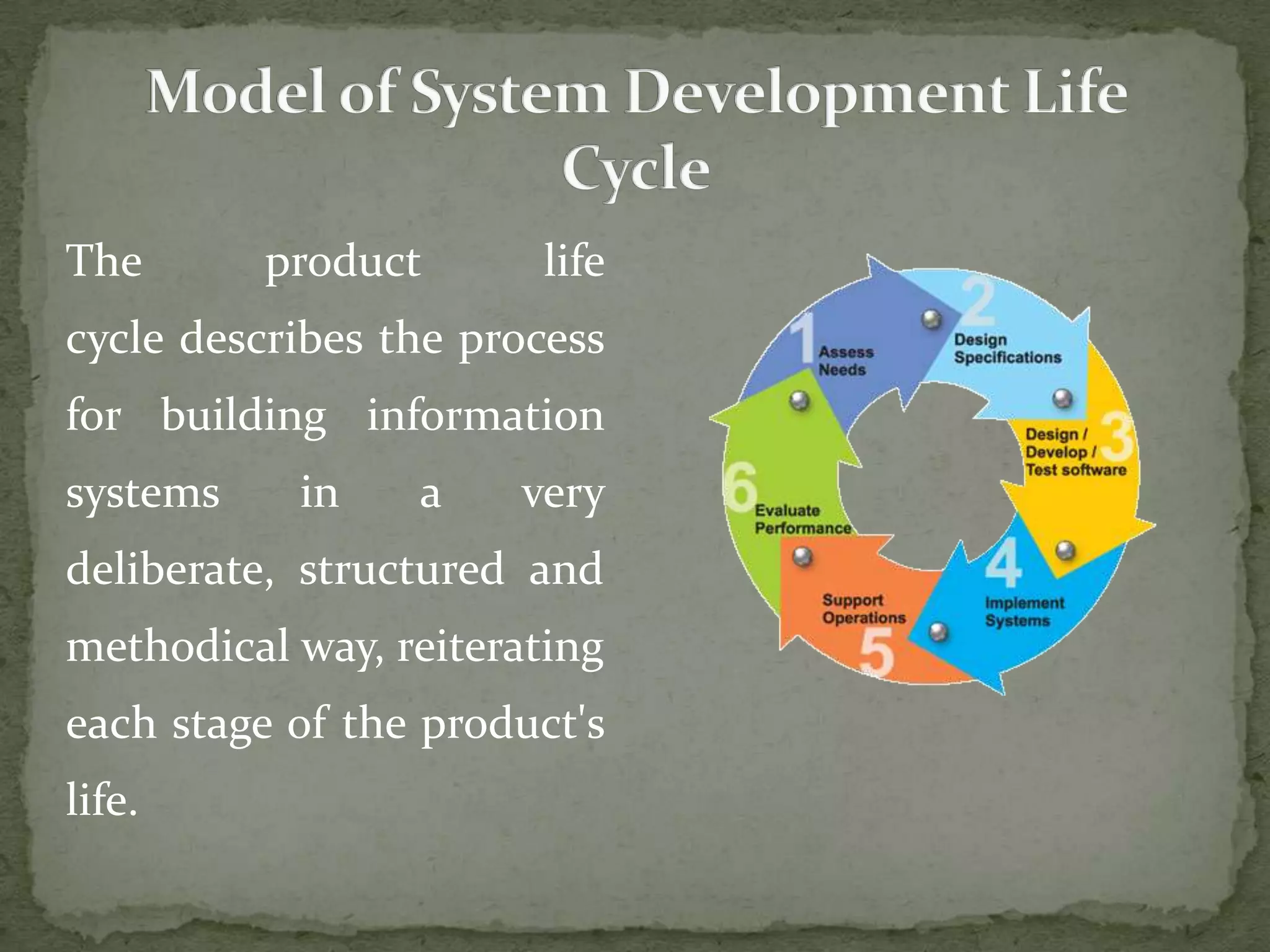
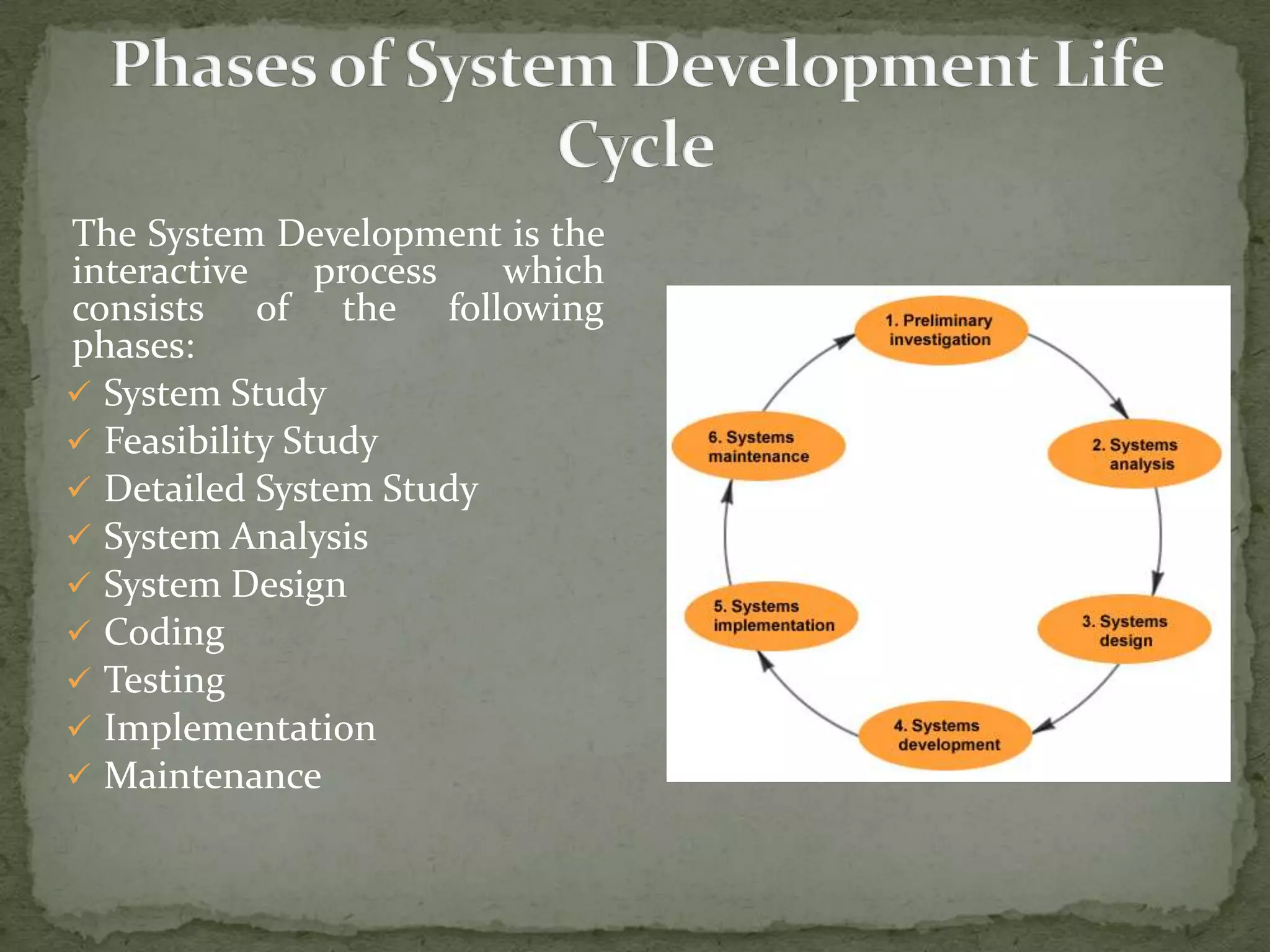
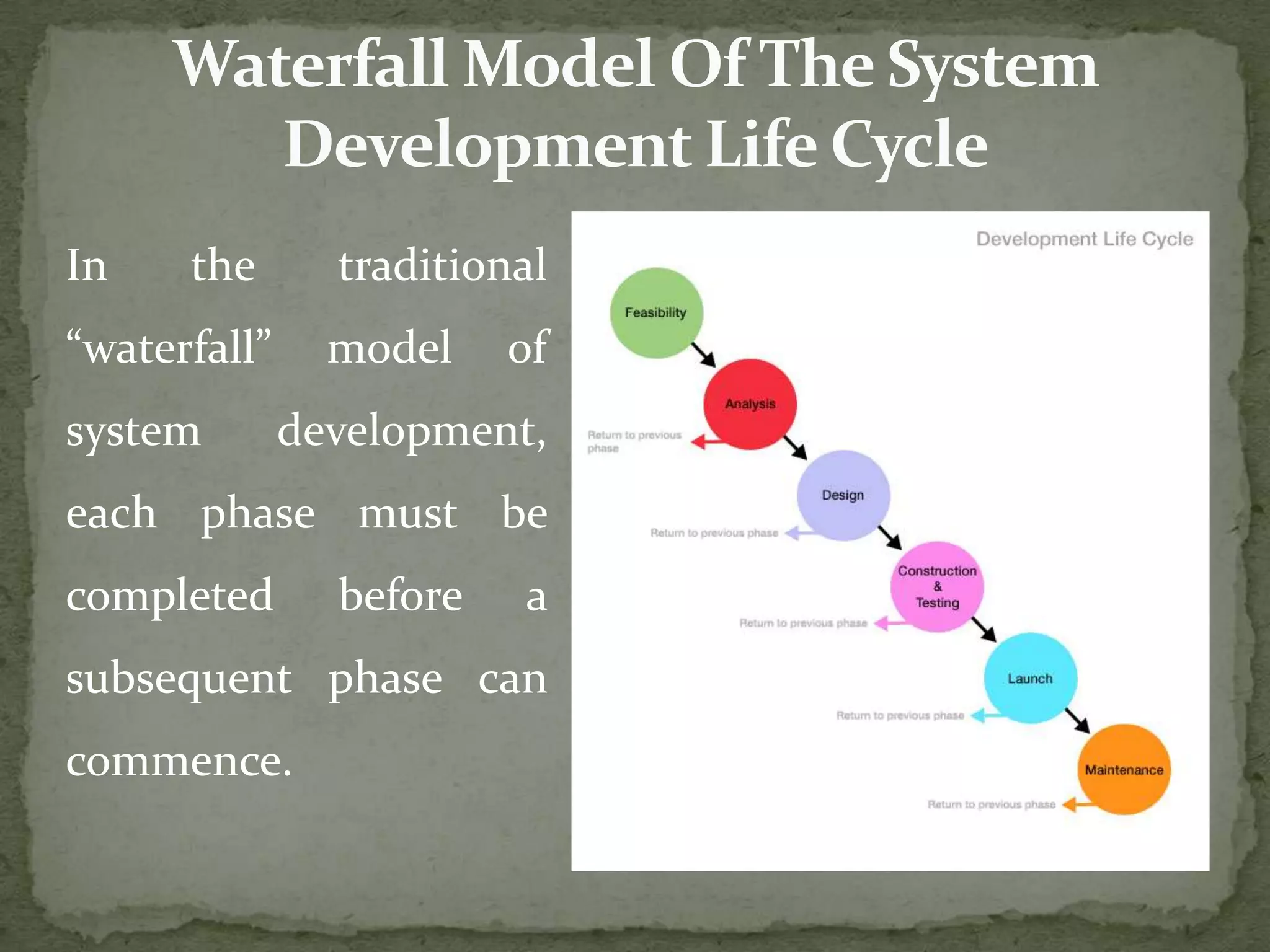
The systems development life cycle (SDLC) describes the process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. It involves preliminary system study, feasibility study, detailed system study, system analysis, system design, coding, testing, implementation, and maintenance. The SDLC follows a structured process to ensure high quality systems while maximizing productivity and providing management controls. It originated in the 1960s to develop large scale business systems.