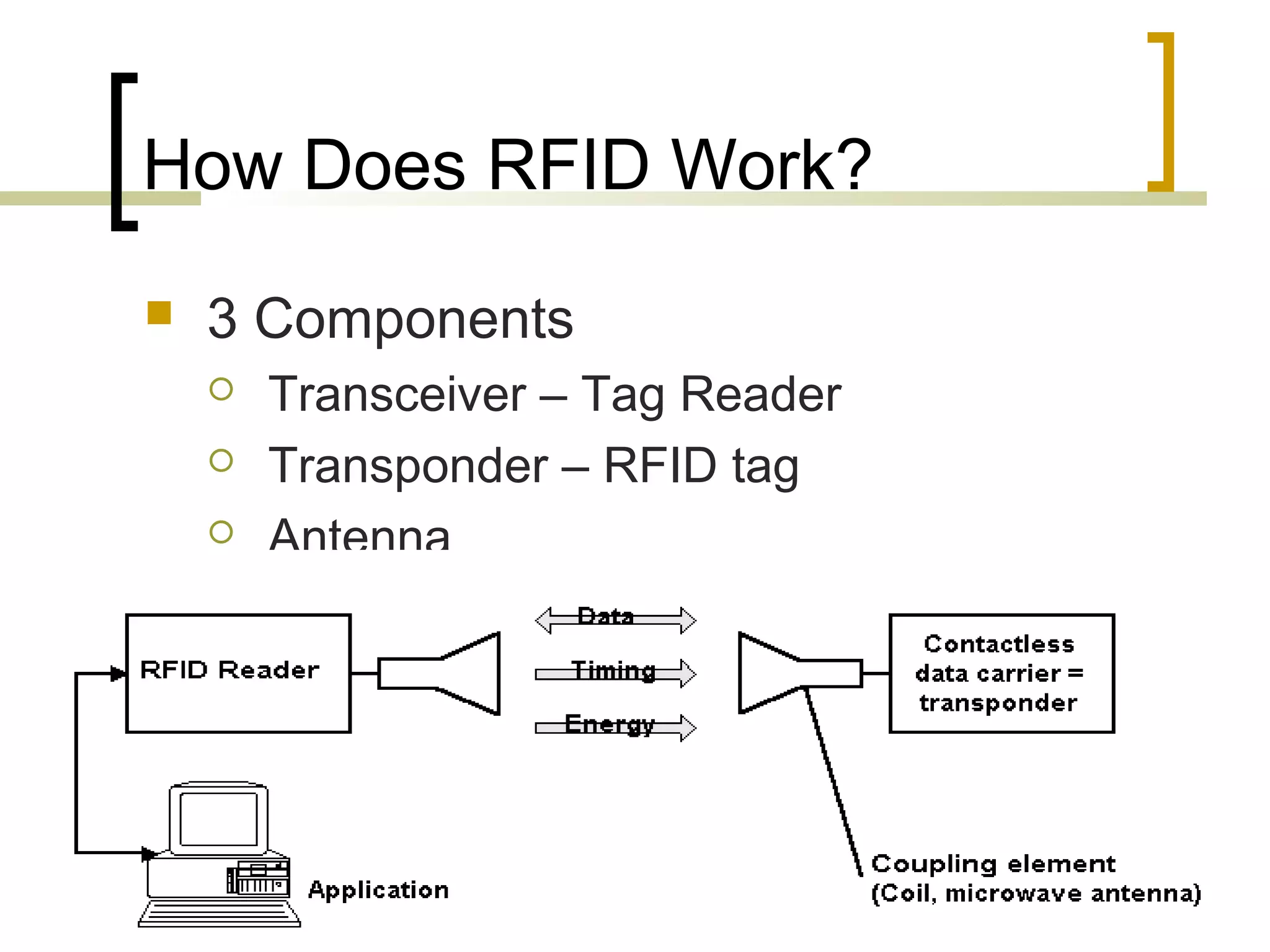
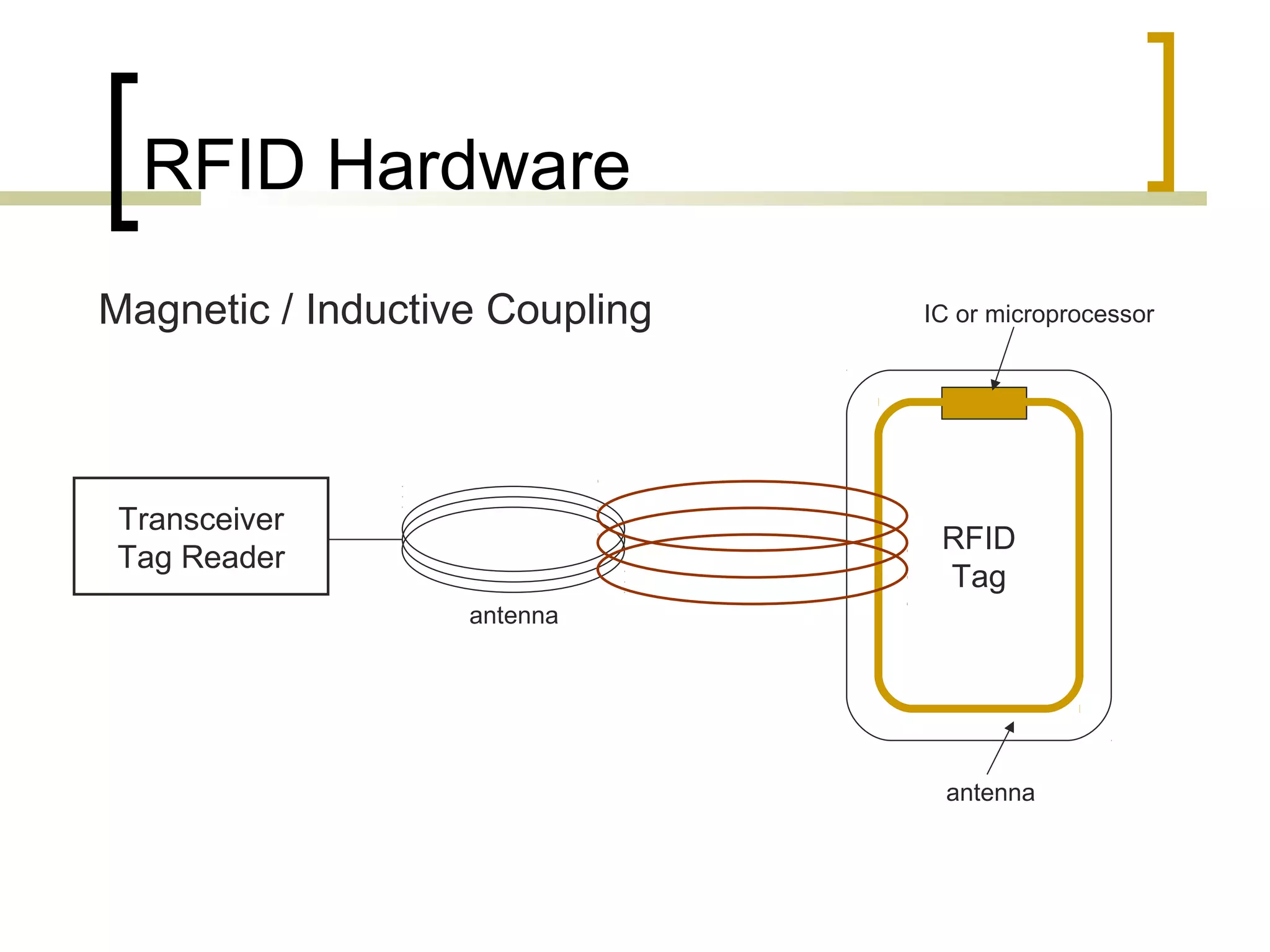
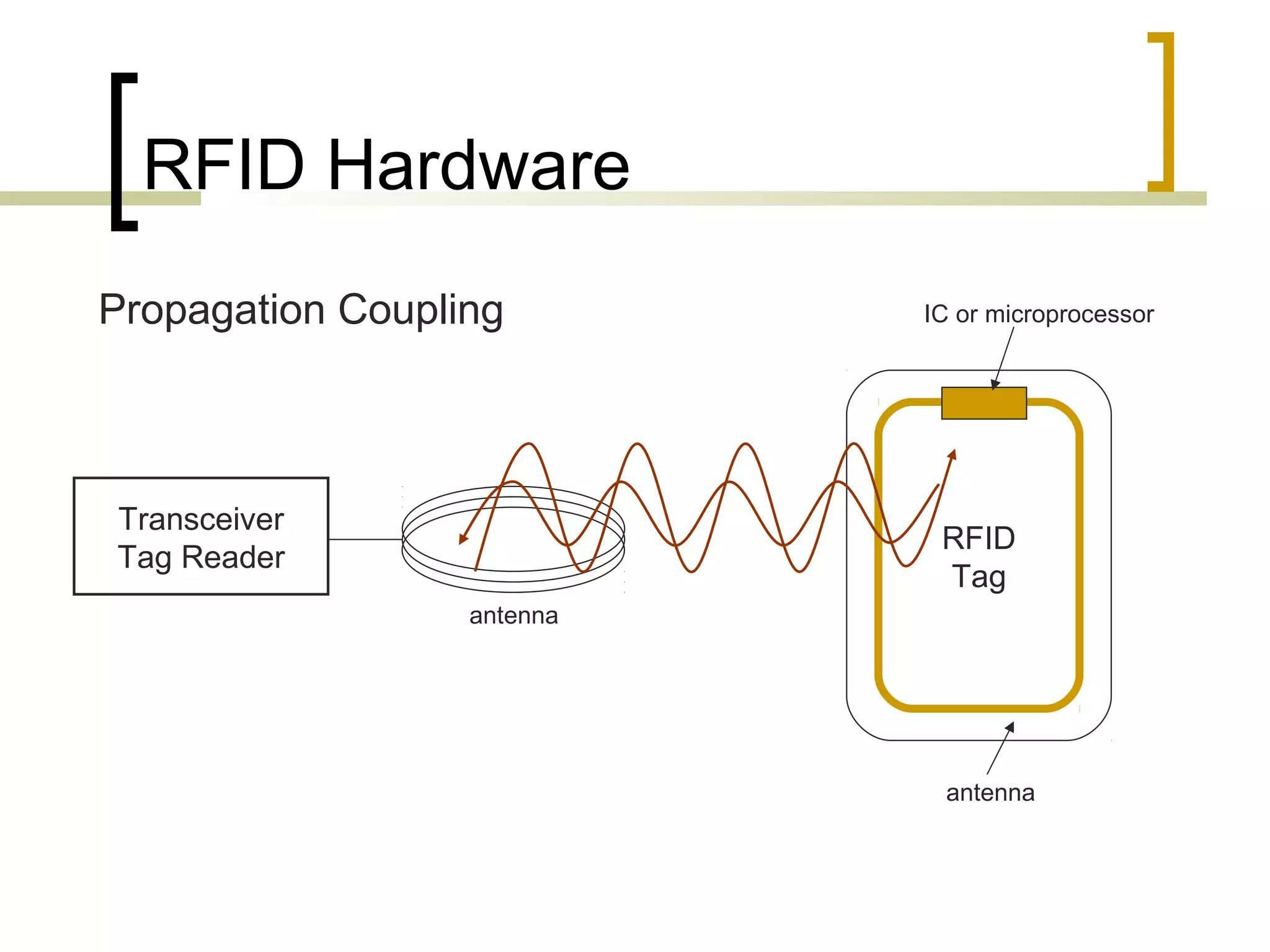
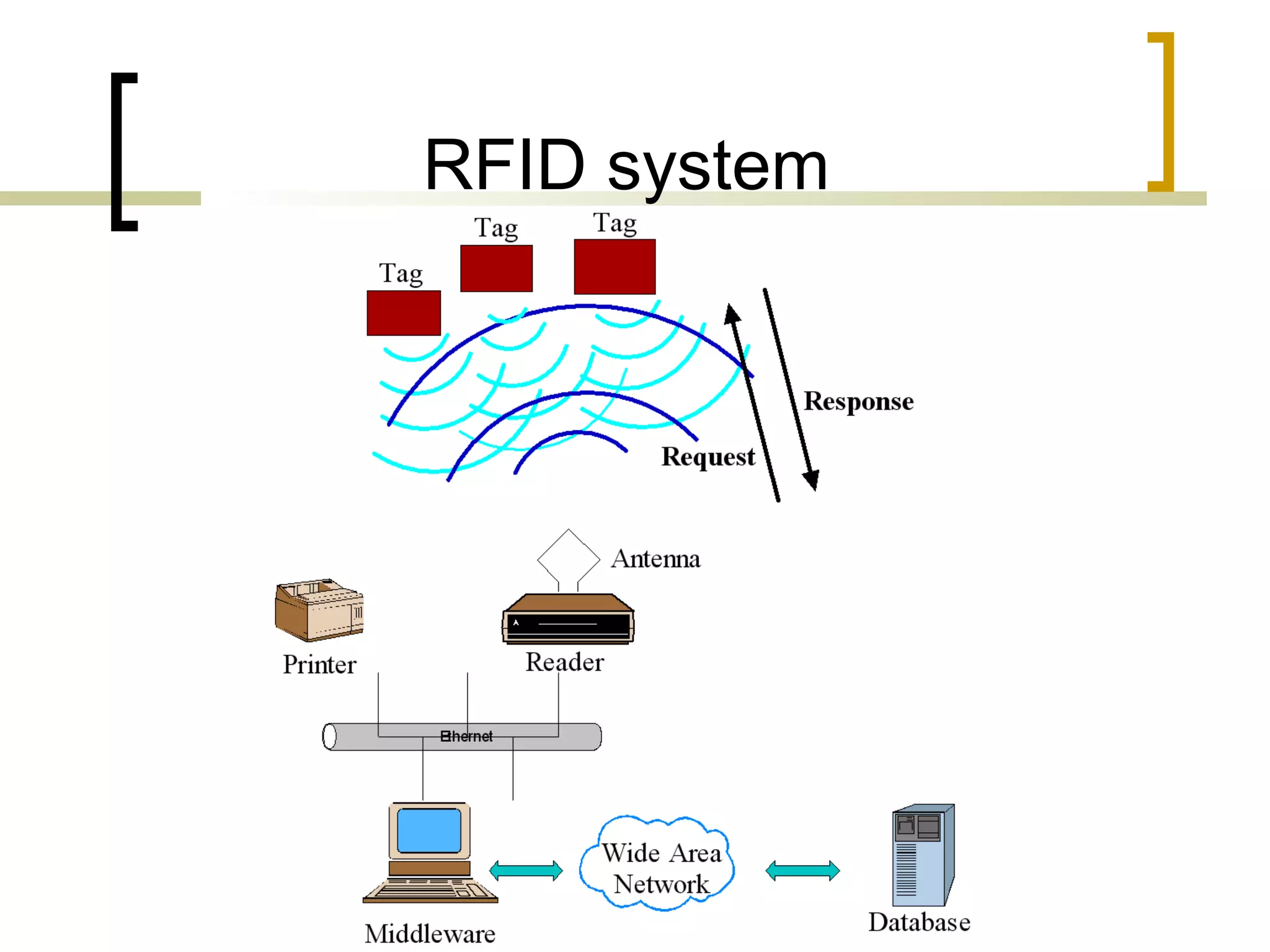
