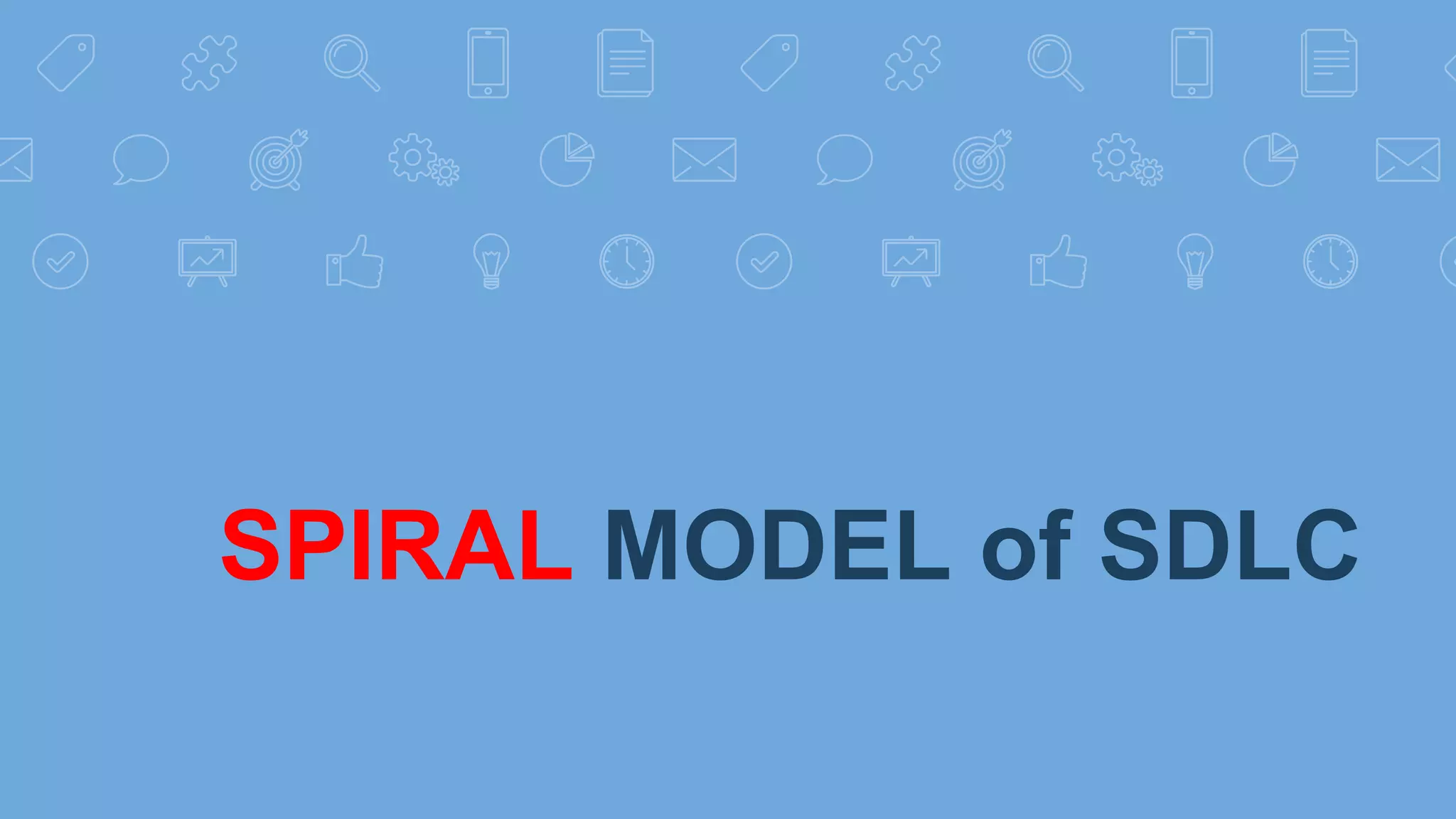
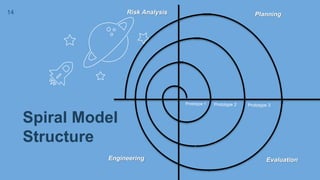
The document describes the spiral model of the software development life cycle (SDLC). It discusses the phases of the spiral model including planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation. The spiral model is an iterative approach that combines elements of both design and prototyping-based development. It allows for incremental adjustments to requirements through repeated cycles. The model helps manage risk on large, complex projects that experience changing requirements over time.

















![References
▸[1] www.tutorialspoint.com, 'SDLC - Spiral Model', 2015. [Online]. Available:
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/sdlc/sdlc_spiral_model.htm. [Accessed: 08- Nov-
2015].
▸[2] Softwaretestinghelp.com, 'Spiral Model - What is SDLC Spiral Model?',
2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/spiral-model-
what-is-sdlc-spiral-model/. [Accessed: 08- Nov- 2015].
▸[3] Istqbexamcertification.com, 'What is Spiral model- advantages,
disadvantages and when to use it?', 2015. [Online]. Available:
http://istqbexamcertification.com/what-is-spiral-model-advantages-
disadvantages-and-when-to-use-it/. [Accessed: 08- Nov- 2015].
▸[4] Onestoptesting.com, 'Spiral Model | History | The Spiral Model |
Applications', 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.onestoptesting.com/sdlc-
models/spiral-model.asp. [Accessed: 08- Nov- 2015].
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spiralmodel-151108172248-lva1-app6892/85/Spiral-model-of-SDLC-22-320.jpg)