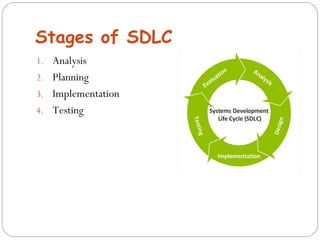
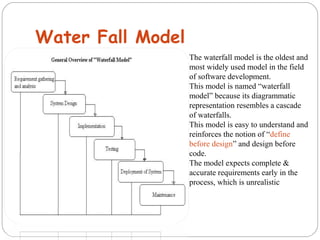
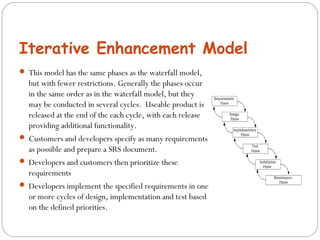
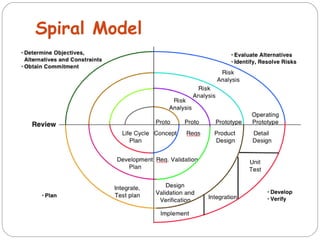
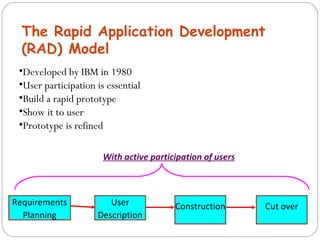
The document discusses the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC), which is a standard model used worldwide to develop software. It describes the main stages of the SDLC as analysis, planning, implementation, and testing. Analysis is the first and most important phase where requirements are determined and the problem is broken down. Planning involves assigning tasks to team members. Implementation is the longest and most expensive phase. Testing is an ongoing phase where thorough testing takes place. The document also discusses various SDLC models including waterfall, iterative enhancement, prototyping, spiral, build and fix, and rapid application development models.