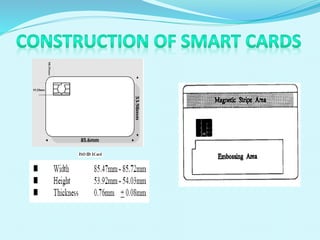
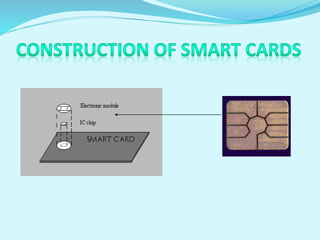
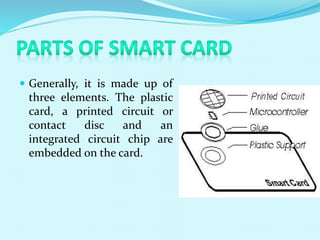
The document discusses the history and development of smart cards from their invention in 1968 to modern applications. It describes how smart cards work, including their construction from a plastic card body with an embedded microchip. Examples are given of different types of smart cards and their uses in payment systems, identification, banking, transportation, and other areas. Advantages include security, portability, and cost effectiveness, while disadvantages relate to tampering risks and reader compatibility issues.