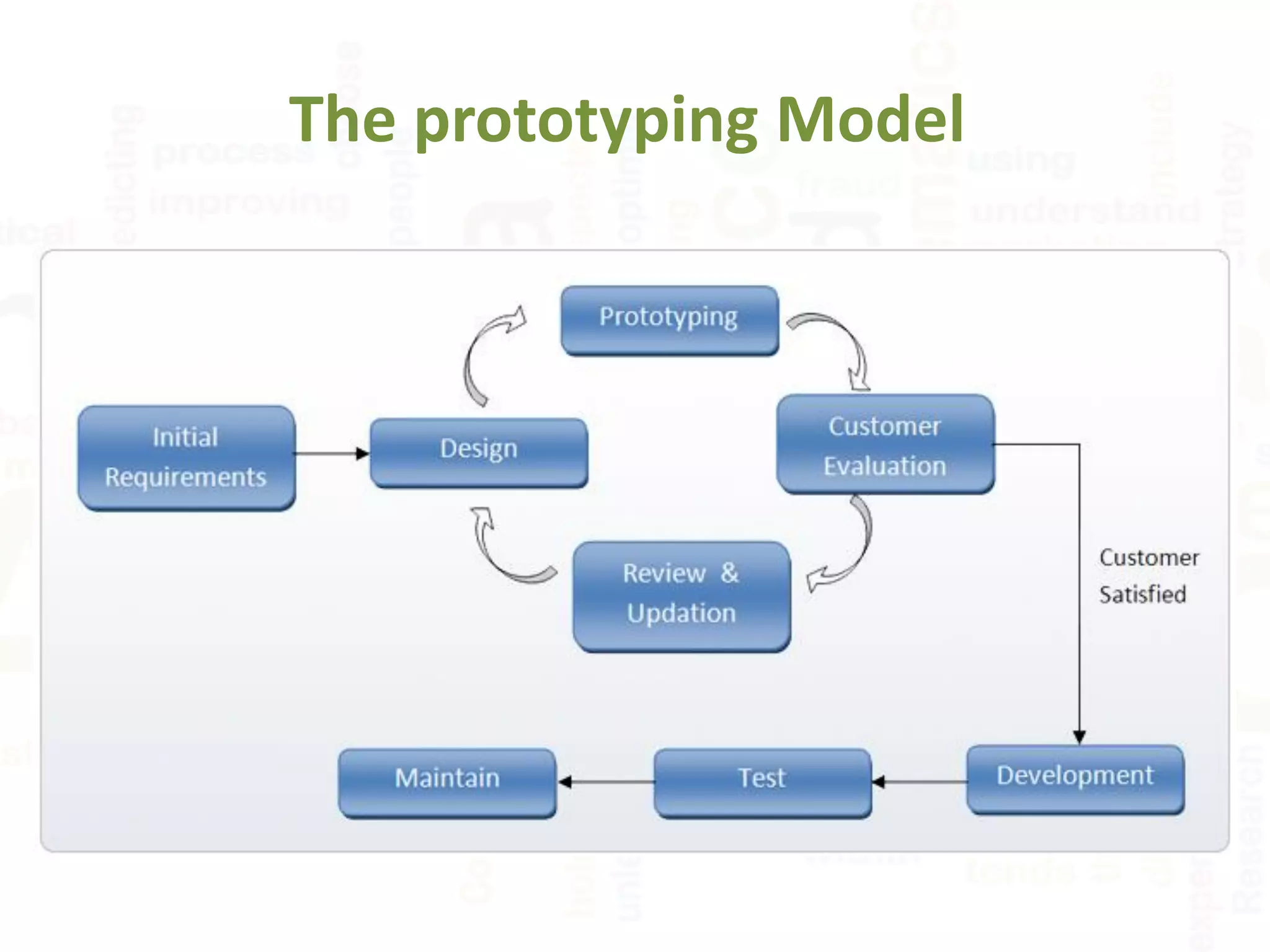
The document provides an overview of several software development life cycle (SDLC) models: Waterfall, Spiral, Agile, and Prototyping. It describes the key stages and processes of each model, when each is best applied, and their advantages and disadvantages. The Waterfall model is linear and sequential, while Spiral and Agile models are iterative with incremental improvements and flexibility. Prototyping focuses on early user involvement through prototypes to refine requirements.




