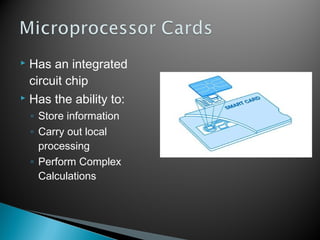
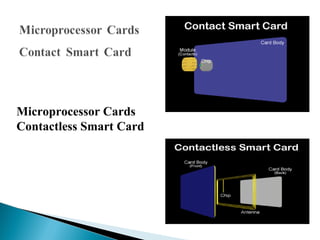
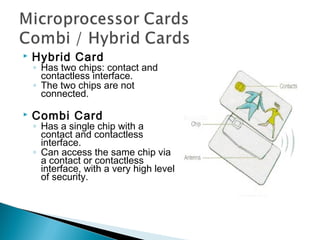
A smart card, or integrated circuit card (ICC), is a small card with embedded circuits that can store and process information for various applications, such as banking and identification. There are different types of smart cards, including microprocessor cards, which can perform complex calculations and are available in contact and contactless forms. Compared to magnetic stripe cards, smart cards offer enhanced security, longer lifespan, and the ability to support multiple applications on a single card.