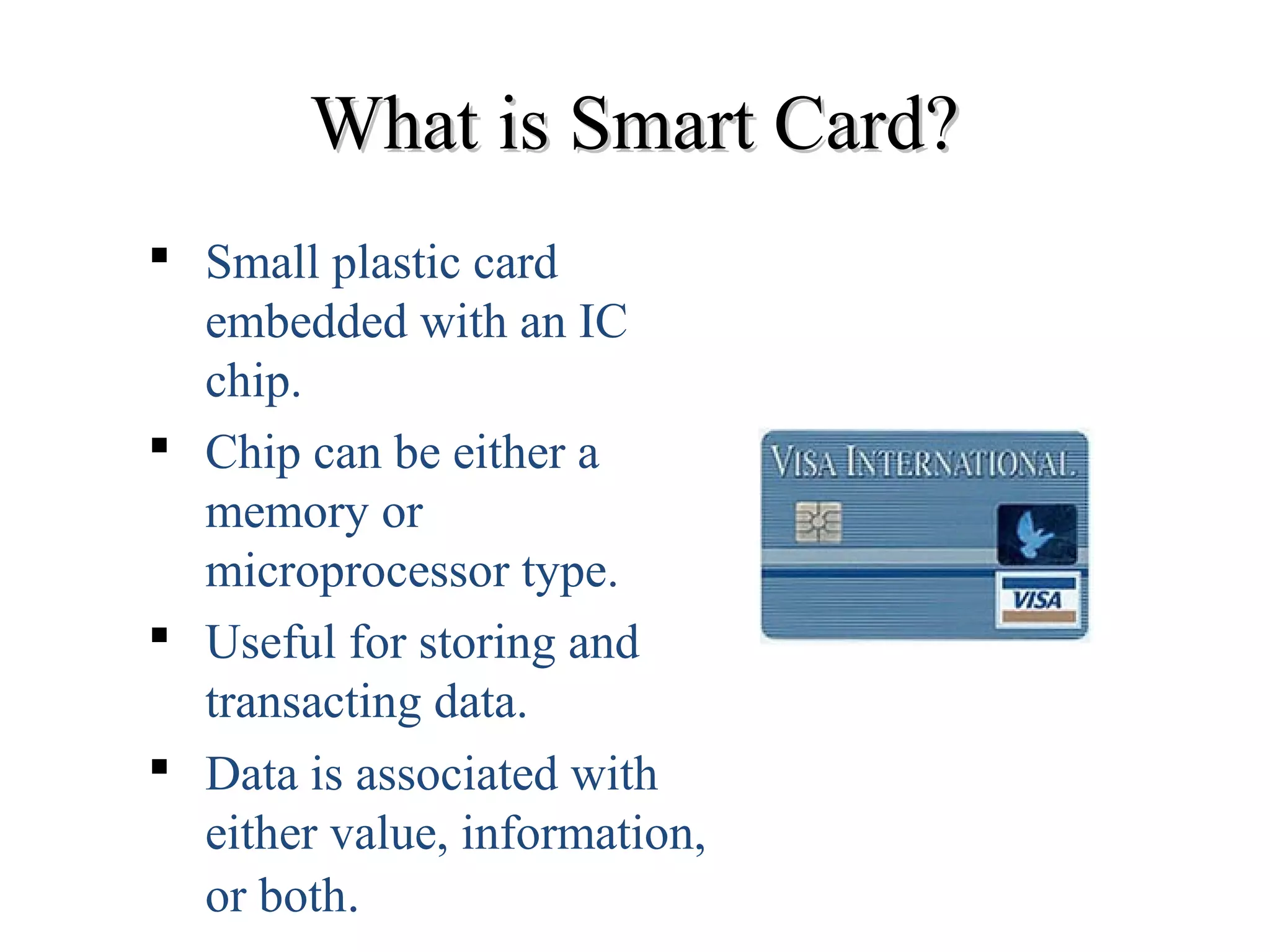
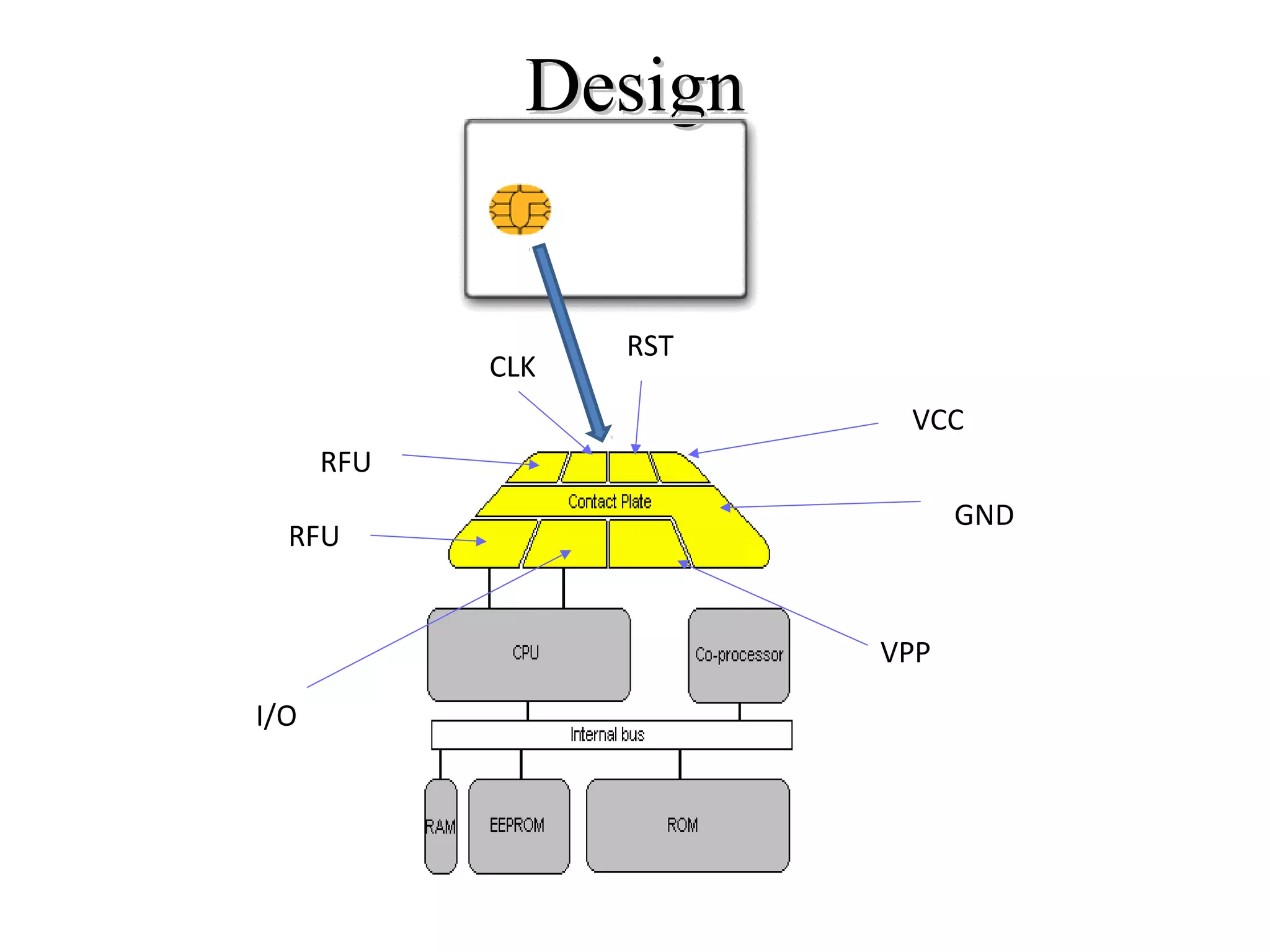
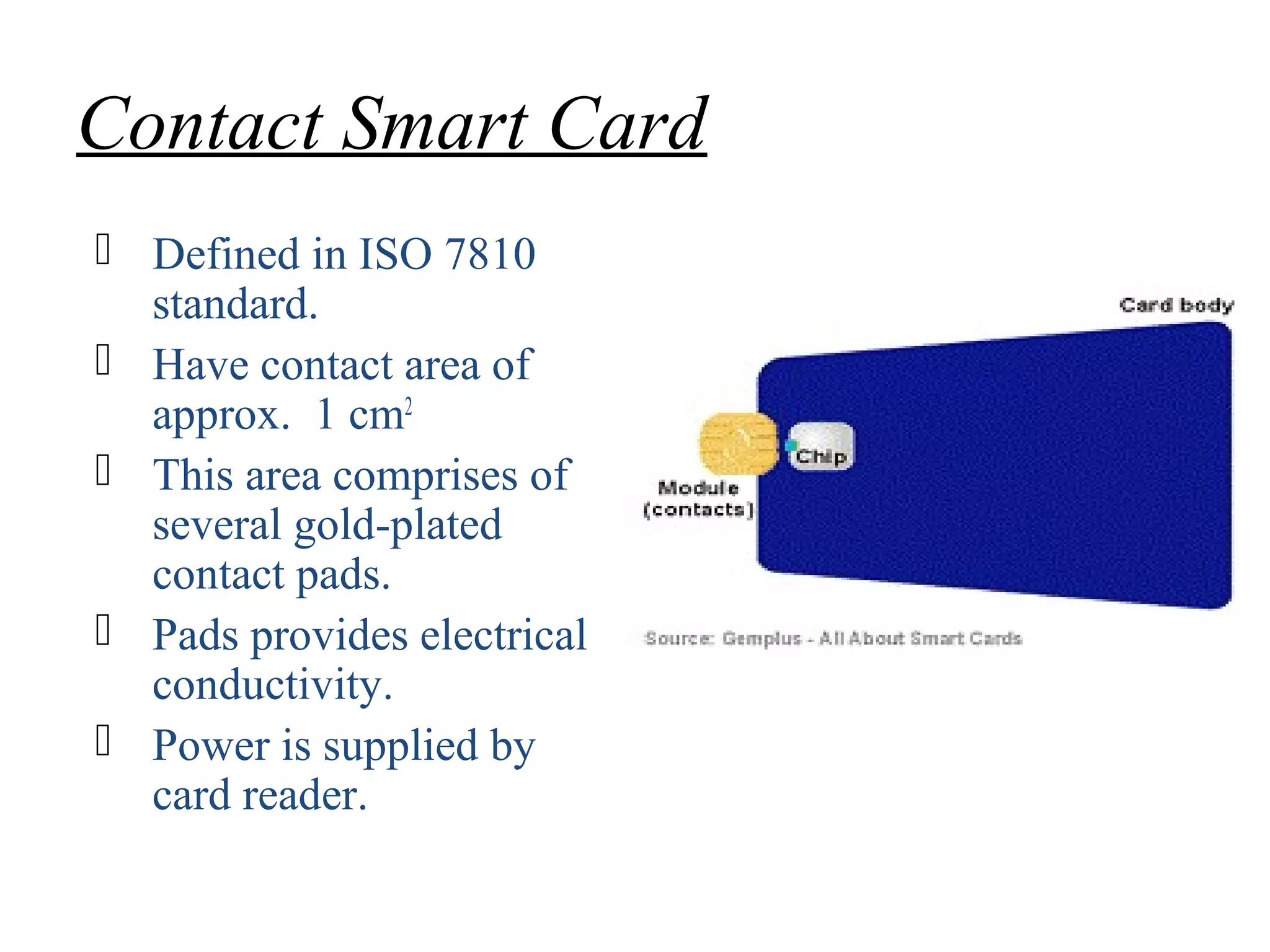
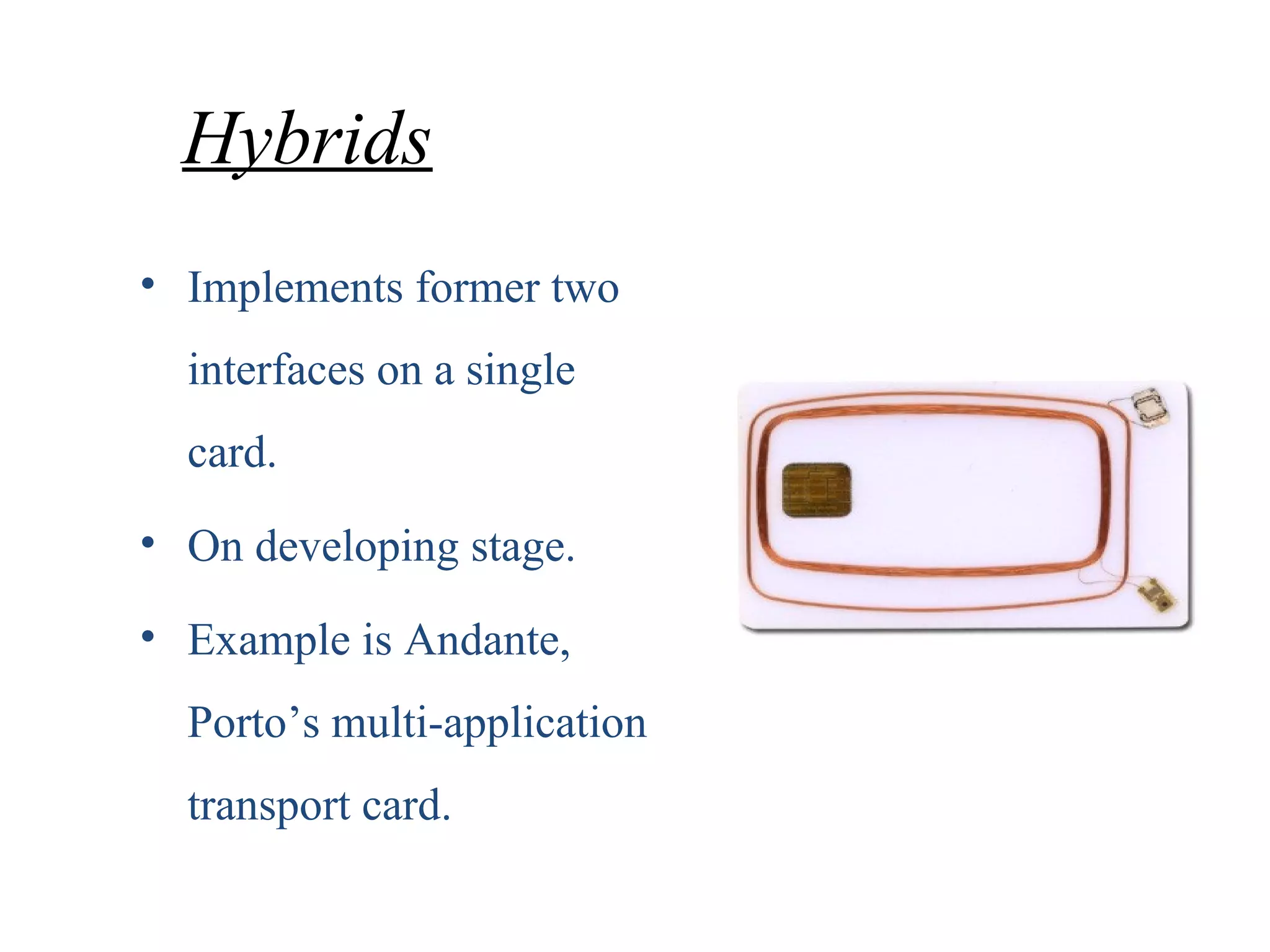
This document provides an overview of smart cards. It defines a smart card as a small plastic card with an embedded integrated circuit chip that can store and transact data. The document then discusses the history of smart cards, their design, types including contact, contactless and hybrid cards, applications such as financial, identification and access control, security features, benefits like convenience and enhanced security, and problems with malware and damage.