Reproductive system and its Classification
- 1. Prepared By: Vipin Kumar Shukla Assistant Lecturer Reproductive System
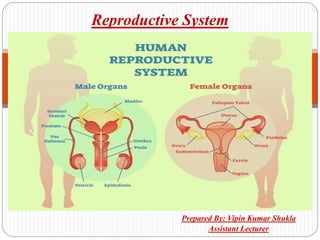
- 3. HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: The reproductive system enables human beings to reproduce another human being. The reproductive system starts the life of every human being. The reproductive system of boys is different from that of girls. The male reproductive system is designed for production and transport of sperm cells. The female reproductive system is designed for child bearing. The male and female reproductive systems are designed to create new life.
- 4. REPRODUCTION: It is a process that makes possible the continuance of life in earth. Males and females have structures specialized for their role in reproduction. The process that produces babies, young animals, or new plants. Is made up of several organs which include the testes, ducts, accessory glands, and penis. It is specifically responsible for producing sperm cells and hormones. An average man can have about 5 000 000 sperm cells in a single drop.
- 5. Parts and Functions: Testes – sex glands located in the scrotum. They produce sperms and the hormone testosterone. Vas deferens– A long muscular tube that serve as passageway of sperm cells released from the testes. Scrotum– is a pair of pouch-like sacs. It serves as skin covering of the testes. Bladder– a sac in the anterior part of the pelvis for temporary retention of urine. Epididymis– is a narrow coiled tube that stores immature sperm cells.
- 6. Contd…. Prostate Gland– is a wall-nut sized gland located between the bladder and the penis Urethra– an opening for sperm and urine passage. Penis– is the external male organ with a tip called glans.
- 8. Contd…. Designed for conception, pregnancy and childbirth. It is made up of several organs which include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina. It is responsible for producing eggs and supporting a developing baby inside a mother’s womb.
- 9. Parts and Functions: FALLOPIAN TUBES– also called oviduct. Lies close to the ovary waiting for the egg to enter. OVARIES (ovary)- produces egg cells and the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. Uterus– also called the womb. Shaped like an upside– down pear. Has smooth, soft, inner lining of the uterus called uterine lining or Endometrium. Fimbriae– the fringe of tissue around the fallopian tube.
- 10. Contd…. Cervix– narrow opening between the uterus and vagina. Enlarges to let the passage of a fetus during birth. Vagina– also called the birth canal. Hollow muscular tube that leads to the opening called vulva.
- 11. The Menstrual Cycle: Menstrual flow happen only among girls. Menstruation is part of a menstrual cycle. Menstruation is the monthly discharge of blood from the uterus through the vagina. When a girl reaches puberty, one egg ripens or matures every 28 days. If no sperm cell arrives from 15 to 28, no fertilization and implantation occurs. The egg cell will then breakdown along with the uterine lining as blood. This marks the beginning of another menstrual cycle.
- 13. Contd…. The first day of the menstruation is the first day of the menstrual cycle. As blood comes out of the vagina, the uterine lining breaks down. Most of your menstrual loss happens during the first 3 days. During the follicular phase, an egg follicle on an ovary gets ready to release an egg. This process can be short or long and plays the biggest role in how long your cycle is. The uterus starts growing a new Endometrium to prepare for pregnancy.
- 14. Contd…. This phase starts on ovulation day, the day the egg is released from the egg follicle on the ovary. During ovulation, some women have less than a day of red spotting or lower pelvic pain. These signs of ovulation are normal. It is the phase of a female's menstrual cycle when an egg(ovule) is released from the ovaries. At day 14, ovulation takes place. Ovulation occurs when an egg is released by the ovary. The egg cells travels along the oviduct and waits for a sperm cell.
- 15. ART: Assisted Reproductive technology is defined as the technology used to achieve pregnancy in procedures such as artificial insemination, in vitro fertilization and surrogacy. In Vitro Fertilization is the uniting of egg and sperm in vitro(in the lab).Subsequently the embryos are transferred into the uterus through the cervix and pregnancy is allowed to begin. It is the technique of letting fertilization of male and female gametes occur outside the female body.
- 16. In Vitro Fertilization: In Vitro Fertilization is the uniting of egg and sperm in vitro(in the lab).Subsequently the embryos are transferred into the uterus through the cervix and pregnancy is allowed to begin. It is the technique of letting fertilization of male and female gametes occur outside the female body.