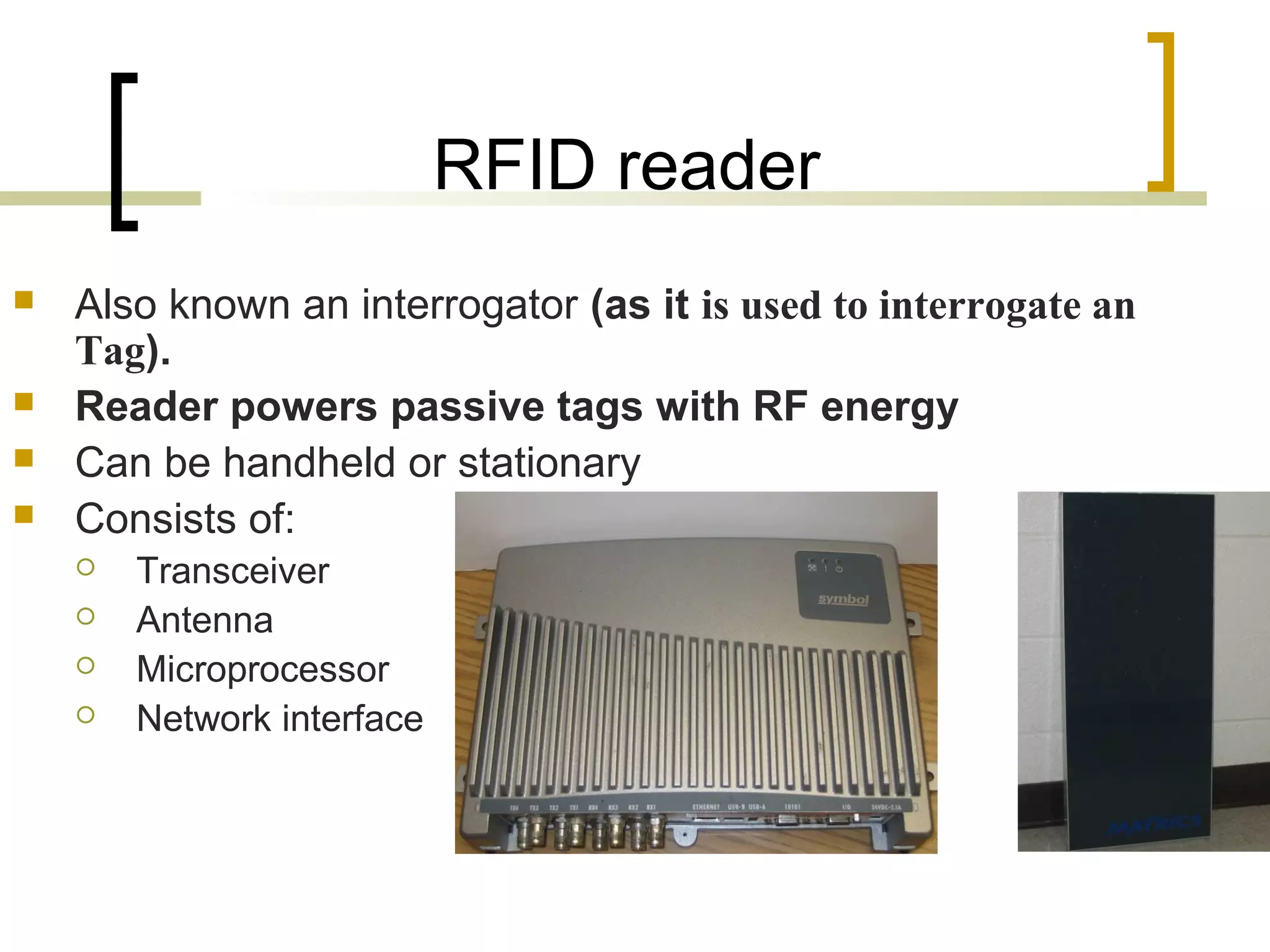
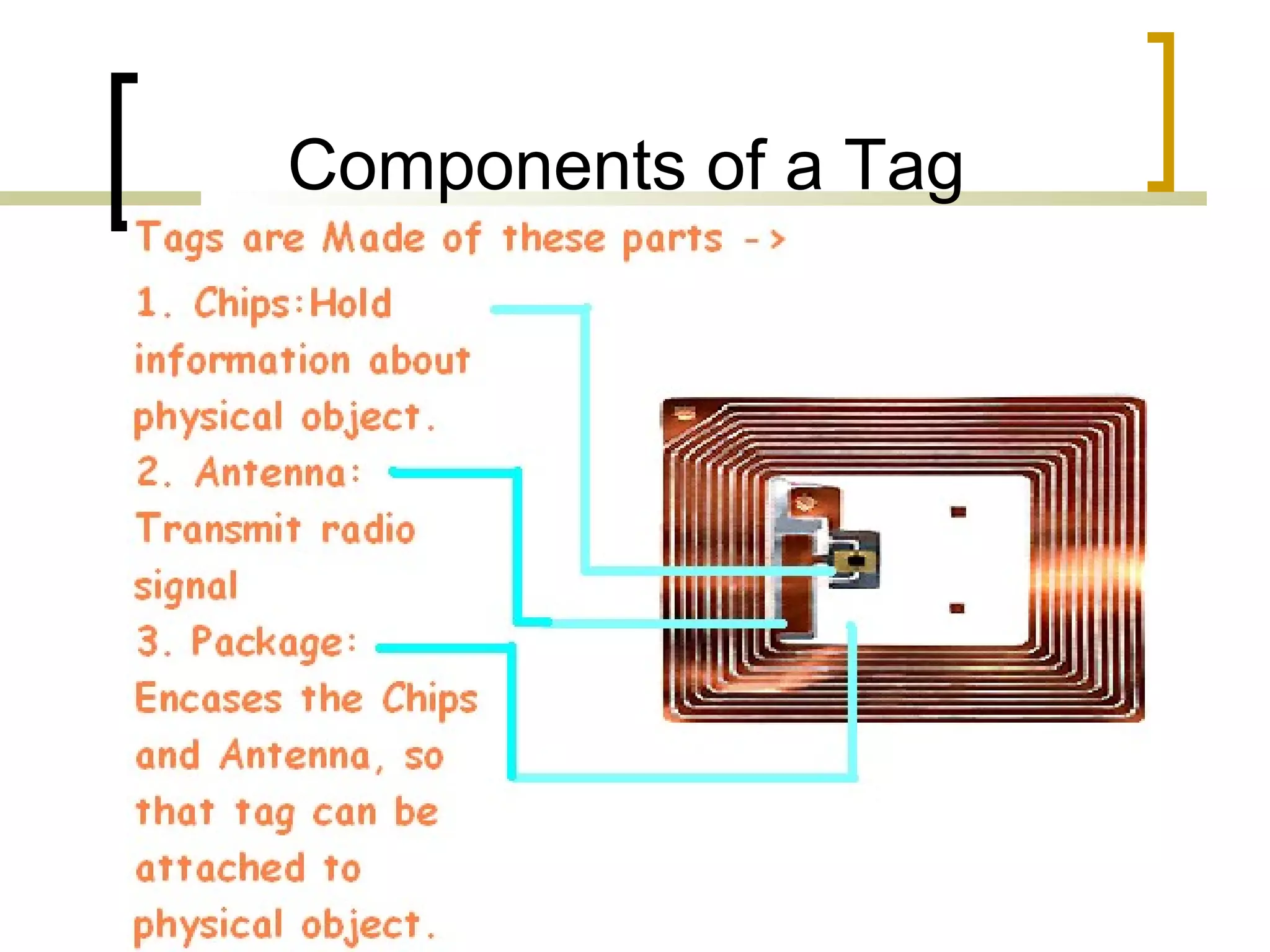
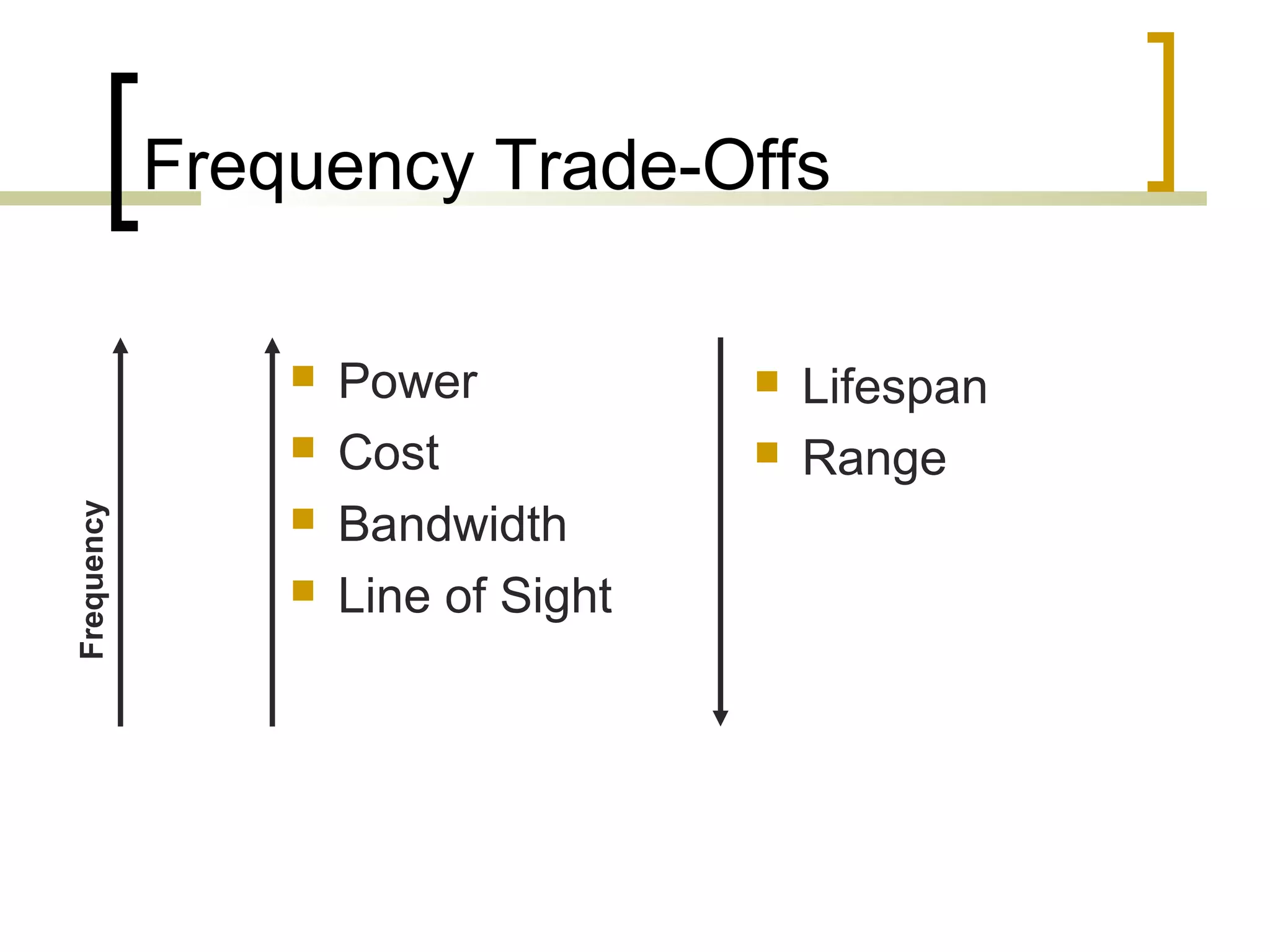
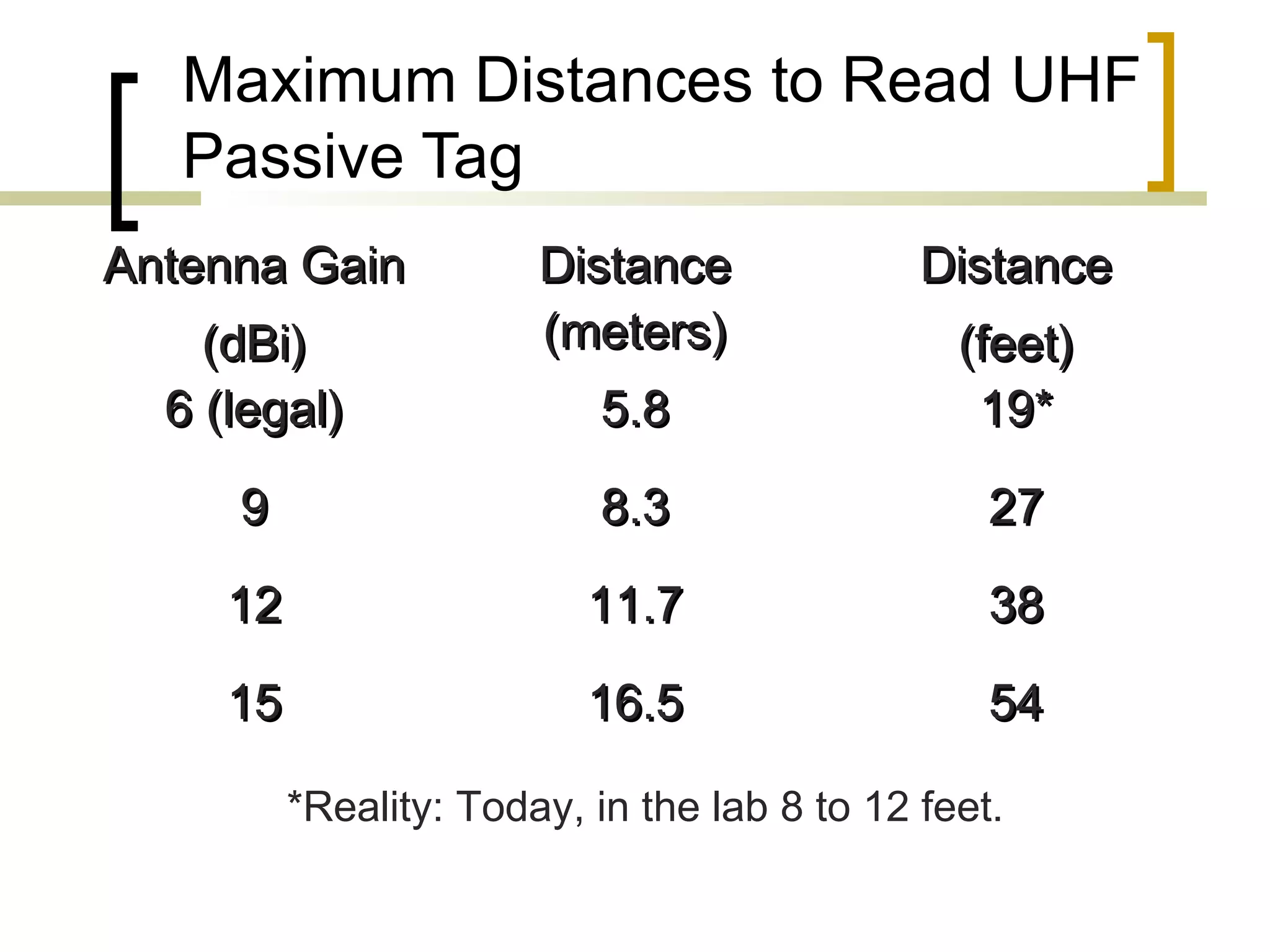