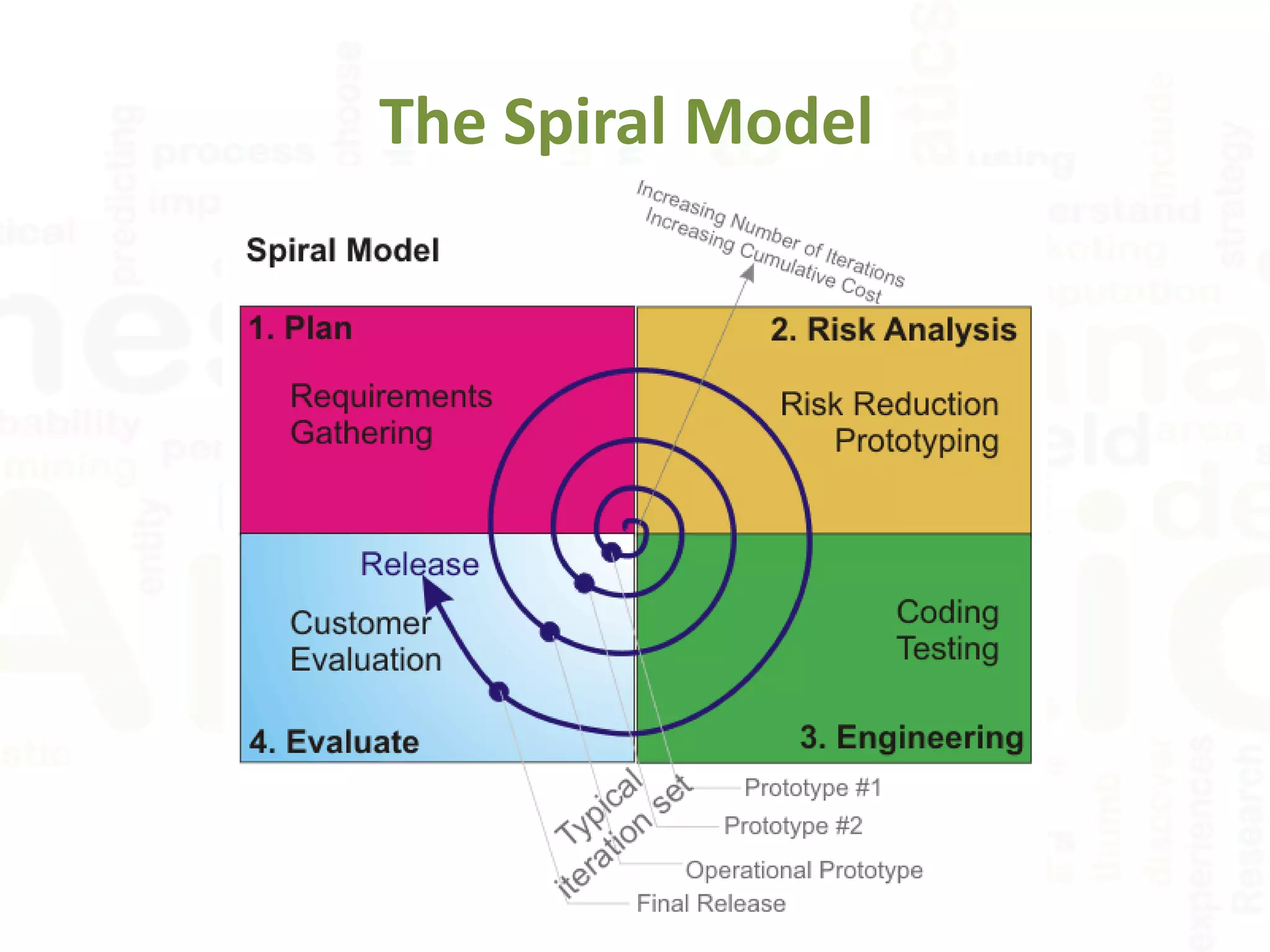



![What is the differences between
Spiral Model and Waterfall Model ?
Spiral ModelWaterfall Model
1] Spiral model is not suitable for small projects.1] Waterfall model is suitable for small projects.
2] Better risk management.2] High amount of risk and uncertainty.
3] Process is complex.3] Easy to understand.
4] The process may go indefinitely.4] Stages are clearly defined.
5] This model is suitable for long and ongoing
projects.
5] This model is not suitable for long and
ongoing projects.
