Embed presentation
Downloaded 209 times




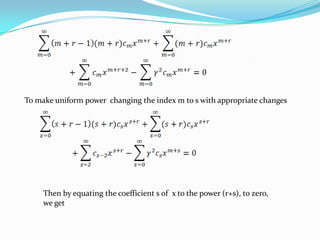
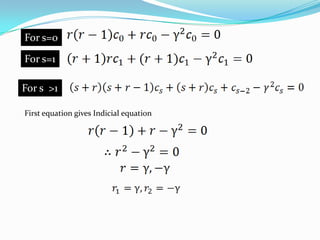

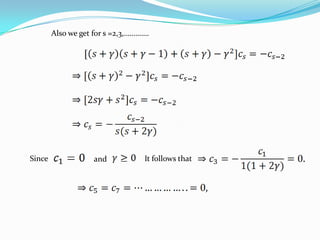

Bessel's equation describes functions that arise in various physical problems, such as vibrating membranes and radar. The equation can be solved using an extended power series method to derive Bessel functions of the first kind, which are characterized by their orthogonality properties and represent solutions as a sum of integer powers of x.








