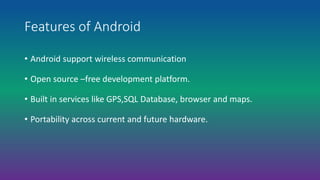
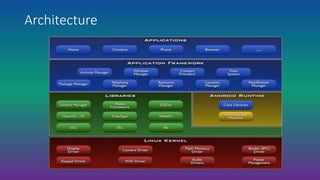
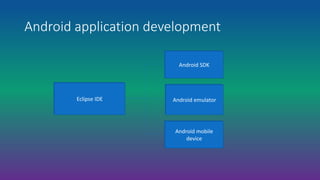
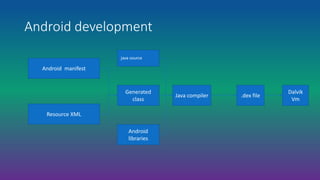
Android is an open-source, Linux-based operating system designed for mobile devices. It was developed by Android Inc., which was purchased by Google in 2005. Android is developed as part of the Open Handset Alliance led by Google. It has gone through many versions and features an open architecture, integration with Google services, and support for additional hardware and software features through third-party apps.