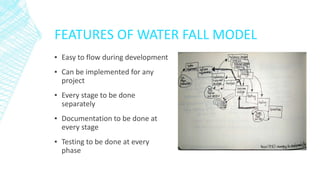
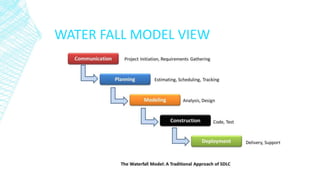
The document discusses the waterfall model of software development. It describes the phases of the waterfall model as requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and maintenance. Each phase must be completed before moving to the next. The advantages are that it is easy to implement and complete one phase at a time. The disadvantages are that not all requirements can be identified up front, the final working model is only seen at the end, and it is not possible to go back to a previous phase.