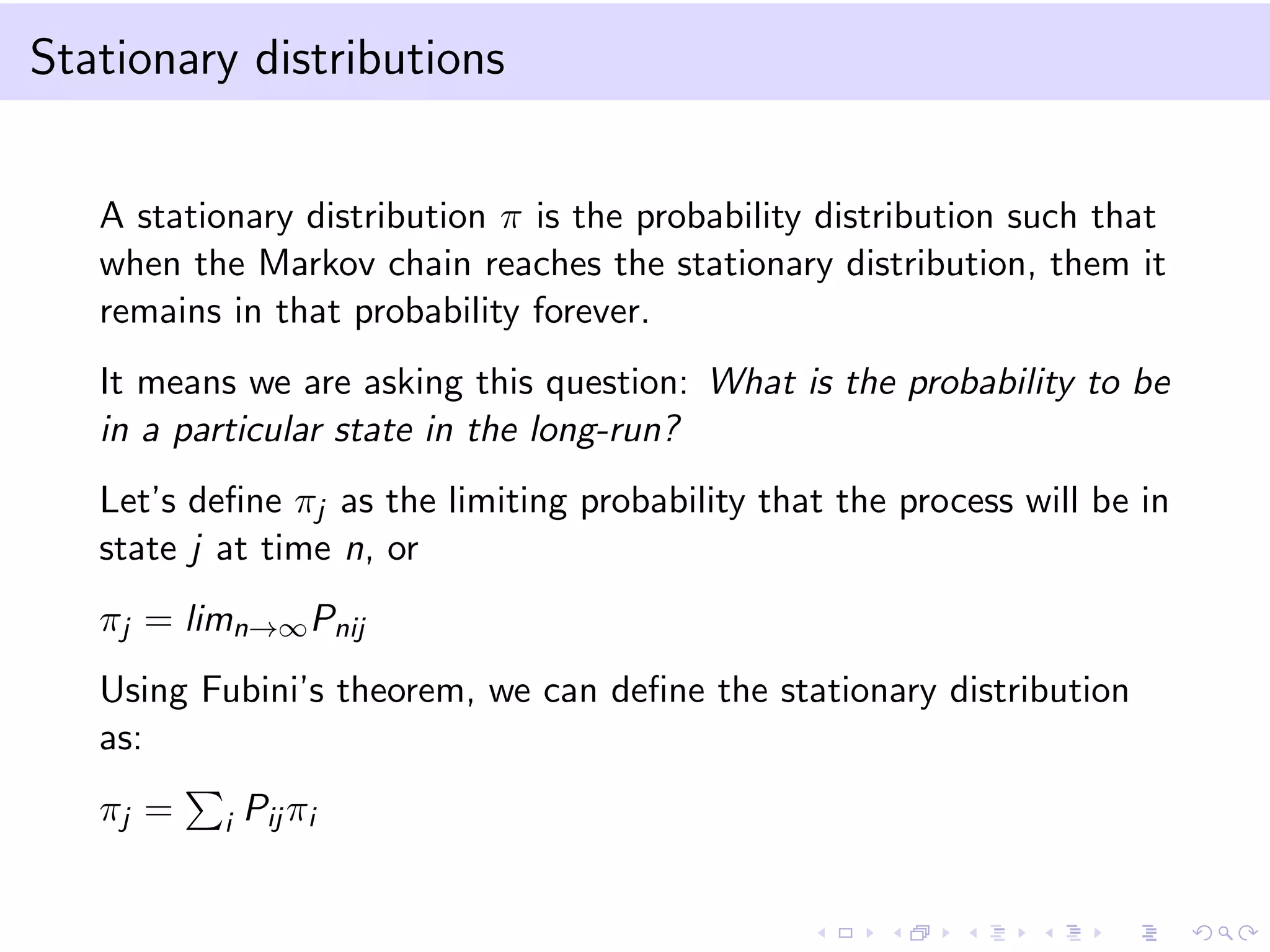
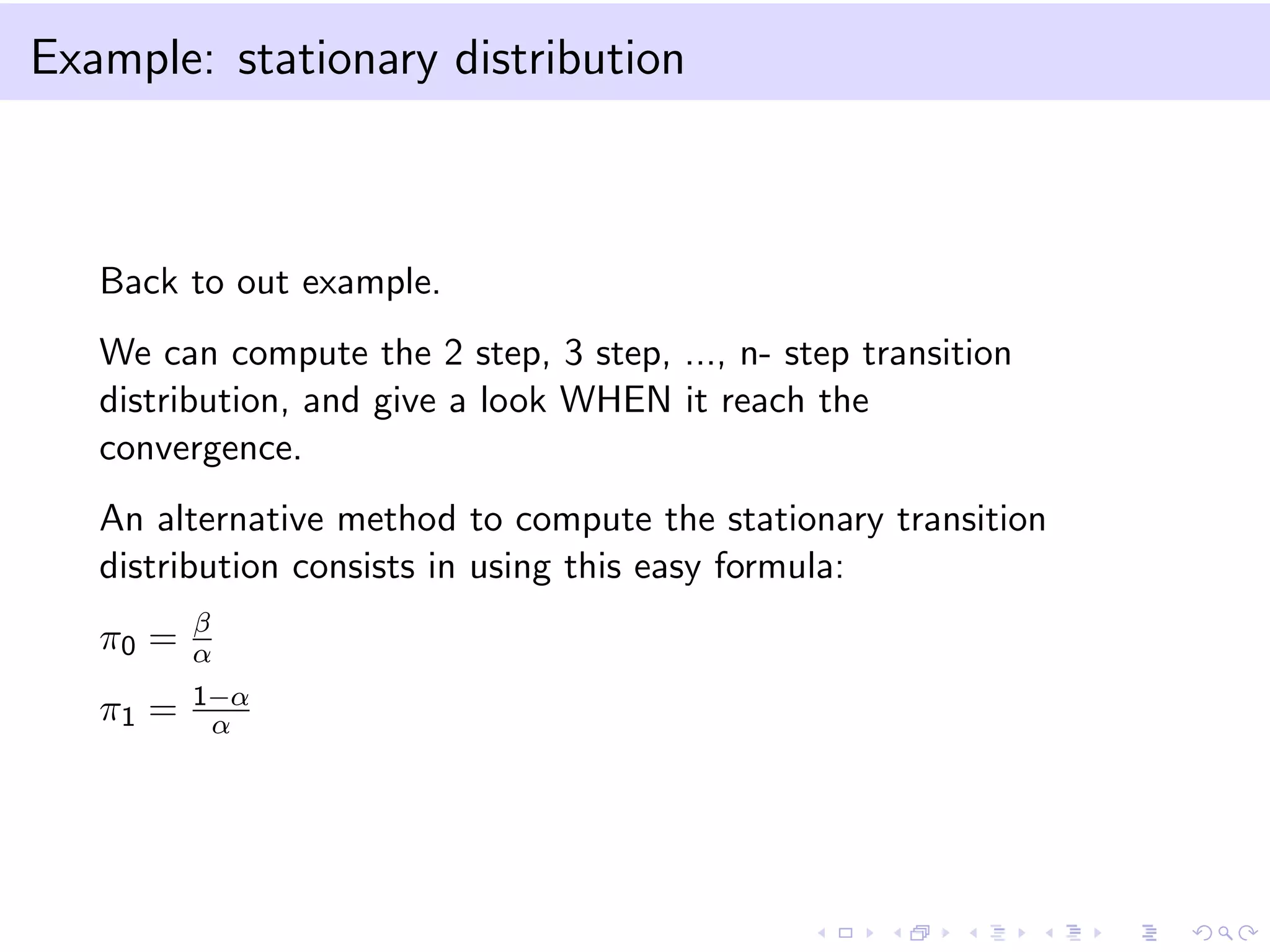
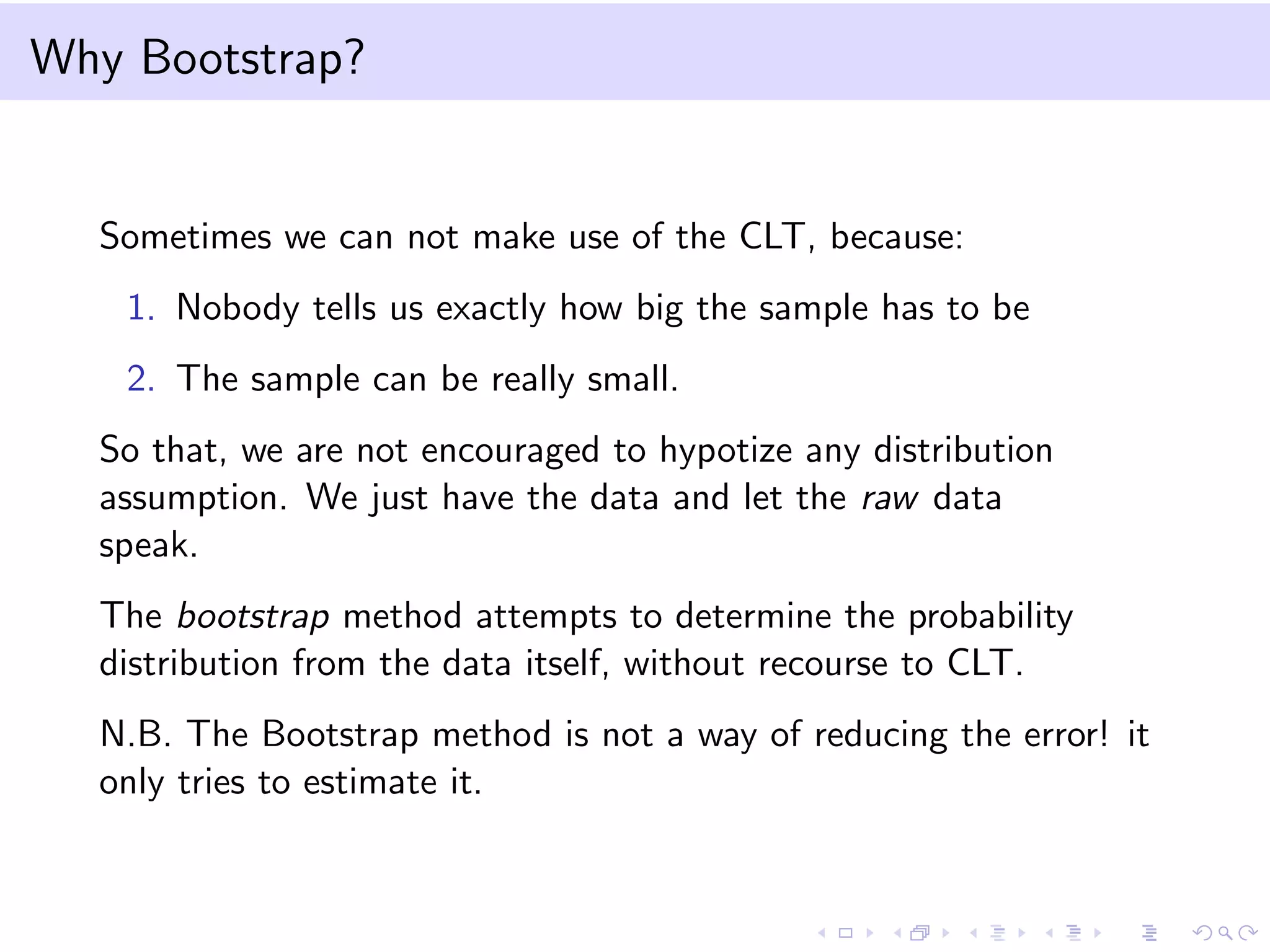
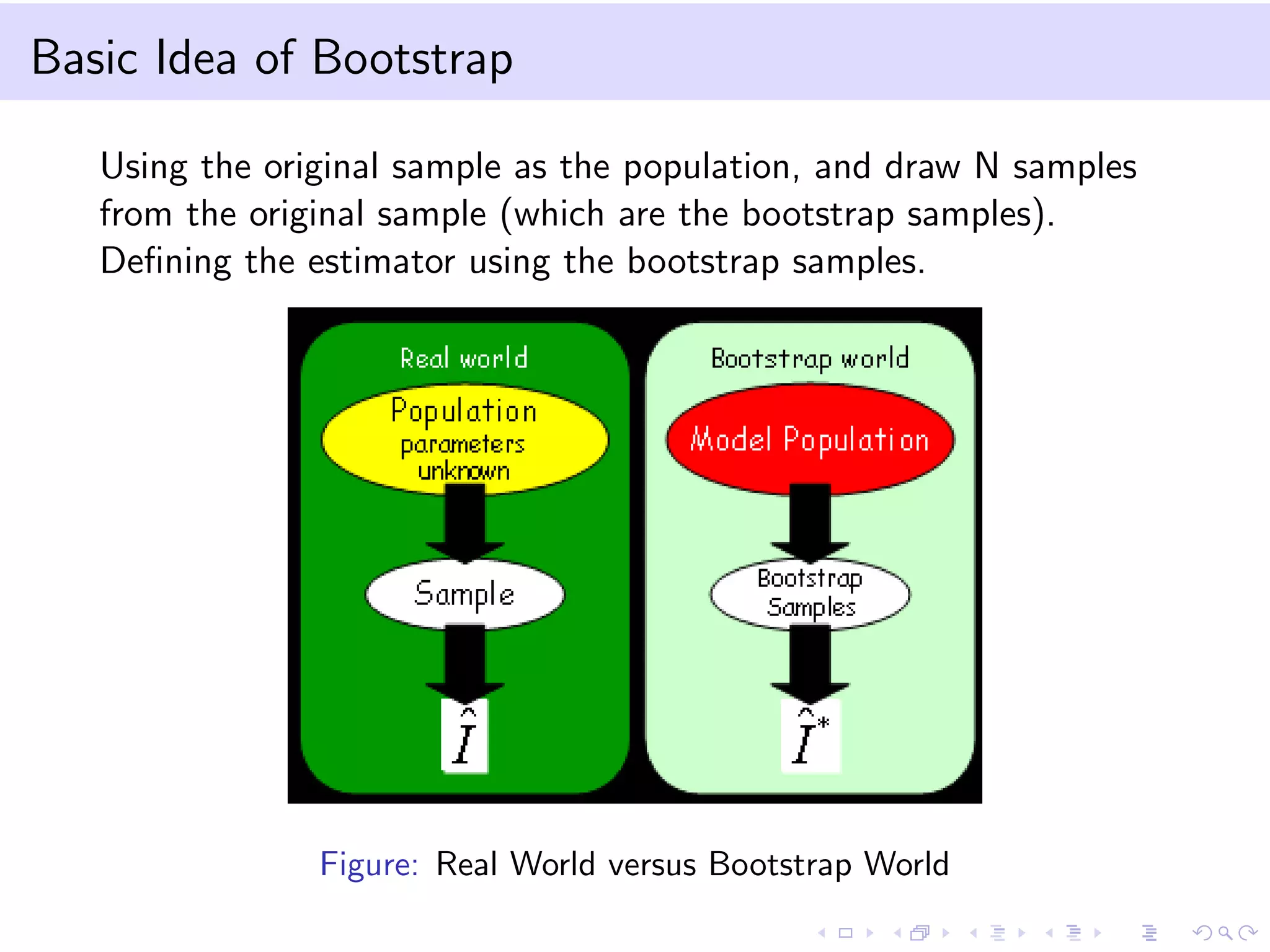
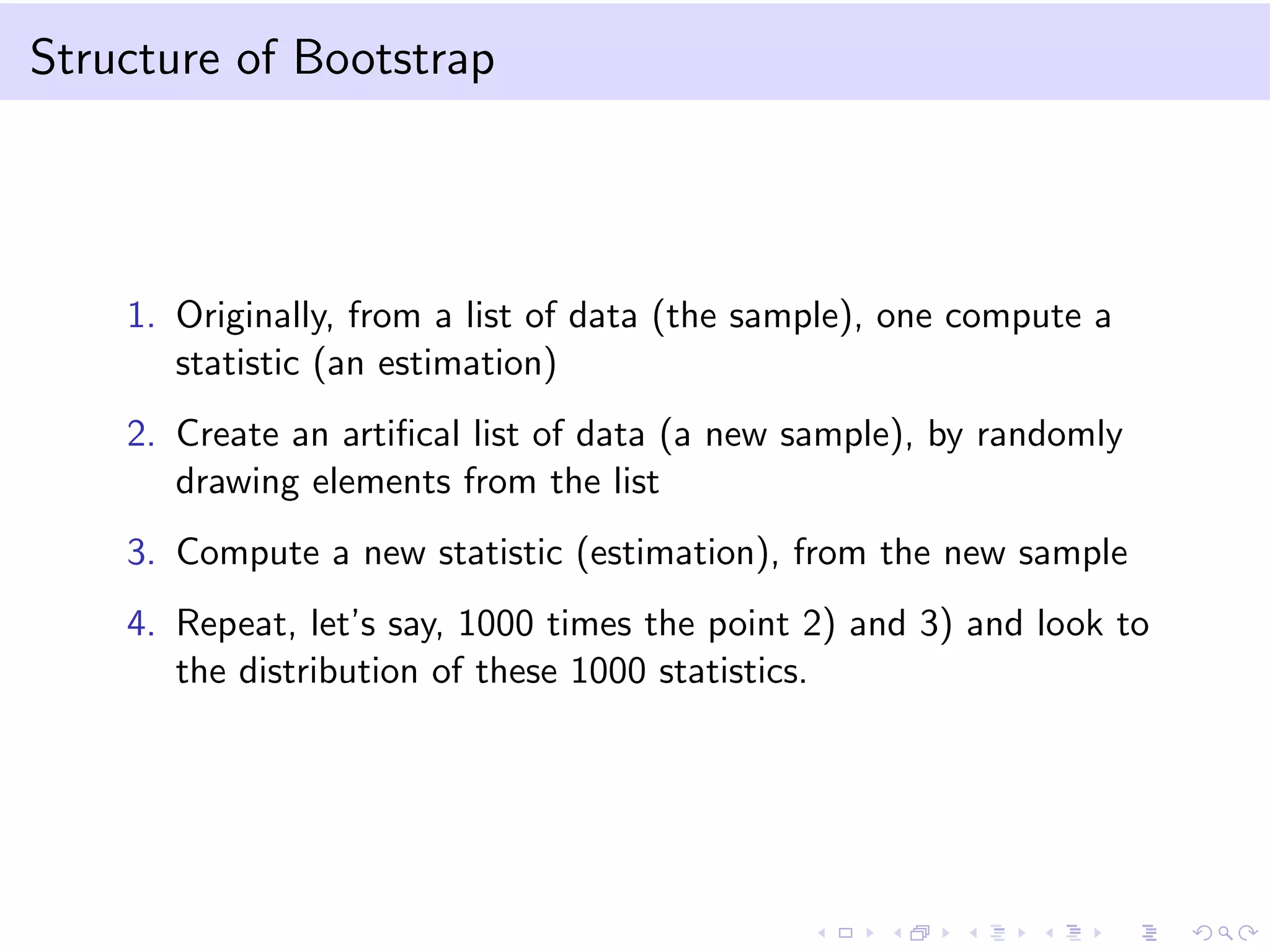
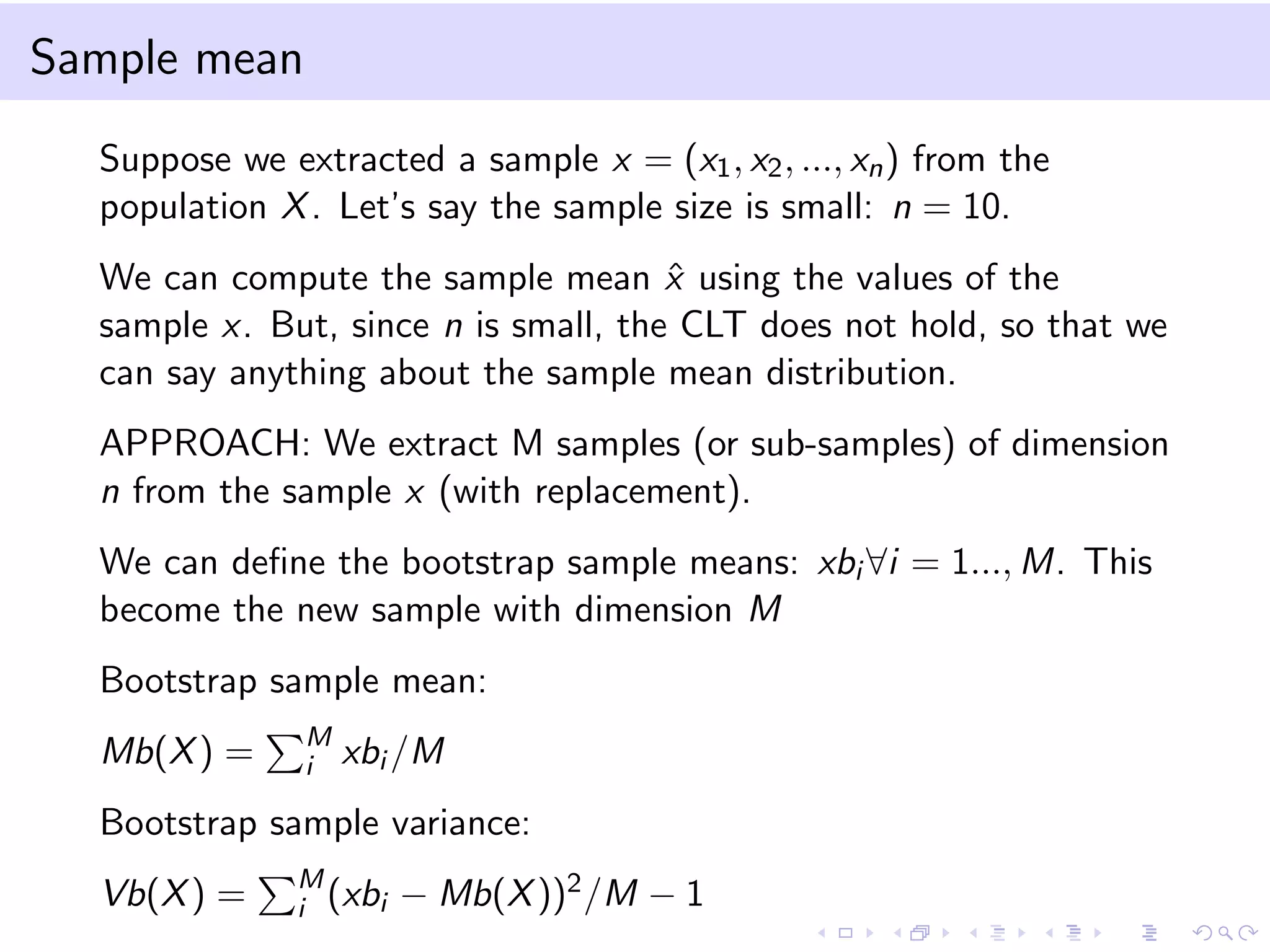
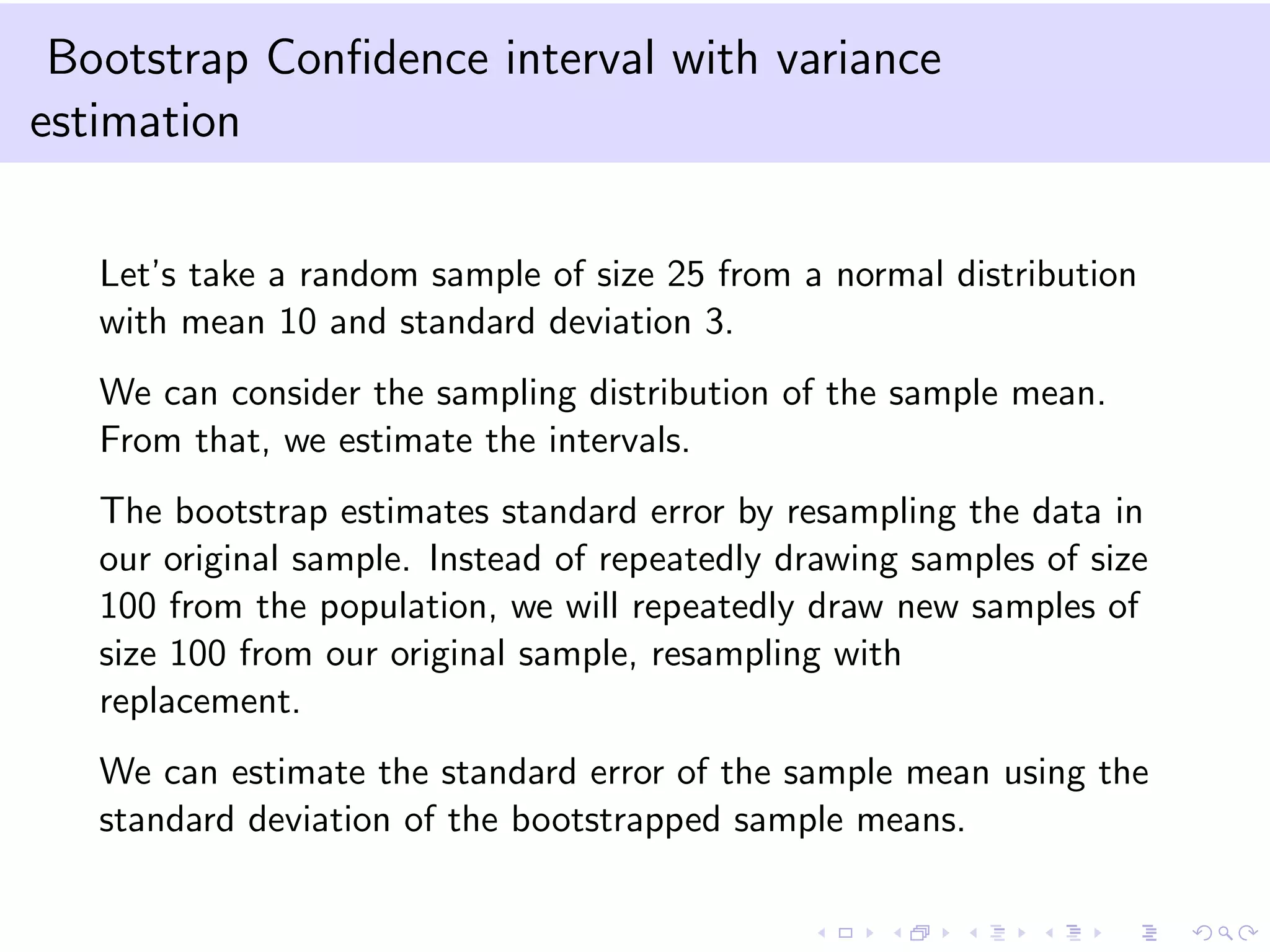
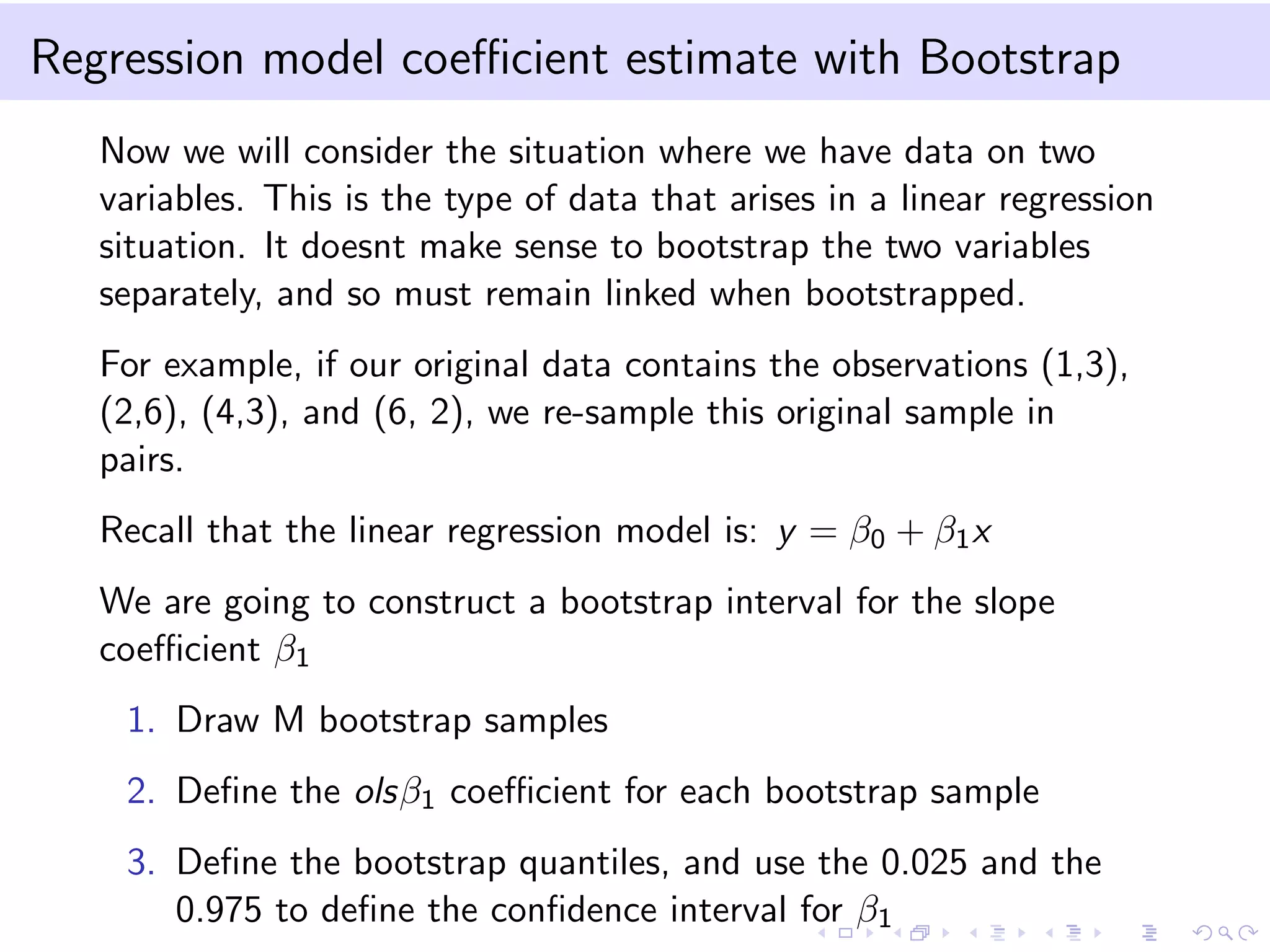
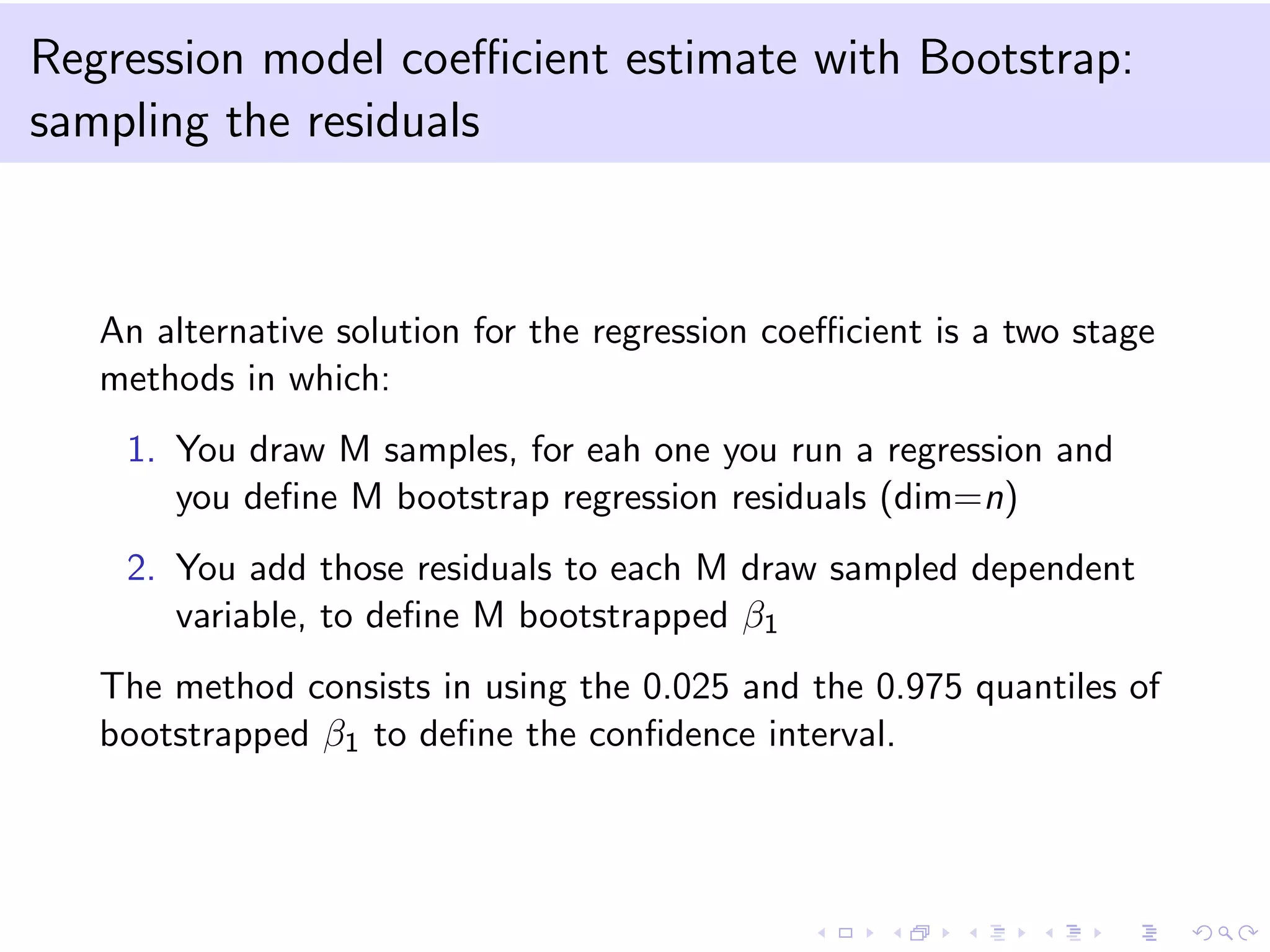
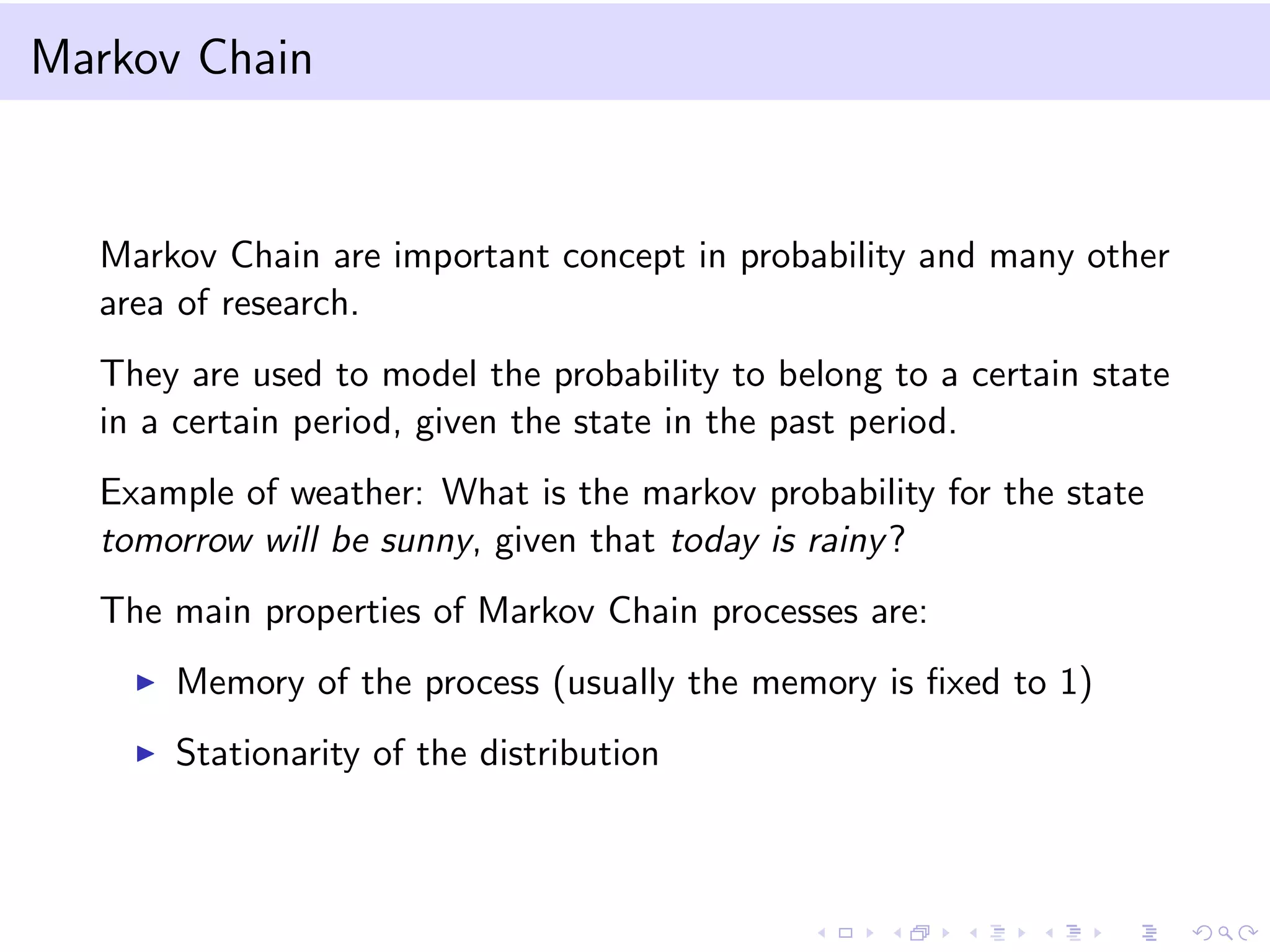
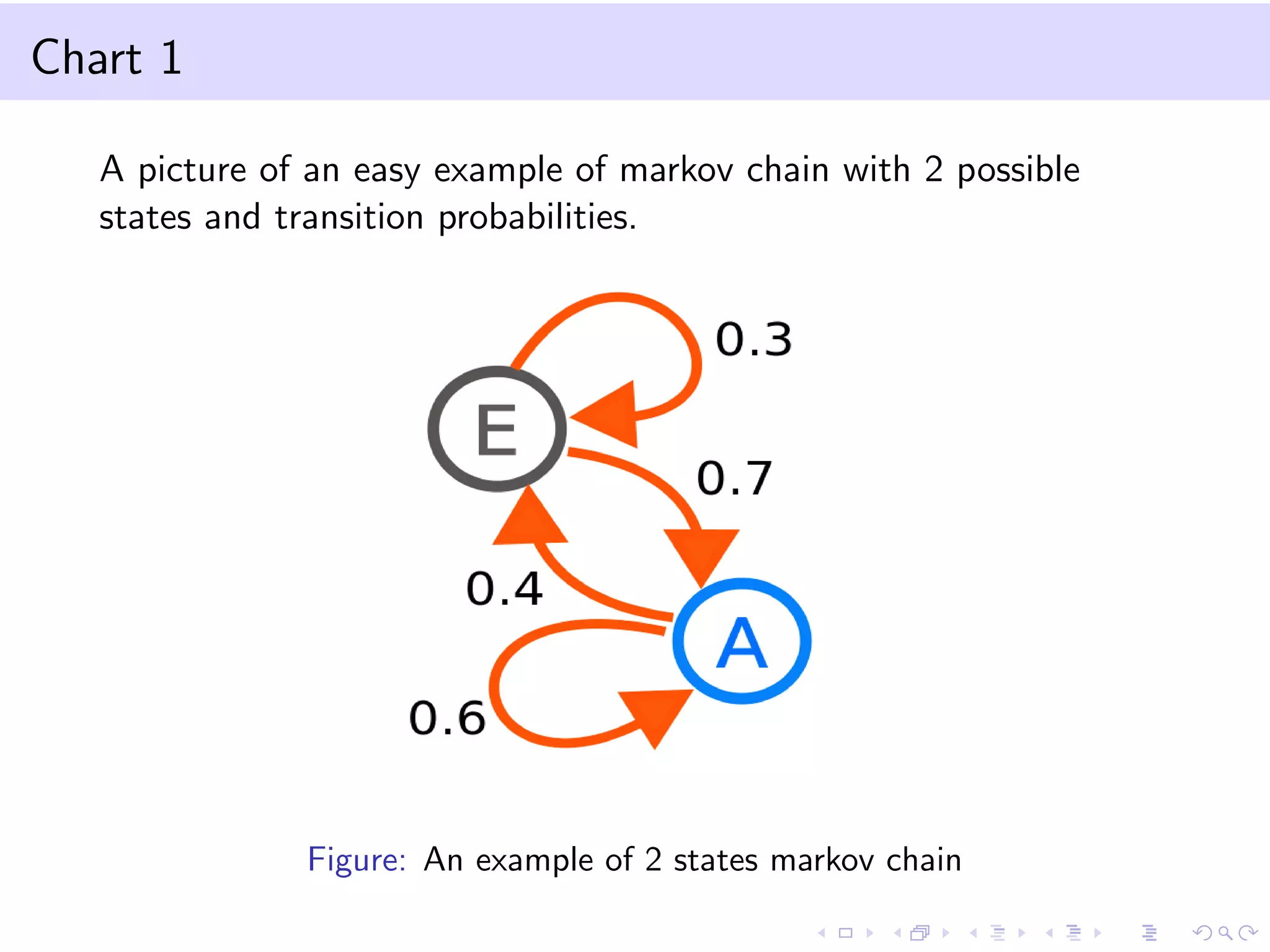
This document provides an introduction to bootstrap methods and Markov chains. It discusses how bootstrap can