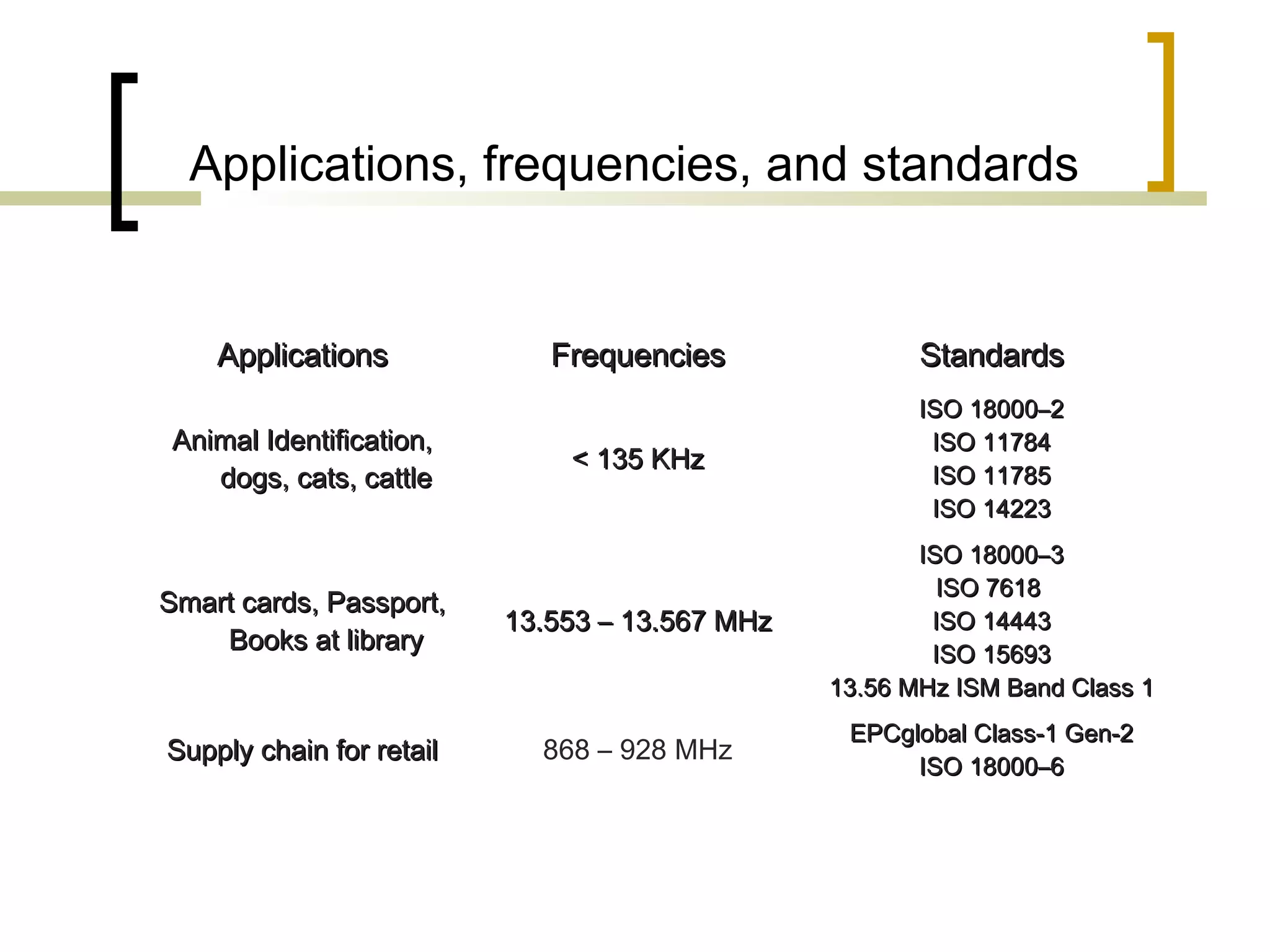
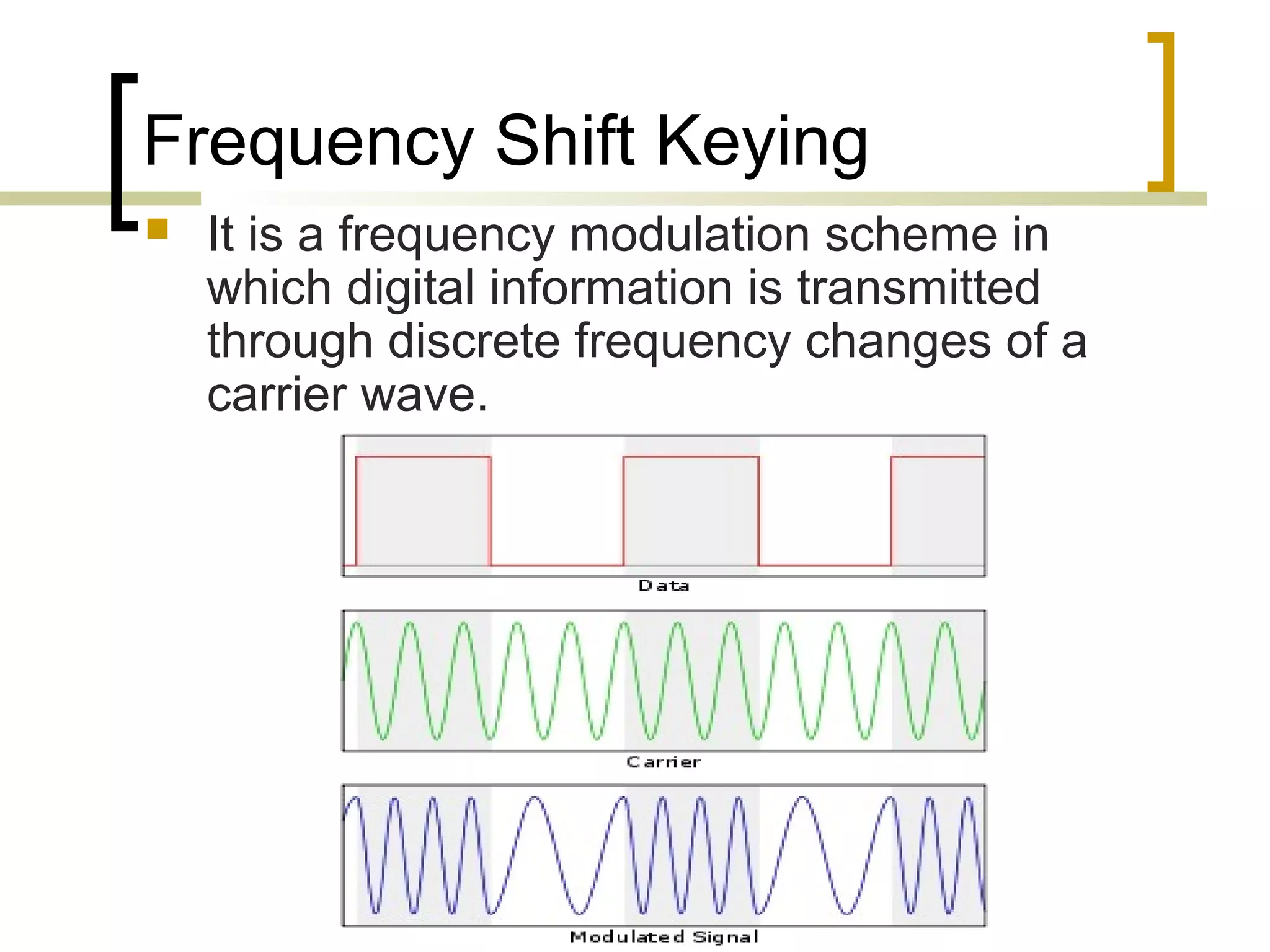
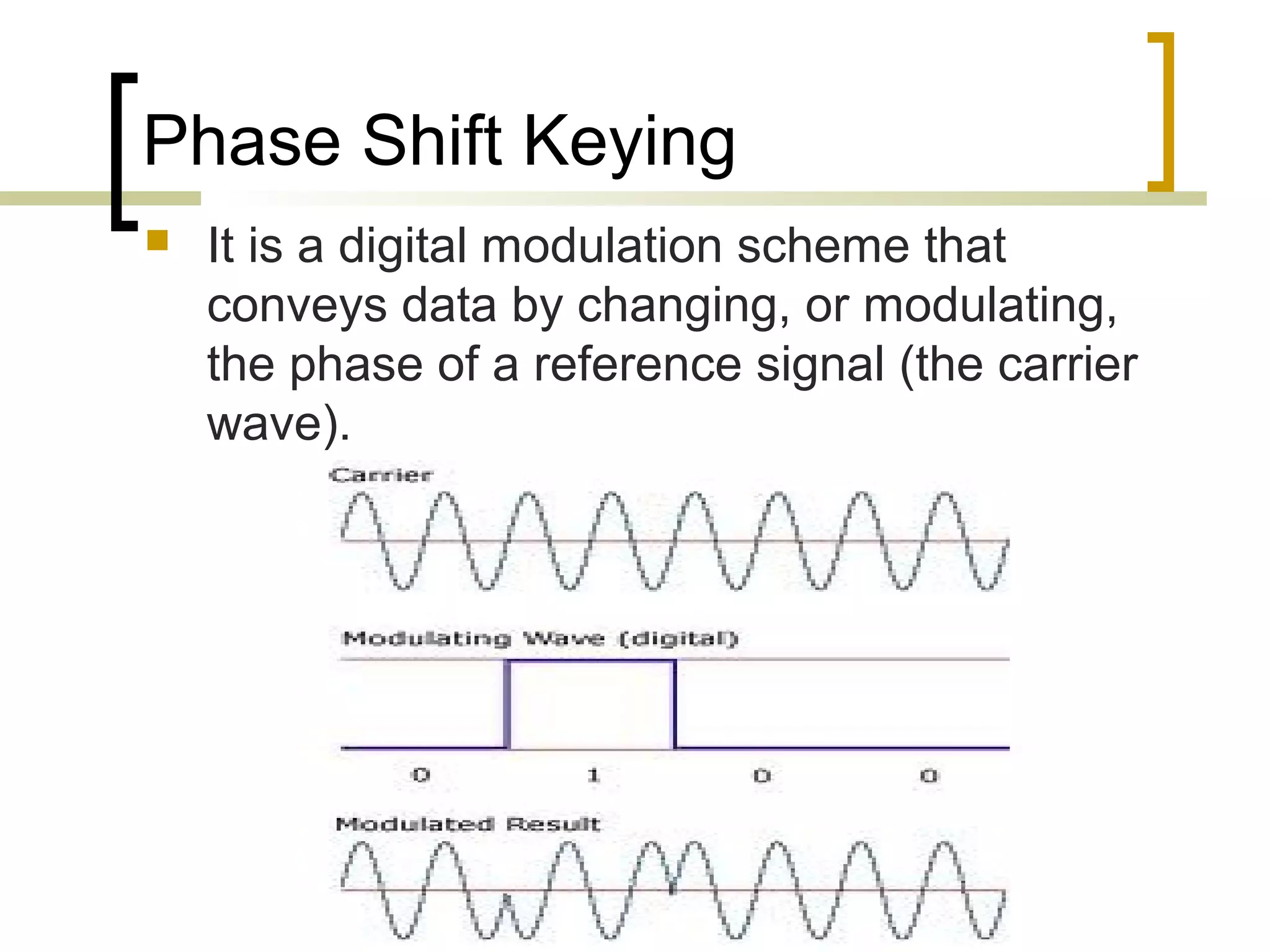
