Embed presentation
Download to read offline

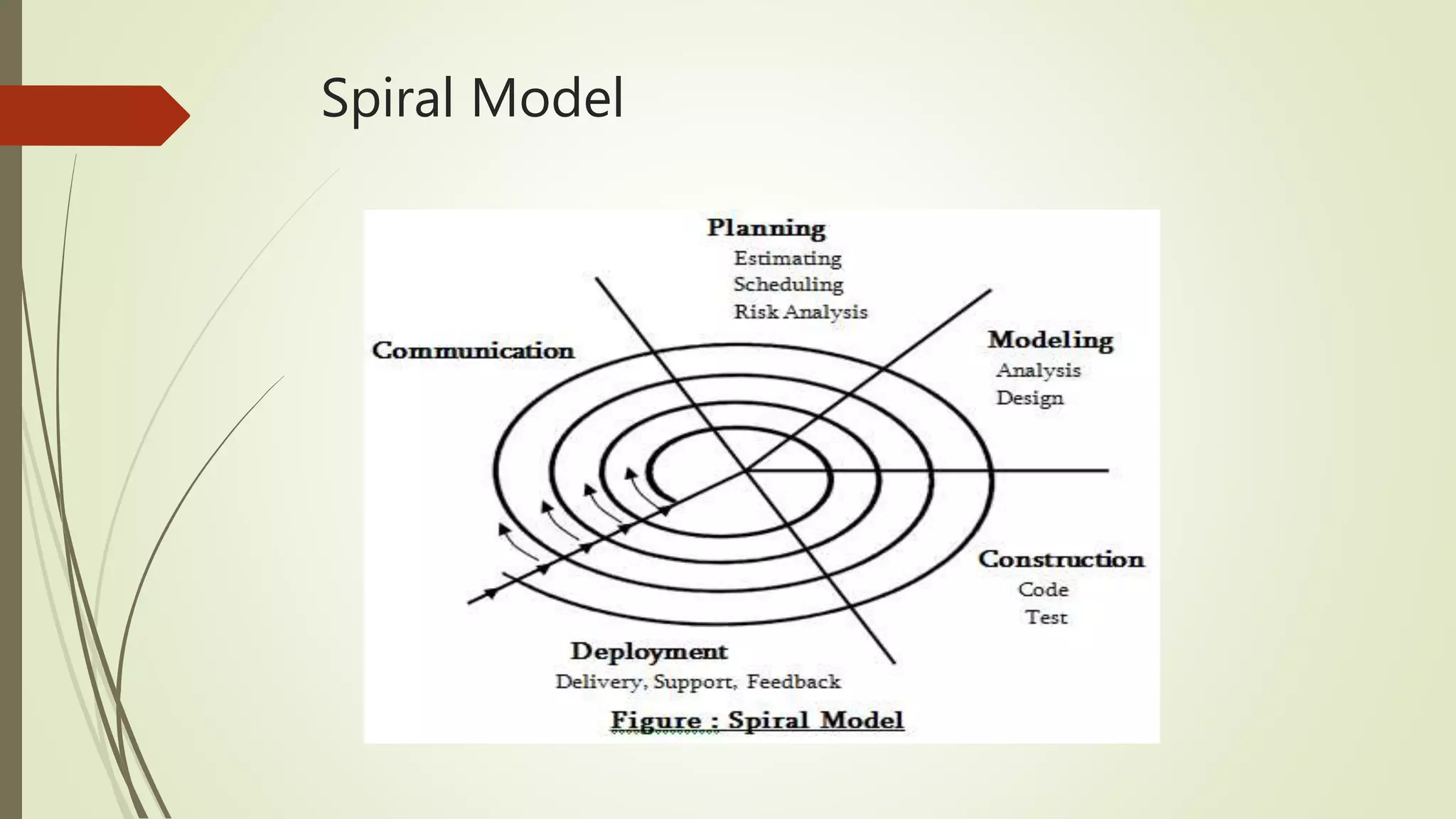









The Spiral Model is a software development process that divides projects into iterations. It consists of four phases - Planning, Risk Analysis, Engineering, and Evaluation - that are repeated within each iteration. In the Planning phase, requirements are gathered. Risk Analysis involves creating prototypes to identify risks. Engineering is when software is developed and tested. Evaluation has customers assess the software and plan the next iteration. The Spiral Model is suited for medium-high risk projects where requirements are complex and changing.











