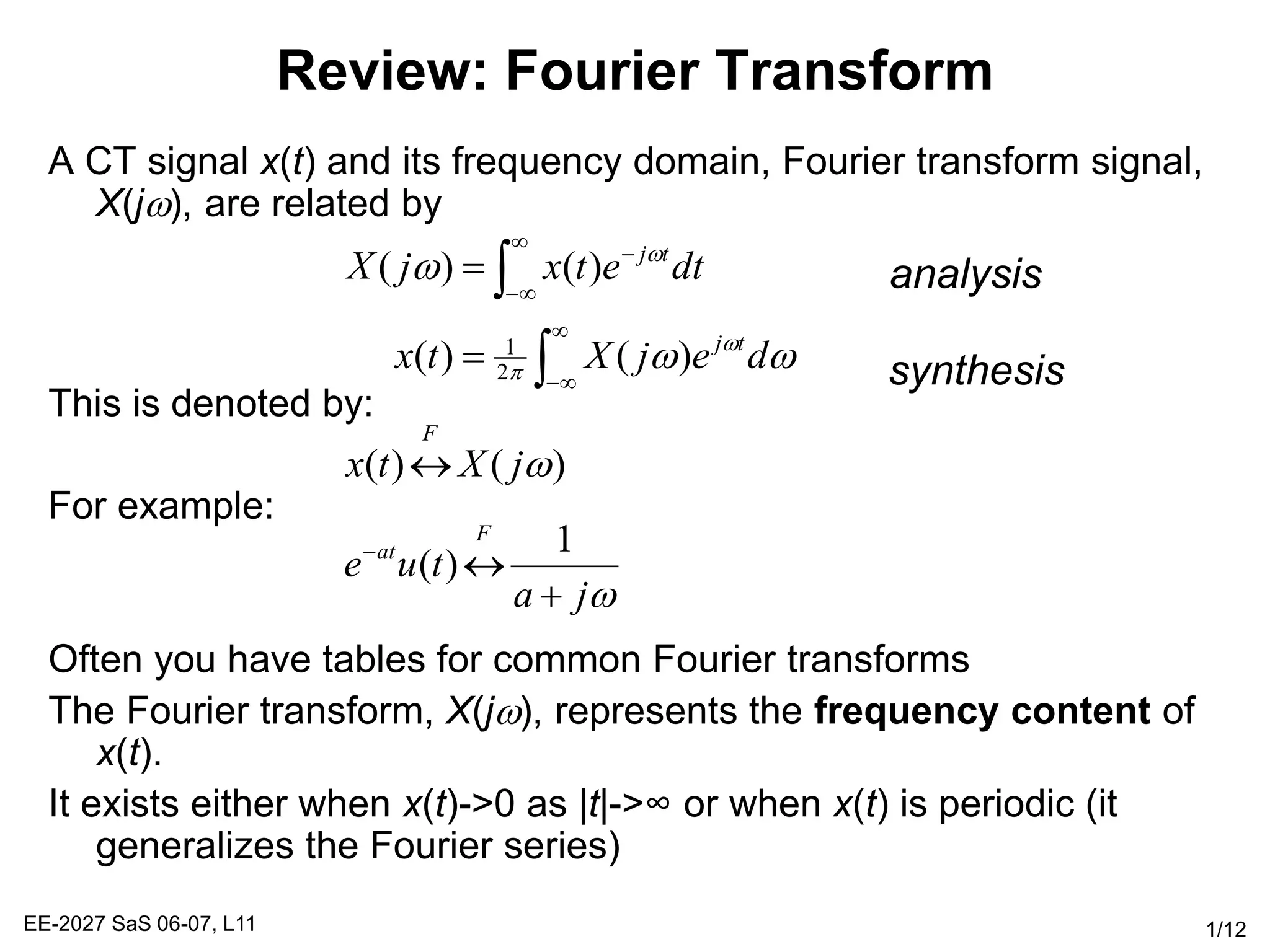
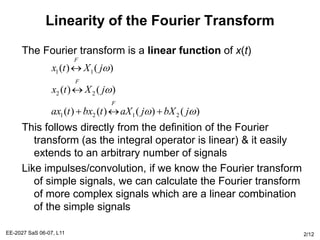
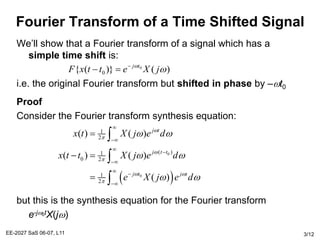
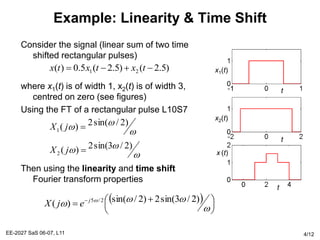
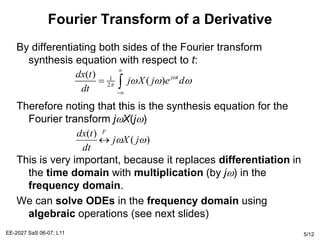
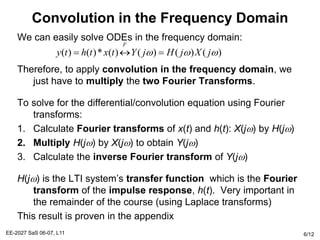
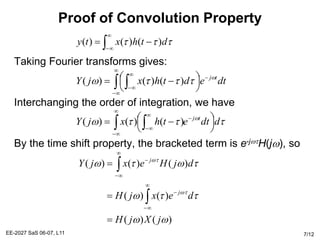
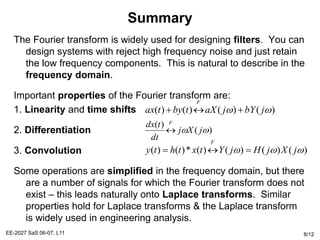
The Fourier transform relates a signal in the time domain, x(t), to its frequency domain representation, X(jw). It represents the frequency content of the signal. The Fourier transform is a linear operation, and time shifts in the time domain result in phase shifts in the frequency domain. Differentiation in the time domain corresponds to multiplication by jw in the frequency domain. Convolution becomes simple multiplication in the frequency domain. These properties allow differential equations and systems with convolution to be solved using algebraic operations by working in the frequency domain.