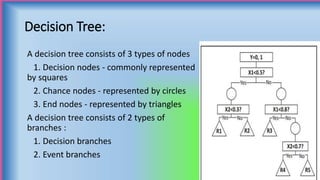
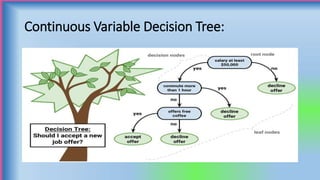
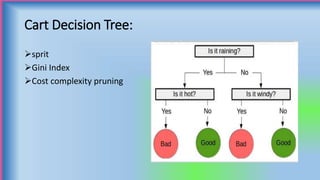
The document discusses decision trees, which are graphical representations of possible solutions to a decision based on certain conditions. It describes the basic components of decision trees, including decision nodes, chance nodes, and end nodes. It also covers different types of decision trees, algorithms for building decision trees like CART and C5.0, advantages like interpretability, and limitations like potential for overfitting. Finally, it provides examples of applications of decision trees in domains like business, healthcare, and engineering.