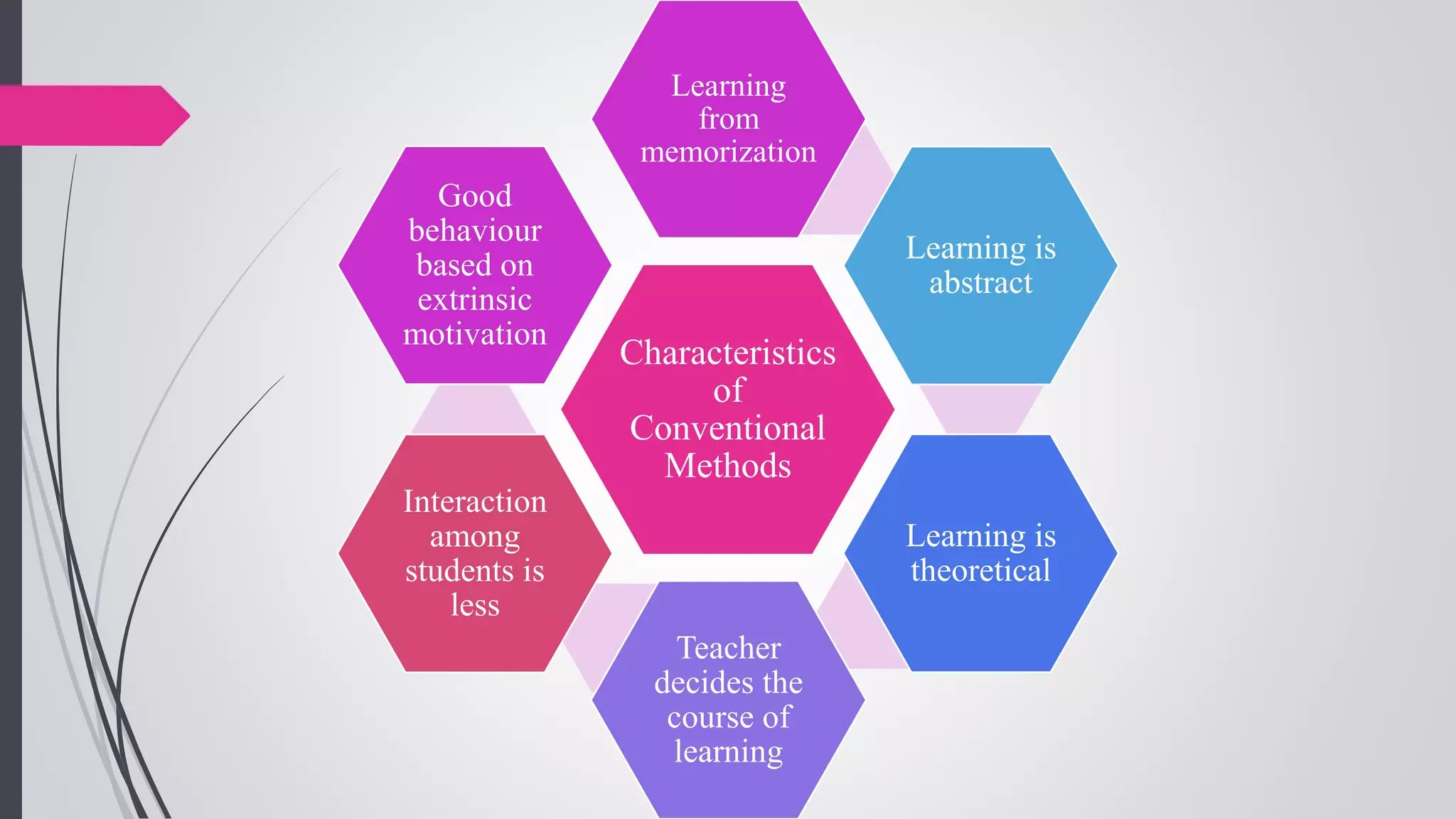
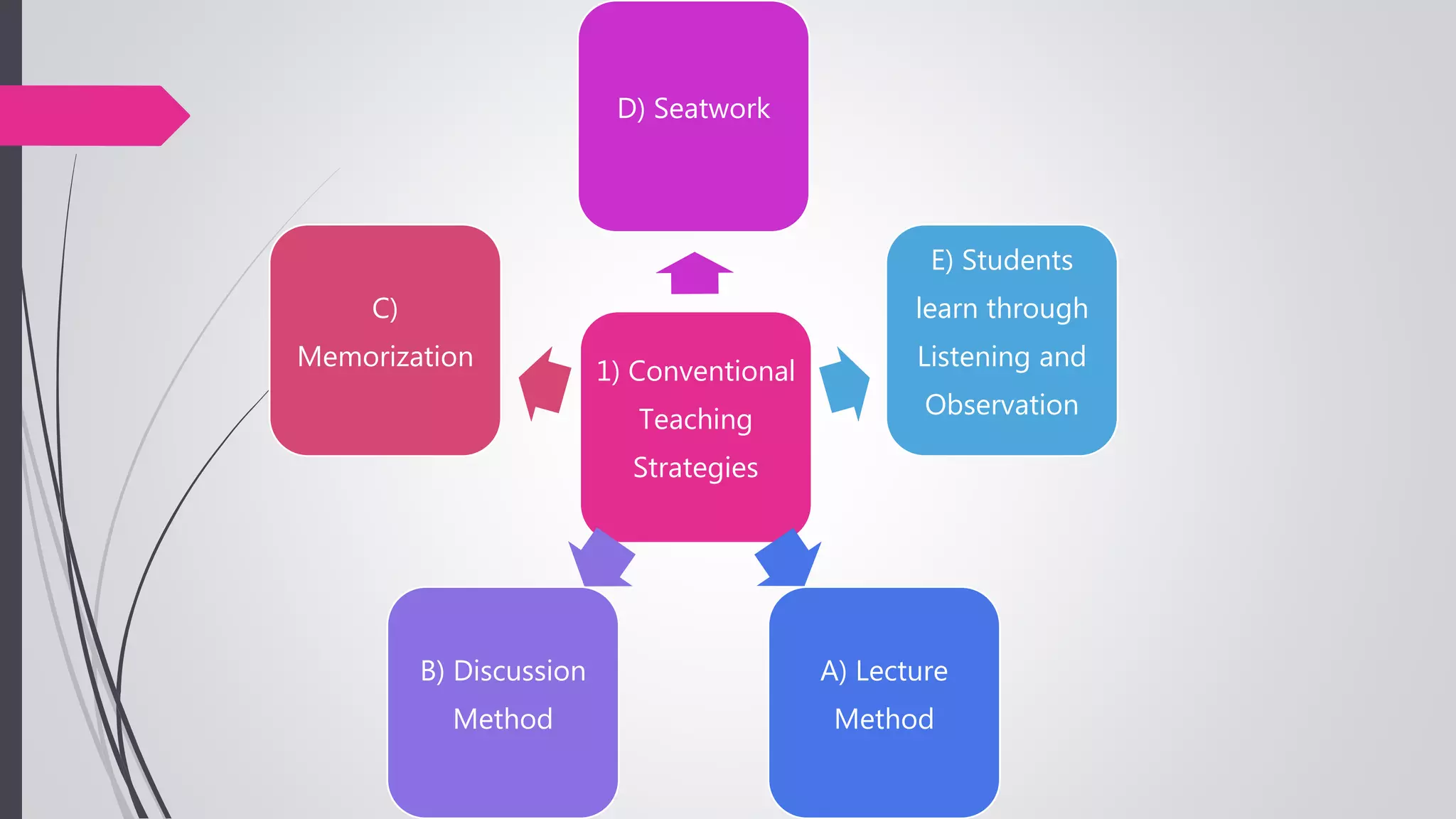
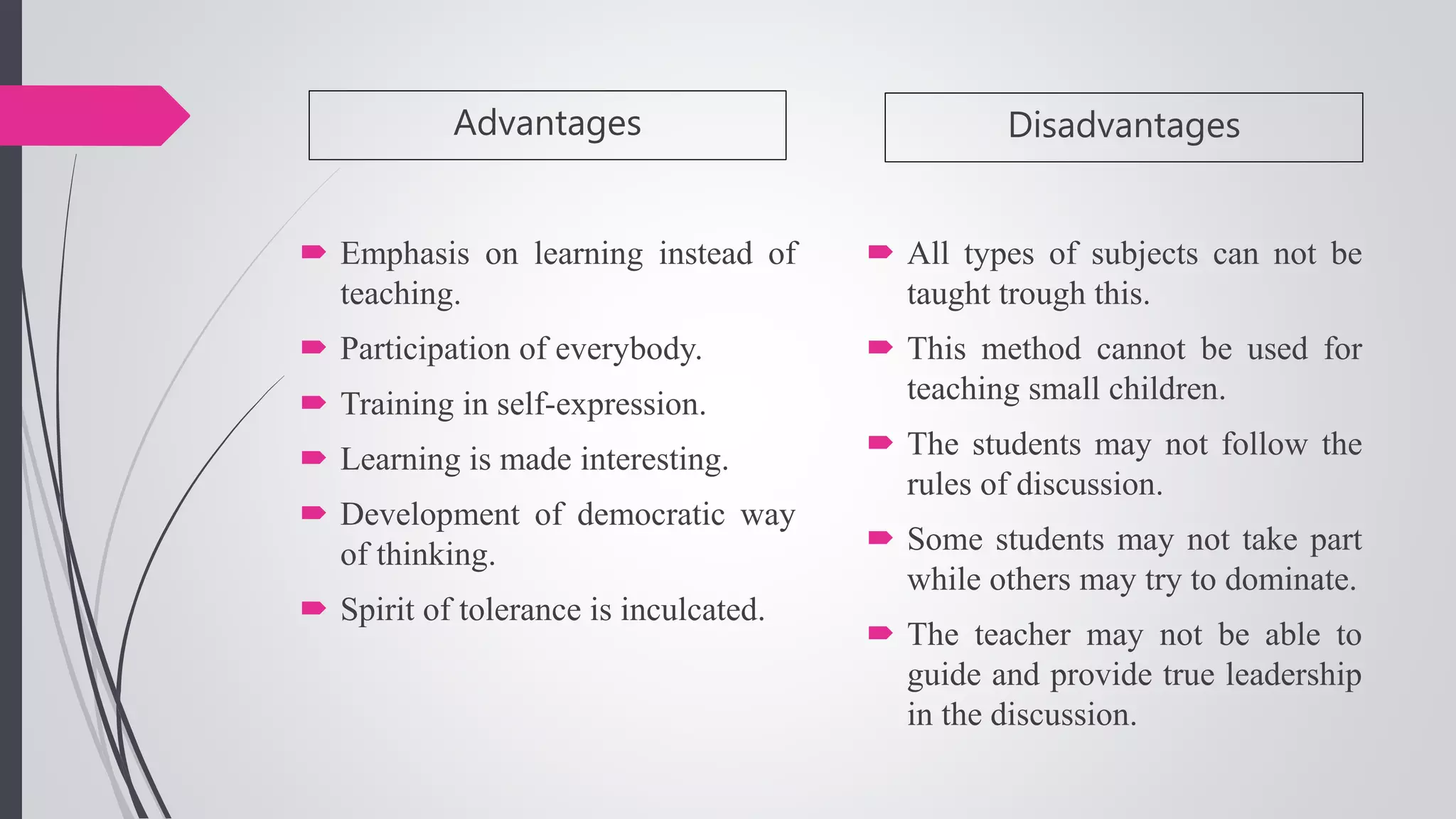