be used to estimate properties of a statistic like mean or variance when the sample is small and assumptions of the central limit theorem may not apply. The basic bootstrap approach resamples the original sample with replacement to create new bootstrap samples and estimates the statistic for each. Markov chains are defined as stochastic processes where the next state only depends on the current state. An example of a 2-state Markov chain is provided along with notation for transition probabilities and computing unconditional probabilities. The document also discusses stationary distributions for Markov chains.
![Confidence interval with quantiles
Suppose we have a sample of data from an exponential distribution
with parameter λ:
ˆ
f (x|λ) = λe −λx (remember the estimation of λ = 1/ˆn ).
x
An alternative solution to the use of bootstrap estimated standard
errors (the estimation of the sd from an exponential is not
straightforward) is the use of bootstrap quantiles.
ˆ
We can obtain M bootstrap estimates λb and define q ∗ (α) the α
quantile of the bootstrap distribution.
The new bootstrap confidence interval for λ will be:
ˆ
ˆ
[2 ∗ λ − q ∗ (1 − α/2); 2 ∗ λ − q ∗ (α/2)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statisticslab-talk5-140123042946-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Bootstrap-and-elements-of-Markov-Chains-8-2048.jpg)


![Notation
We define a stochastic process {Xn , n = 0, 1, 2, ...} that takes on a
finite or countable number of possible values.
Let the possible values be non negative integers (i.e.Xn ∈ Z+ ). If
Xn = i, then the process is said to be in state i at time n.
The Markov process (in discrete time) is defined as follows:
