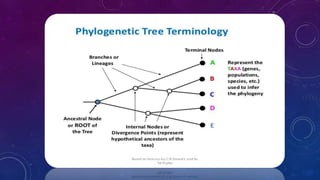
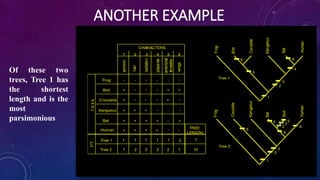
This document provides an overview of parsimony methods for phylogenetic tree analysis. It defines key terms like rooted vs unrooted trees and describes the basic steps of parsimony analysis. Parsimony methods infer the phylogenetic tree that requires the fewest evolutionary changes to explain the observed similarities and differences in species' characteristics. The analysis proceeds by identifying informative sites in a sequence alignment, calculating the number of character changes on possible trees, and selecting the tree with the smallest number of changes as the most likely phylogenetic tree.