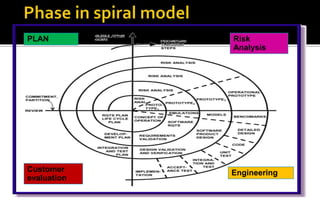
The document discusses the spiral model of software development. The spiral model is an iterative approach that combines prototyping and aspects of the waterfall model. It was defined by Barry Boehm in 1988 as a way to address risks through iterative evaluation and improvement of prototypes. The spiral model is best for medium to high risk projects where requirements are complex or expected to change. It involves evaluating prototypes, defining new prototypes based on learnings, and repeating this process until the final product is delivered.