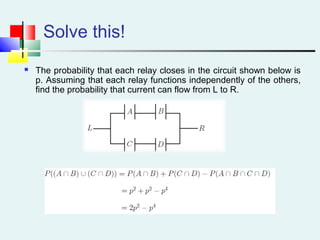
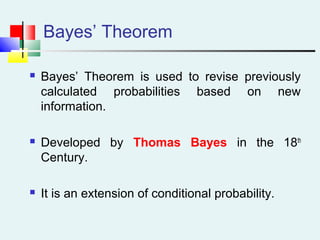
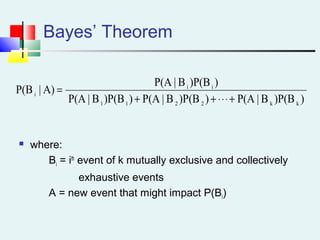
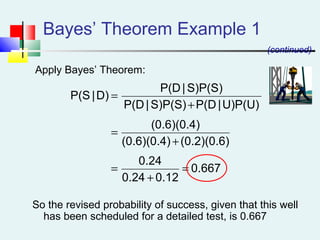
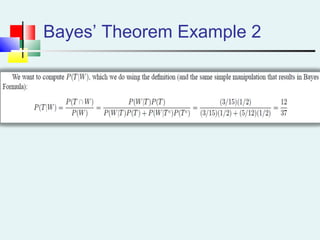
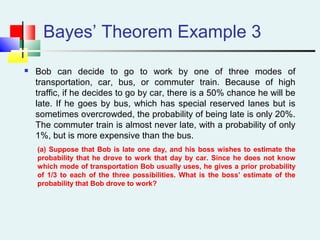
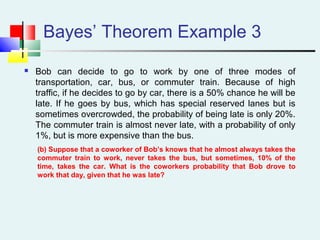
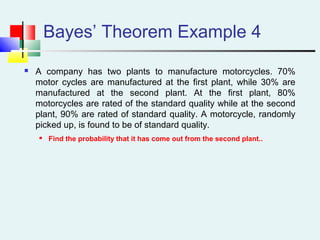
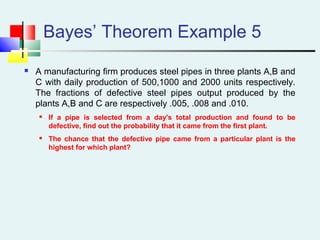
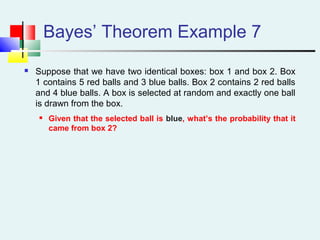
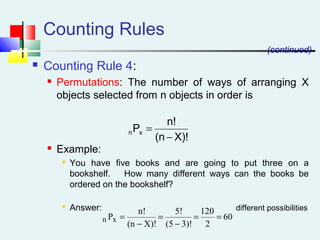
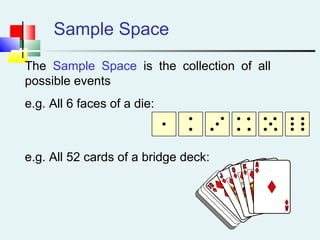
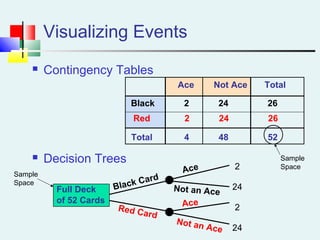
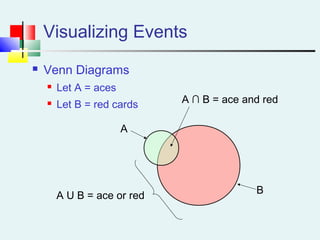
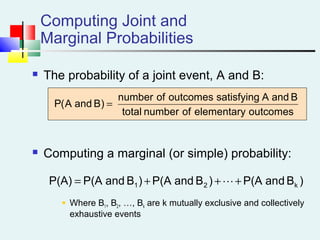
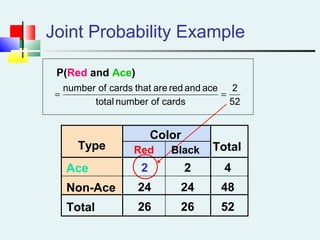
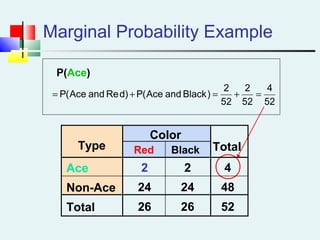
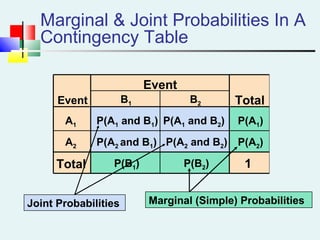
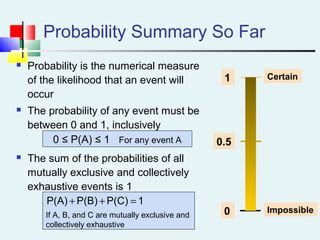
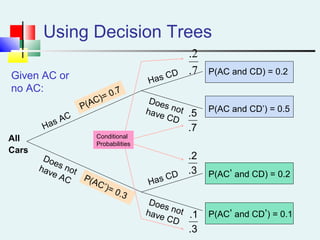
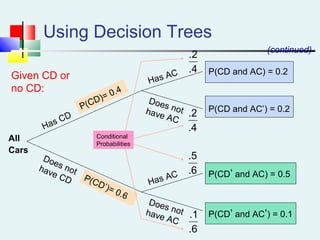
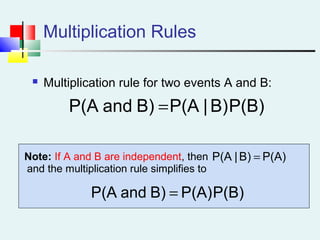
Probability can be calculated using three approaches: a priori, empirical, and subjective. A priori probability is based on prior knowledge, empirical on observed outcomes, and subjective on personal analysis. Simple events have a single characteristic while joint events have multiple. The sample space includes all possible outcomes. Conditional probability is the probability of one event given another. Independence means one event does not affect another's probability.









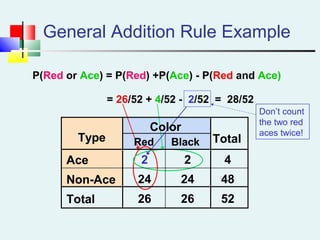

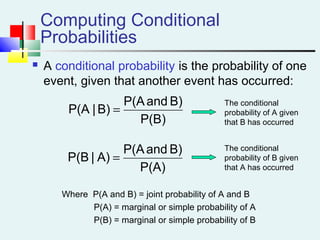

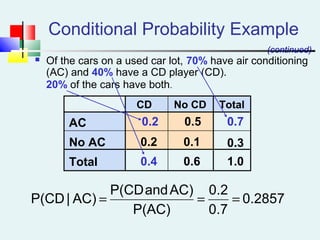
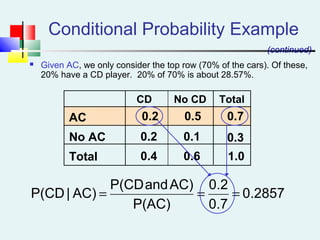





![Multiplication Rules [contd…]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probabilitydistribution-150117052614-conversion-gate02/85/Probability-distribution-33-320.jpg)