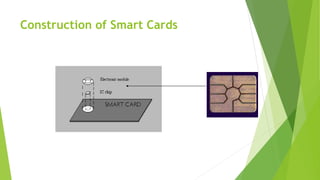
This seminar report discusses the history and applications of smart cards. It begins with the 1968 German patent filing for combining microchips with plastic cards. Key developments include the first single-chip microcontroller for smart cards in 1979 and nationwide prepaid card projects in Denmark in 1992. The report defines smart cards as credit card-sized cards with embedded microchips, which can store up to 32,000 bytes of data. It describes the construction of smart cards and lists applications such as payment systems, identification, and transportation. The report also outlines the advantages of smart cards including flexibility, security, and portability.