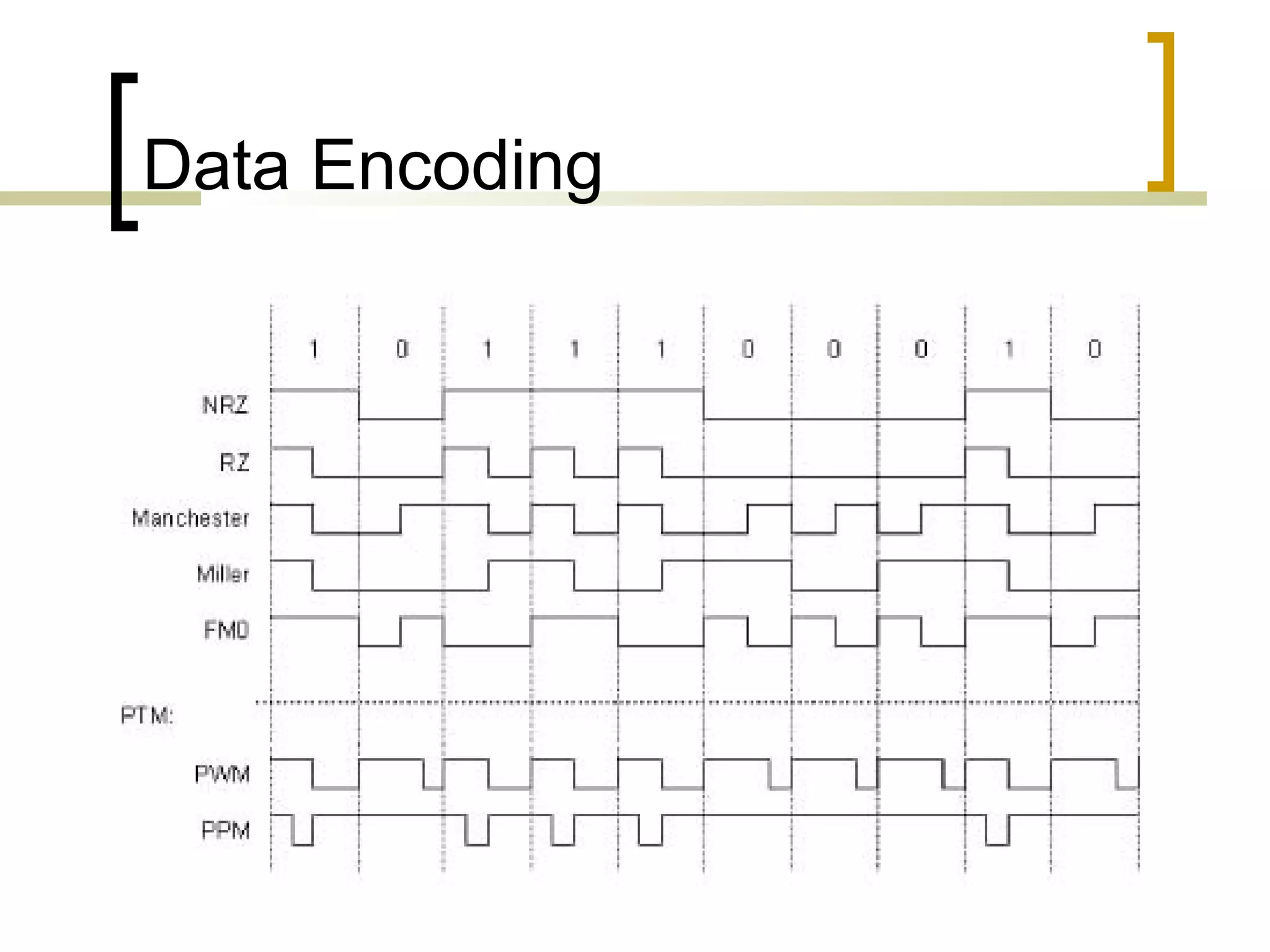
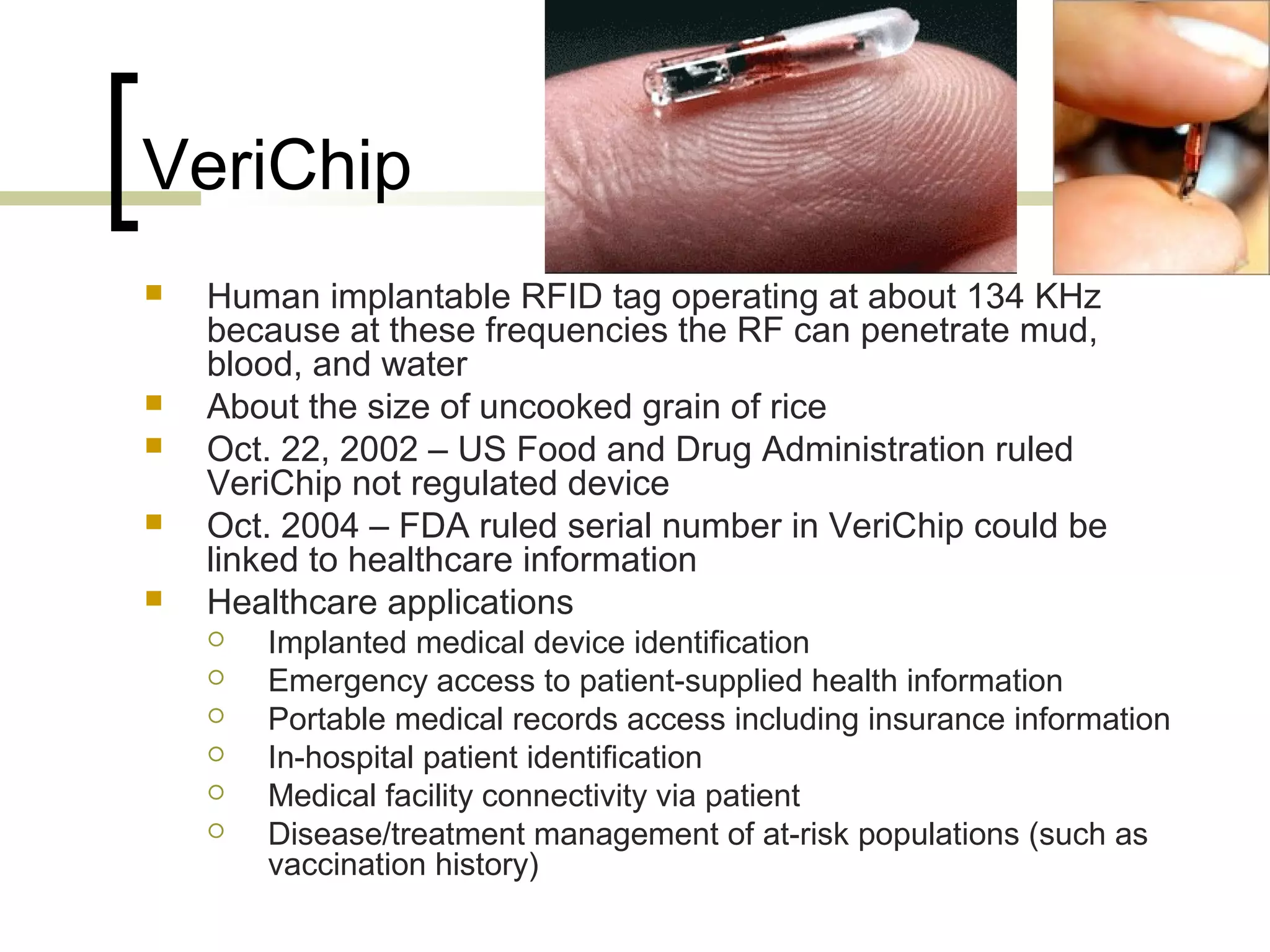
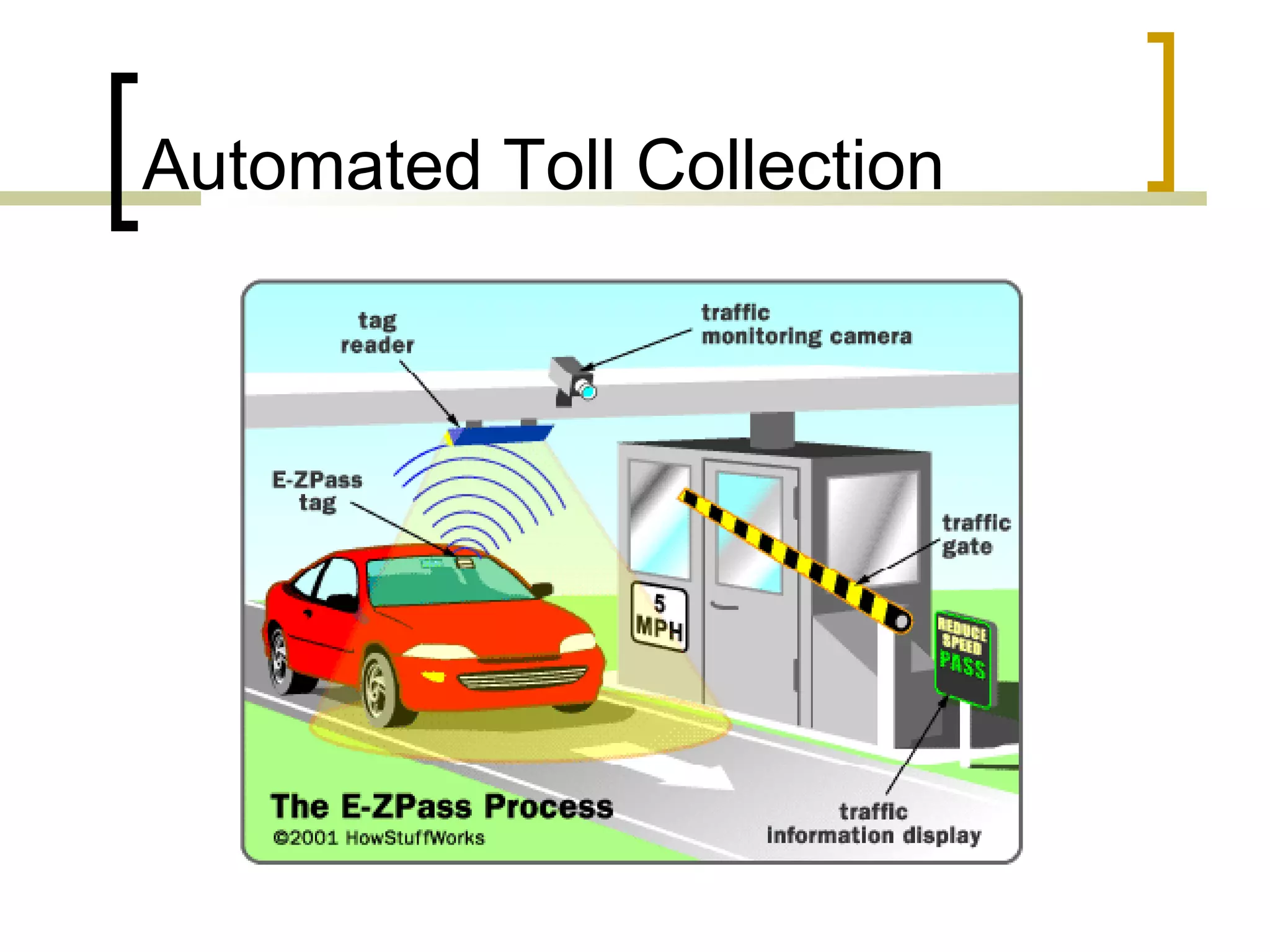
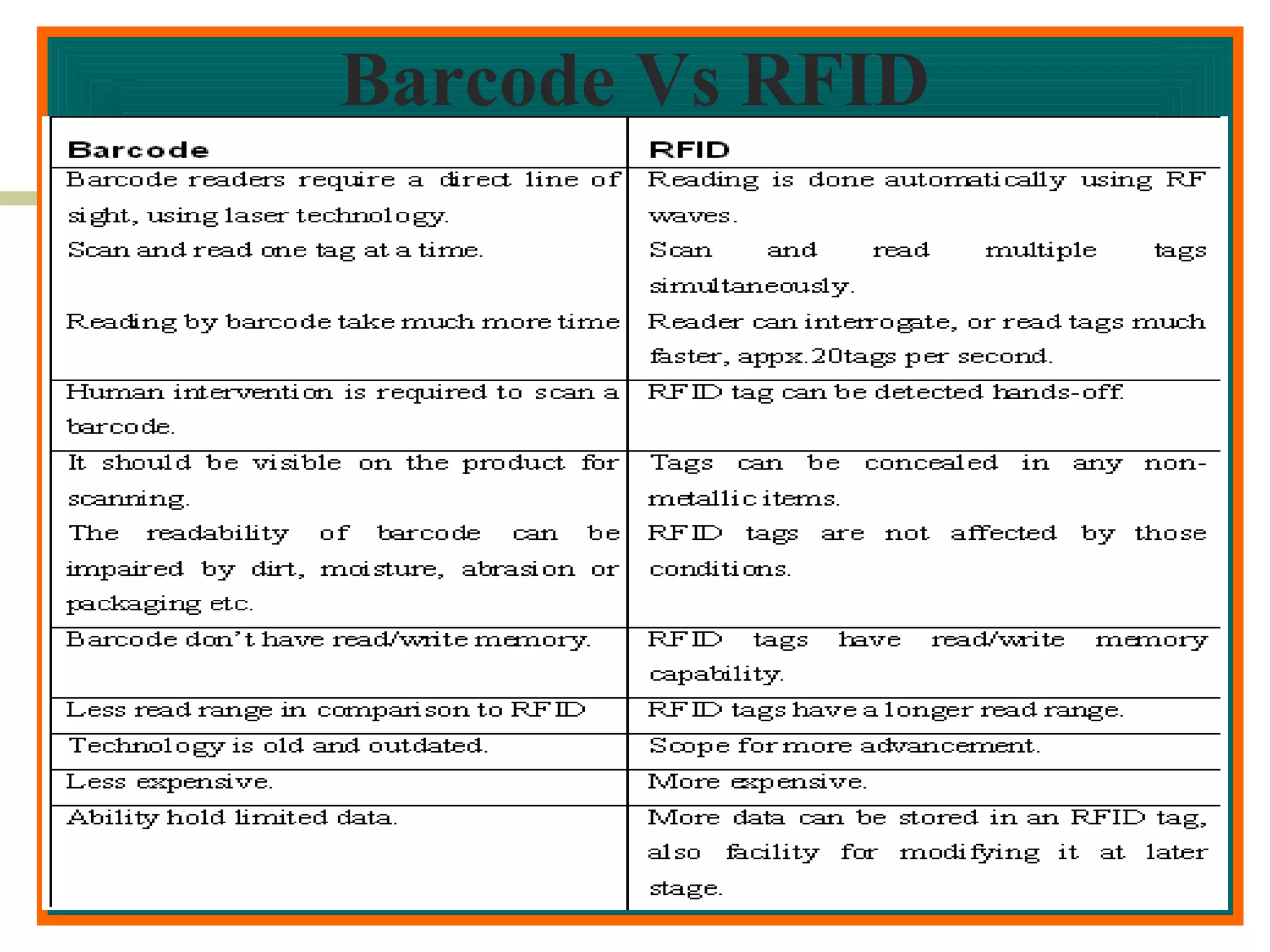