- 17. Techniques: Most commonly used are: Transvaginal ovum retrieval (OCR)fallopian Embryo Transfer Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer Surrogacy
- 18. Less commonly used are: Cytoplasmic Transfer Assisted Zona Hatching Egg Donors Sperm donation Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis Embryo Splitting Cryopreservation
- 19. Transvaginal Oocytes Retrieval: It is also known as Oocytes retrieval is a technique used to remove Oocytes from the ovary of the female enabling fertilization outside the body. Transvaginal Oocytes retrieval is more properly referred to as Transvaginal ovum retrieval when the Oocytes has matured in the ova.
- 20. Process: Under ultrasound guidance, the operator inserts a needle through the vaginal wall and into an ovarian follicle, taking care not to injure organs located between the vaginal wall and the ovary. The other end of the needle is attached to a suction device. Then the follicular fluid and cellular material is suctioned with the needle. The procedure usually lasts 10-20 minutes
- 21. ICSI, Intra Cytoplasmic Injection: It is an in vitro fertilization procedure in which a single sperm is injected directly into an egg. It is beneficial in the case of male factor infertility where sperm counts are very low. The first child borne from gamete micromanipulation was a child in Singapore born in April of 1989. The first activated embryo by ICSI was produced in1990, but the first successful birth by ICSI took place on January 14, 1992.
- 23. Which are the patients who need ICSI: Low sperm count Poor sperm motility Abnormally high amount of morphologically atypical sperm Obstruction in the Epididymis due to past inflammation Retrograde ejaculation Immunological factors
- 24. Embryo Transfer: It refers to a step in the process of assisted reproduction in which embryos are placed in the uterus of the female to establish the pregnancy In embryo transfer the embryos are placed in a woman’s uterus. The goal is to create a pregnancy. The embryos can be either fresh or frozen. If they are frozen, they can thawed right before they are transferred. It is the last step in a type of fertility treatment.
- 26. Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer: It is an infertility treatment used when a blockage in the fallopian tubes prevents the normal binding of sperm to the egg. Egg cells are removed from a woman’s ovaries, and in vitro fertilized. The resulting zygote is placed into the fallopian tube by the use of laparoscopy. It has the success rate of 64.8% in all the cases.
- 28. Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer: It is a tool of assisted reproductive technology against infertility. Eggs are removed from a woman’s ovaries , and placed in one of fallopian tubes , along with the man’s sperm. The first attempt was made by Steptoe and Edwards. It takes on average four to six weeks to complete the cycle of GIFT.
- 29. Steps of GIFT: The woman must take a fertility drug to stimulate egg production in the ovaries. Monitoring the growth of the ovarian follicles. Once they are mature, the woman will be injected the hCG. After 36 hours, the eggs will be harvested mixed with the man’s sperm and placed back into the woman’s fallopian tubes using a laparoscope.
- 30. Surrogacy: Surrogacy is when another woman carries and gives birth to a baby for the couple who want to have a child. It is the carrying of a pregnancy for intended parents. In this a woman agrees to became pregnant and deliver a child for a contracted party.
- 31. Types of Surrogacy: Traditional surrogacy: It is the simplest and least expensive form of surrogacy and is also known as artificial insemination. The surrogate mother uses an insemination kit to became pregnant using an intended father’s semen. Gestational surrogacy: It is physically more complicated and more expensive. Here both the eggs and sperm are taken from intended father and mother
- 32. Steps involved in surrogacy: Three Steps: Egg Donation Fertilization Transfer
- 33. Other techniques: Cytoplasmic transfer: It is the technique in which the contents of a fertile egg from a donor are injected into the infertile of the patient along with the sperm. Assisted Zona hatching: It is performed shortly before the embryo is transferred to the uterus . A small opening is made in the Zona pellucida using a micromanipulator , thereby facilitating Zona hatching to occur
- 34. Contd…. Egg Donors: In egg donors eggs are retrieved from a donors ovaries, fertilized in laboratory with the sperm from recipients partner and resulting healthy embryos are returned to recipients uterus. Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis: It helps in identify genetically abnormal embryos and improve healthy outcomes. Embryo Splitting: It can be used for twinning to increase
