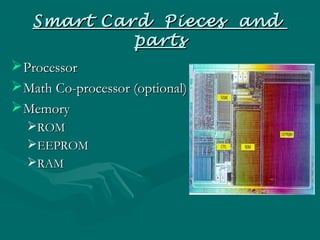
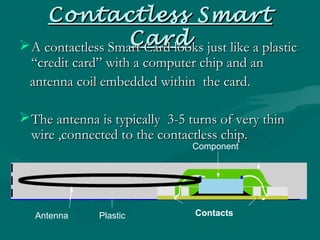
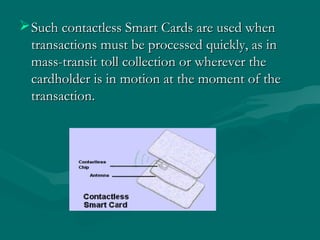
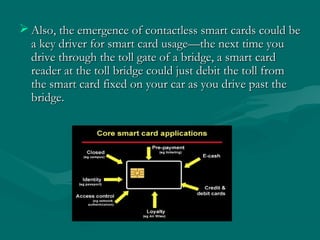
A smart card is a plastic card that contains an embedded microchip which can store and process data. The microchip allows smart cards to carry out encryption and authentication functions. Smart cards come in contact and contactless varieties. They offer benefits like security, intelligence, and convenience. Smart cards are used in applications like mobile phones, healthcare, and transportation to store user data, enable authentication, and process transactions securely. Their use is expected to grow significantly in the future as more services migrate to using smart card technology.