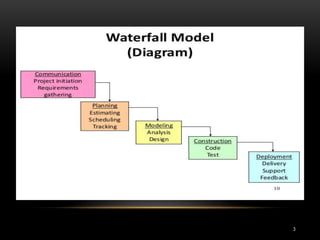
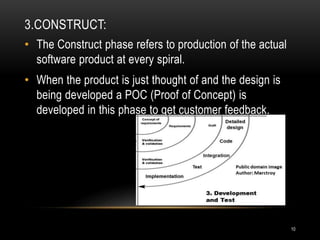
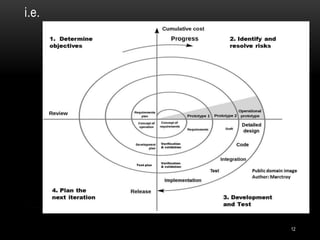
The document discusses two software development life cycle (SDLC) models: the waterfall model and the spiral model. The waterfall model is a sequential design process where each phase must be completed before the next can begin. It is simple but not suitable for complex or long-term projects where requirements may change. The spiral model is an iterative approach that allows for incremental releases and refinement through each cycle. It focuses on risk evaluation and is well-suited to large, expensive projects with changing needs.