The document outlines 5 key characteristics of a system:
1. Organization - The structure and arrangement of components to achieve objectives. For example, a business system's hierarchy or a computer system's input/output components.
2. Interaction - The interrelationship between each component as they function together, such as departments interacting in an organization.
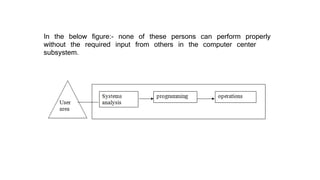
3. Interdependence - The components depend on one another to function, such as employees relying on each other in a computer center subsystem.
4. Integration - How the system is tied together so parts work as a whole to achieve central objectives, even if each part has a unique function.
5. Central objective - The overall goal that the system aims to accomplish through the interaction