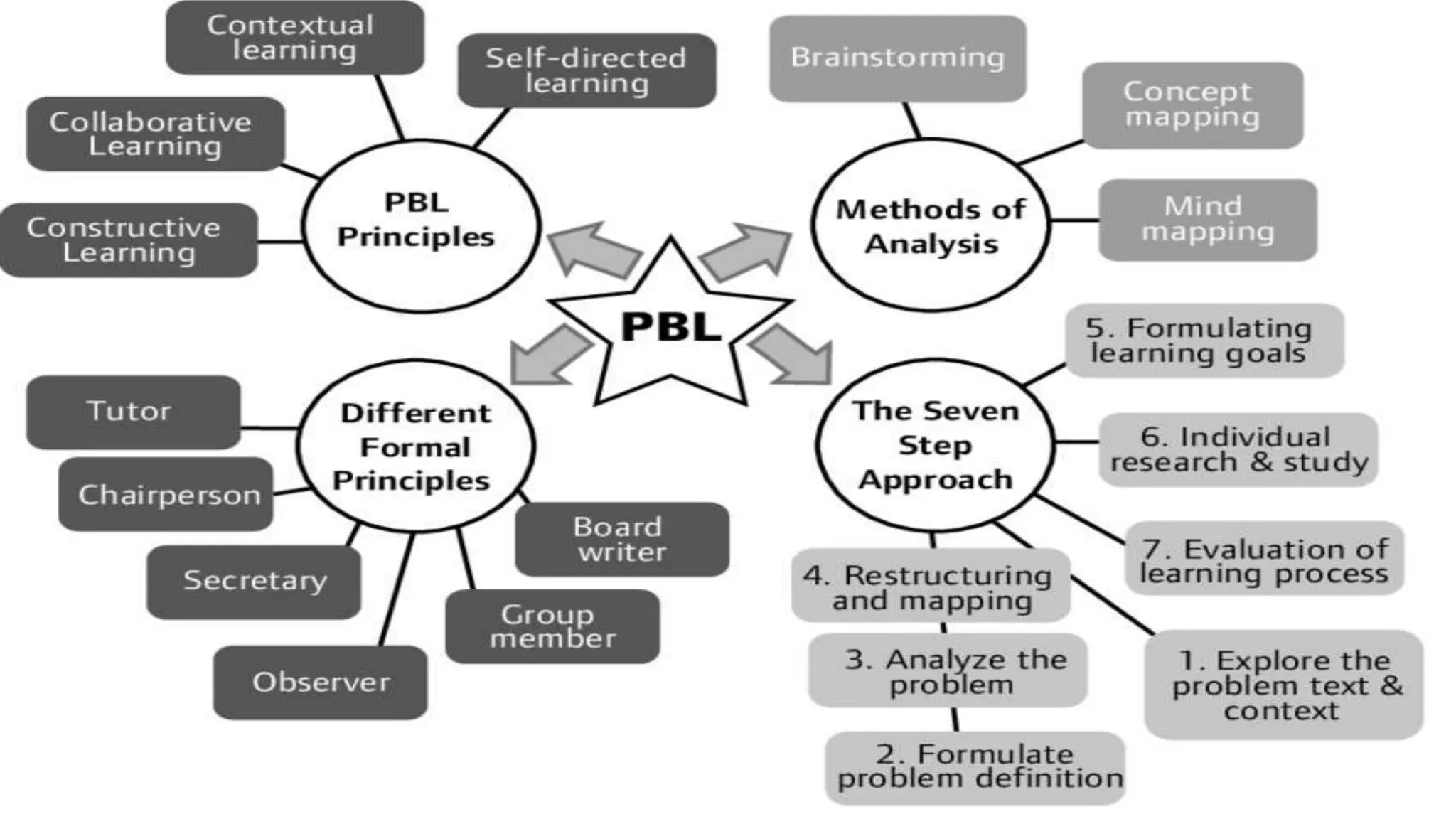
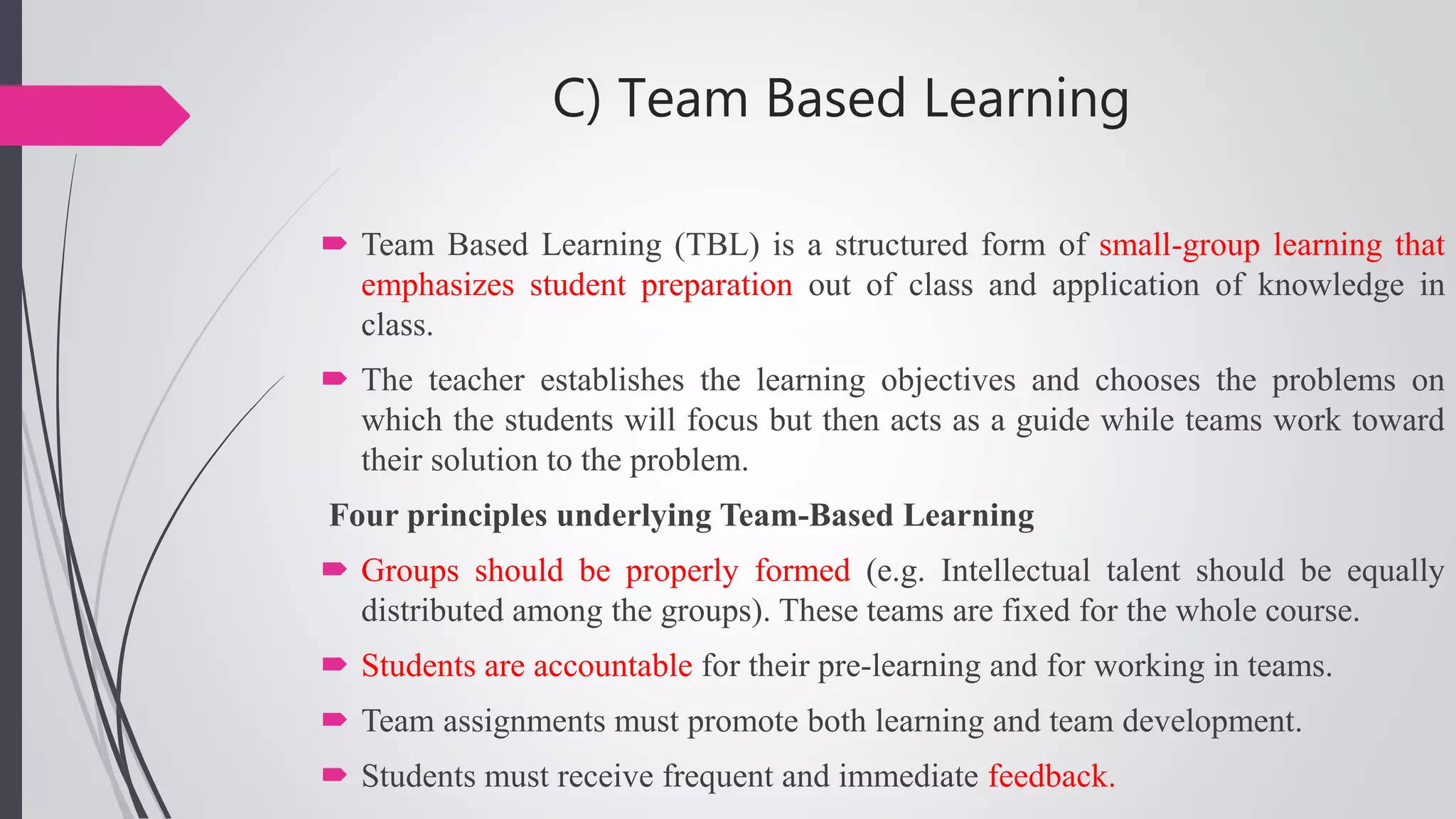
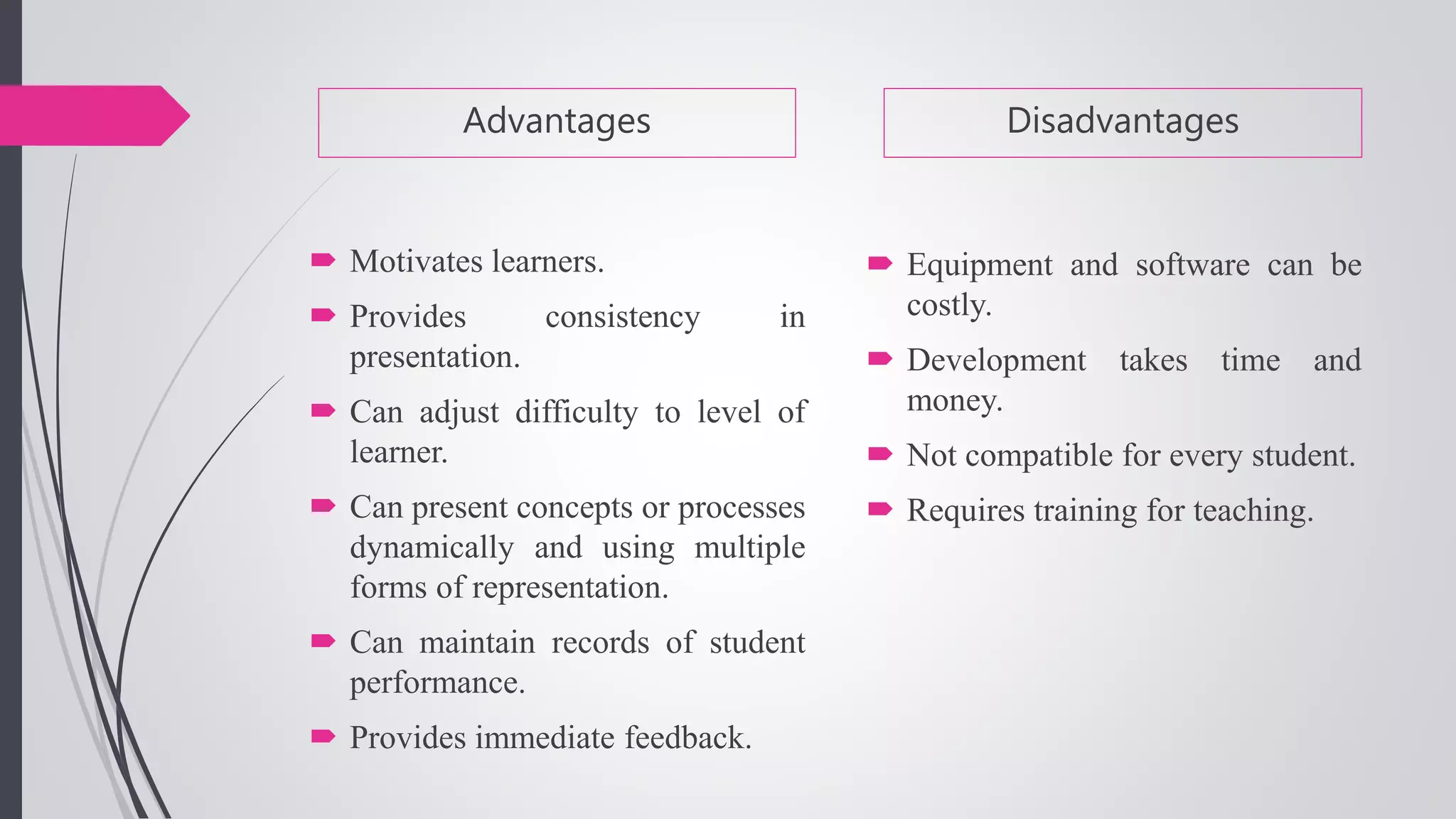
The document compares conventional and non-conventional teaching methods. Conventional methods include lecture-based instruction, memorization, and individual work. Non-conventional methods incorporate more active learning approaches like problem-based learning, peer instruction, group projects, and flipped classrooms. While conventional methods are efficient, non-conventional methods promote critical thinking, collaboration, and develop skills like communication. The document advocates that modern classrooms should integrate non-conventional, student-centered methods to engage today's learners.