6] Iterations are followed6] Sequence is followed
7] Flexible with user requirements7] Requirements once fixed cannot be modified
8] Refinements are easily possible8] Refinements are not so easy
9] Phases are repeated itself9] Phases are processed and completed one at a
time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaredevelopmentlifecycle-151028113415-lva1-app6892/75/Software-development-life-cycle-13-2048.jpg)
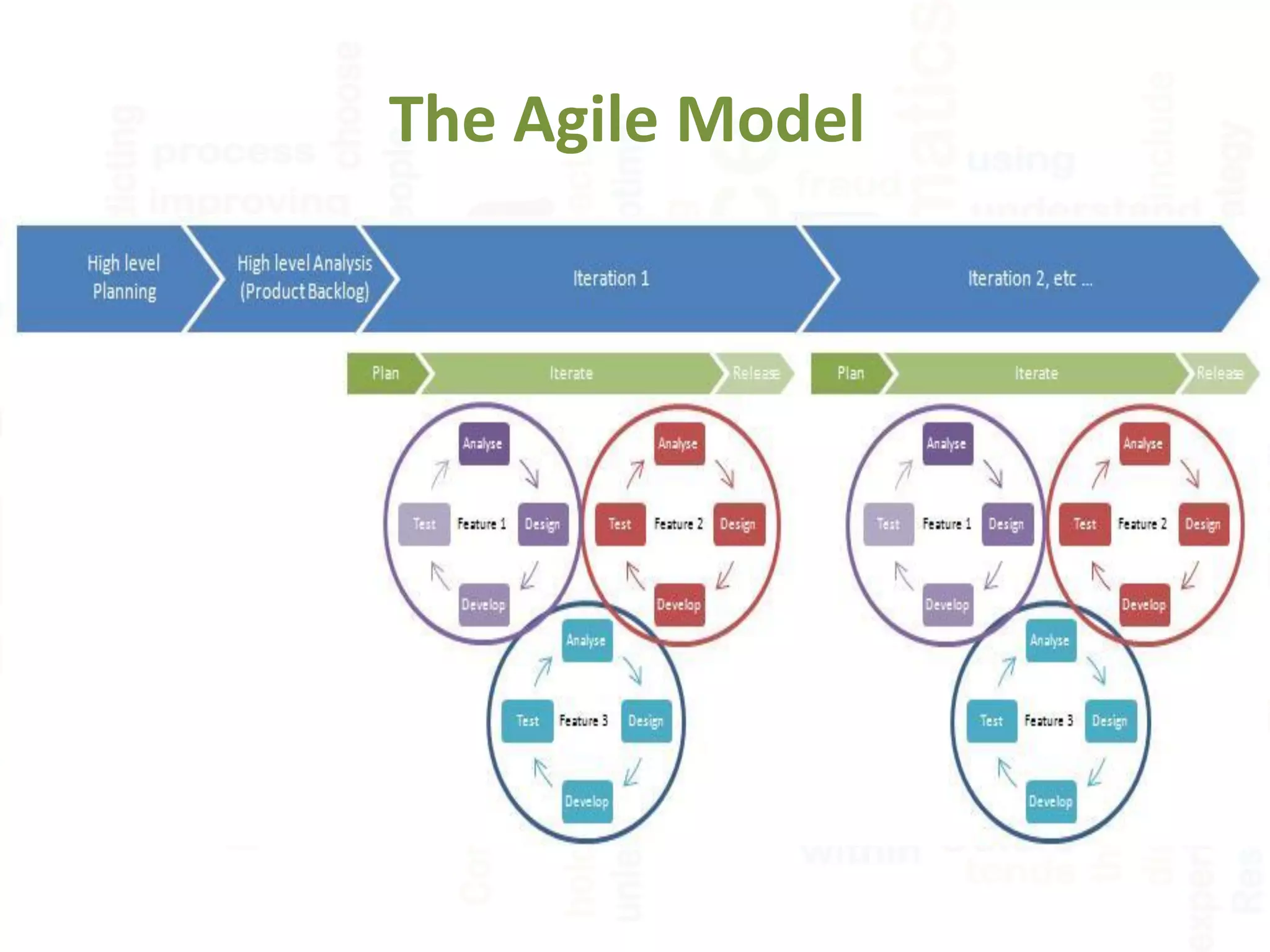

![What is the differences between
Spiral Model and Agile Model ?
Agile ModelSpiral Model
1] Little or no planning required.1] Planning is required.
2] Easy to manage.2] Management is more complex.
3] Early delivery of partial working solutions.3] End of project may not be known.
4] Suitable for small projects.4] Not suitable for small or low risk projects.
5] Depends heavily on customer interaction5] Does not depend heavily on customer
interaction
6] Every iteration is a separate model6] Every iteration is not a separate model
7] Agile is the combination of iterative and
incremental
7] Spiral is the combination of iterative and
waterfall](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwaredevelopmentlifecycle-151028113415-lva1-app6892/75/Software-development-life-cycle-18-2048.jpg)