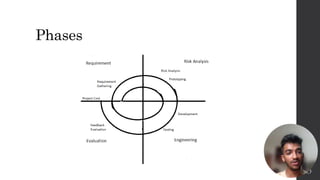
The Spiral Model is a software development process combining elements of both waterfall and prototyping models. It consists of four phases - Planning, Risk Analysis, Engineering, and Evaluation - that are repeated in iterations or "spirals" throughout the project. Each spiral phase begins with designing the goals for that phase and ends with the client reviewing the progress. The Spiral Model emphasizes risk analysis and is well-suited for large, complex projects where requirements are not fully known.