Pij = P[Xn+1 = j|Xn = in , Xn−1 = in−1 , ..., X0 = i0 ] = P[Xn+1 =
j|Xn = in ], ∀i, j ∈ Z+
We call Pij a 1-step transition probability because we moved from
time n to time n + 1.
It is a first order Markov Chain (memory = 1) because the
probability of being in state j at time (n + 1) only depends on the
state at time n.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statisticslab-talk5-140123042946-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Bootstrap-and-elements-of-Markov-Chains-15-2048.jpg)
![Notation - 2
The n − step transition probability
Pnij = P[Xn+k = j|Xk = i], ∀n ≥ 0, i, j ≥ 0
The Champman Kolmogorov equations allow us to compute these
n − step transition probabilities. It states that:
Pnij =
k
Pnik Pmkj , ∀n, m ≥ 0, ∀i, j ≥ 0
N.B. Base probability properties:
1. Pij ≥ 0, ∀i, j ≥ 0
2.
j≥0 Pij
= 1, i = 0, 1, 2, ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statisticslab-talk5-140123042946-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Bootstrap-and-elements-of-Markov-Chains-16-2048.jpg)
![Example: conditional probability
Consider two states: 0 = rain and 1 = no rain.
Define two probabilities:
α = P00 = P[Xn+1 = 0|Xn = 0] the probability it will rain
tomorrow given it rained today
β = P01 = P[Xn+1 = 1|Xn = 0] the probability it will rain
tomorrow given it did not rain today.
What is the probability it will rain the day after tomorrow given it
rained today?
The transition probability matrix will be:
P = [α, β, 1 − α, 1 − β]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statisticslab-talk5-140123042946-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Bootstrap-and-elements-of-Markov-Chains-17-2048.jpg)
![Example: uncoditional probababily
What is the unconditional probability it will rain the day after
tomorrow?
We need to define the uncoditional or marginal distribution of the
state at time n:
P[Xn = j] =
i
P[Xn = j|X0 = 1]P[X0 = i] =
i
Pnij ∗ αi ,
where αi = P[X0 = i], ∀i ≥ 0
and P[Xn = j|X0 = 1] is the conditional probability just computed
before.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statisticslab-talk5-140123042946-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Bootstrap-and-elements-of-Markov-Chains-18-2048.jpg)