The document outlines the key concepts in systems analysis and design including:
1) It defines systems, analysis, and design and describes the role of the systems analyst in performing analysis and design to improve existing systems.
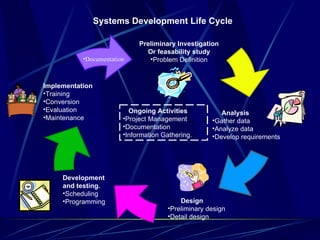
2) It describes the principal phases of the systems development life cycle including preliminary investigation, analysis, design, development, implementation, and ongoing maintenance.
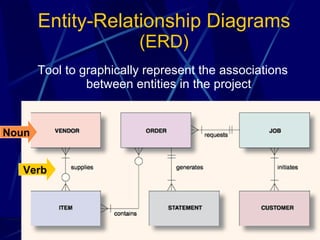
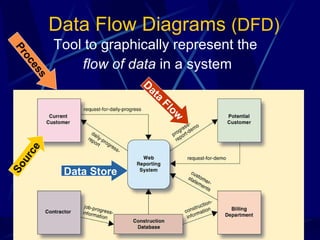
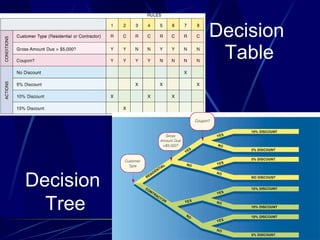
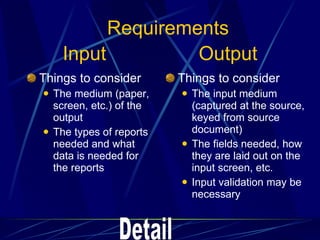
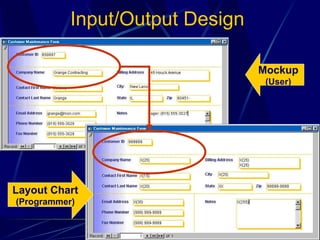
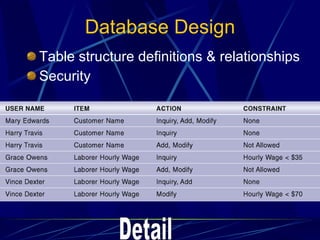
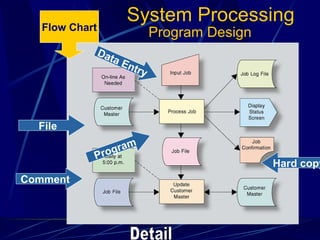
3) It provides an overview of various tools used in systems analysis and design like entity relationship diagrams, data flow diagrams, documentation, and prototypes.