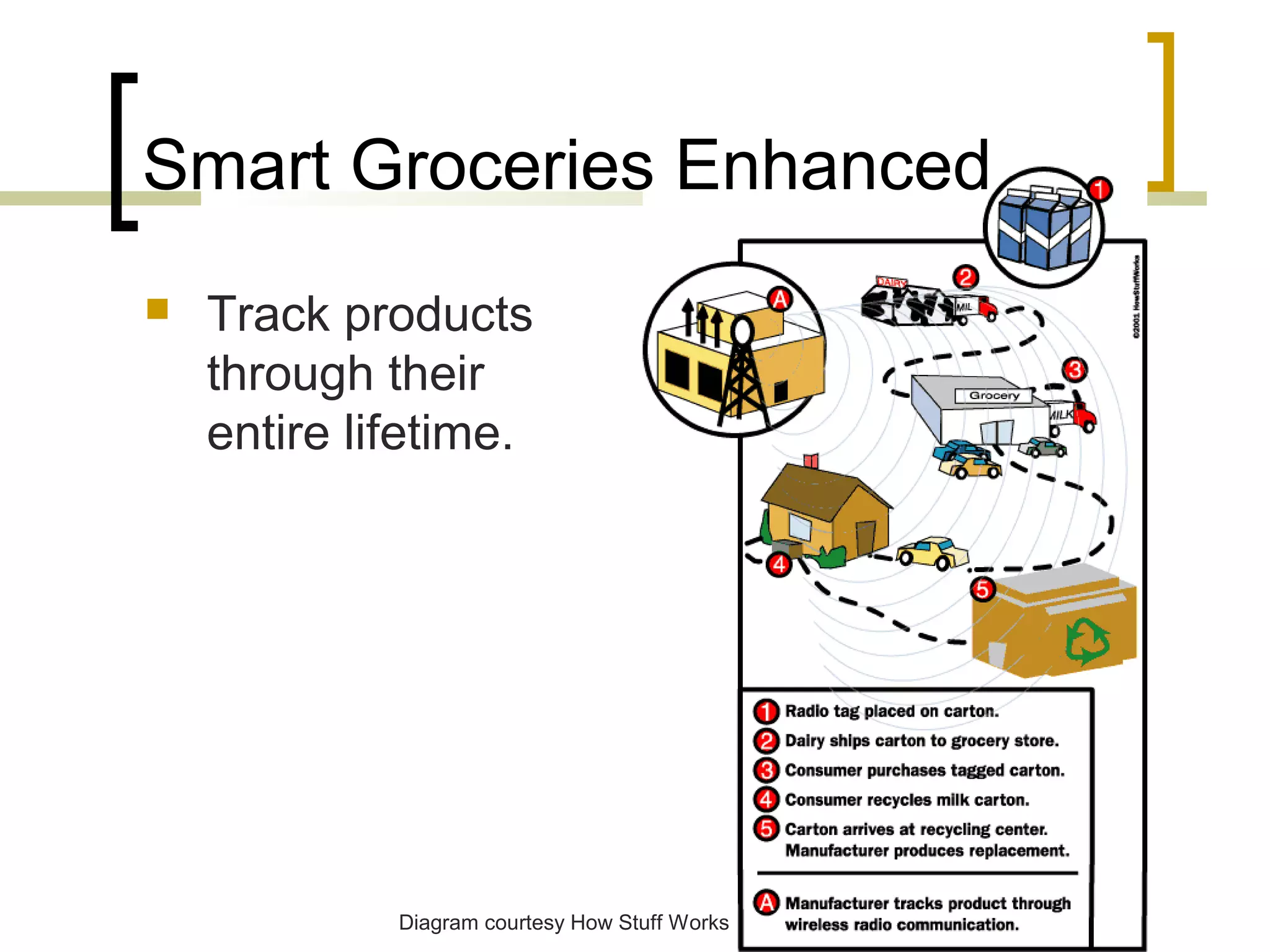
RFID (radio frequency identification) allows objects to be identified using radio waves transmitted from tags attached to objects. RFID systems consist of tags, readers, and an antenna. Tags can be passive (powered by reader), active (internal battery), or semi-passive (battery assisted). Common applications include supply chain management, livestock tagging, toll payment, and electronic passports. While RFID provides advantages like wireless data transfer and ability to work in harsh environments, concerns around privacy, security, and lack of standards remain open challenges.