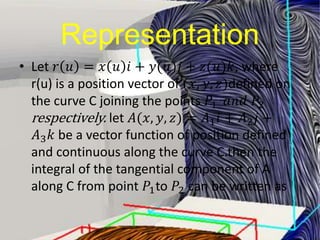
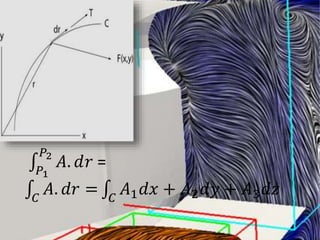
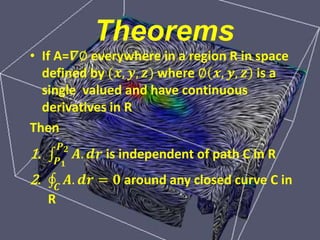
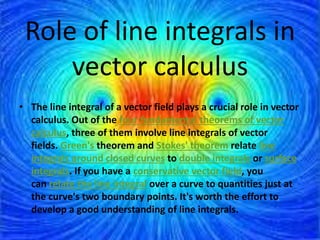
This document defines and explains line integrals. It defines a line integral as the integral of a function along a line or curve, where the function has a continuously varying value along that line. It discusses how line integrals were developed to solve problems involving fluid flow, forces, electricity, and magnetism. It provides representations of line integrals using vector notation and explains that if the vector field is conservative, the line integral is path independent and can be written as the difference of a potential function between two points.